This mode is inspired by [n2n](https://github.com/ntop/n2n). There 2 types of node: SuperNode and EdgeNode
EdgeNode must connect to SuperNode first,get connection info of other EdgeNode from the SuperNode
The SuperNode runs [Floyd-Warshall Algorithm](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Floyd–Warshall_algorithm),and distribute the result to all other EdgeNodes.
There are new type of DstID called `SuperMsg`(65534). All packets sends to and receive from super node are using this packet type.
This packet will not send to any other edge node, just like `DstID == self.NodeID`
## Control Message
In Super mode, Beside `Normal Packet`. We introduce a new packet type called `Control Message`. In Super mode, we will not relay any control message. We just receive or send it to target directly.
We list all the control message we use in the super mode below.
### Register
This control message works like this picture:
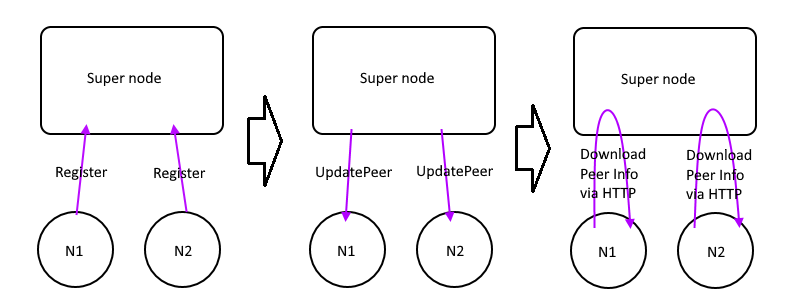
While supernode get a `Pong` message, it will update the `Distance matrix` and run the [Floyd-Warshall Algorithm](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Floyd–Warshall_algorithm) to calculate the NextHopTable.
If there are any changes of this table, it will distribute `UpdateNhTable` to all edges to till then download the latest NextHopTable via HTTP API as soon as possible.
And `UpdateXXX` itself is not reliable, maybe it didn't reach the edge node at all.
So the information of `UpdateXXX` carries the `state hash`. Bring it when with HTTP API. When the super node receives the HTTP API and sees the `state hash`, it knows that the edge node has received the `UpdateXXX`.
Otherwise, it will send `UpdateXXX` to the node again after few seconds.
1. nexthoptable: If the `graphrecalculatesetting` of your super node is in static mode, you need to provide a new `NextHopTable` in json format in this parameter.
RePushConfigInterval| The interval of push`UpdateXXX`
HttpPostInterval | The interval of report by HTTP Edge API
PeerAliveTimeout | The time of inactive which marks peer offline
SendPingInterval | The interval that send pings/pongs between EdgeNodes
[LogLevel](../static_mode/README.md#LogLevel)| Log related settings
[Passwords](#Passwords) | Password for HTTP ManageAPI, 5 API passwords are independent
[GraphRecalculateSetting](#GraphRecalculateSetting) | Some parameters related to [Floyd-Warshall algorithm](https://zh.wikipedia.org/zh-tw/Floyd-Warshall algorithm)
[NextHopTable](../static_mode/README.md#NextHopTable) | `NextHopTable` used by StaticMode
EdgeTemplate | for HTTP ManageAPI `peer/add`. Refer to this configuration file and show a sample configuration file of the edge to the user
UsePSKForInterEdge | Whether to enable pre-share key communication between edges.<br>If enabled, SuperNode will generate PSK for edges automatically
[Peers](#EdgeNodes) | EdgeNode information
<aname="Passwords"></a>Passwords | Description
--------------------|:-----
ShowState | HTTP ManageAPI Password for `super/state`
AddPeer | HTTP ManageAPI Password for `peer/add`
DelPeer | HTTP ManageAPI Password for `peer/del`
UpdatePeer | HTTP ManageAPI Password for `peer/update`
UpdateSuper | HTTP ManageAPI Password for `super/update`
TimeoutCheckInterval | The interval to check if there any `Pong` packet timed out, and recalculate the NhTable
RecalculateCoolDown | Floyd-Warshal is an O(n^3)time complexity algorithm<br>This option set a cooldown, and prevent it cost too many CPU<br>Connect/Disconnect event ignores this cooldown.
<aname="EdgeNodes"></a>Peers | Description
--------------------|:-----
NodeID | Peer's node ID
PubKey | Peer's public key
PSKey | Pre shared key
[AdditionalCost](#AdditionalCost) | AdditionalCost(unit:ms)<br>`-1` means uses client's self configuration.
SkipLocalIP | Ignore Edge reported local IP, use public IP only while udp-hole-punching
[SuperNode](#SuperNode) | SuperNode related configs
[P2P](../p2p_mode/README.md#P2P) | P2P related configs
[NTPConfig](#NTPConfig) | NTP related configs
<aname="SuperNode"></a>SuperNode | Description
---------------------|:-----
UseSuperNode | Enable SuperMode
PSKey | PreShared Key to communicate to SuperNode
EndpointV4 | IPv4 Endpoint of the SuperNode
PubKeyV4 | Public Key for IPv4 session to SuperNode
EndpointV6 | IPv6 Endpoint of the SuperNode
PubKeyV6 | Public Key for IPv6 session to SuperNode
EndpointEdgeAPIUrl | The EdgeAPI of the SuperNode
SkipLocalIP | Do not report local IP to SuperNode.
SuperNodeInfoTimeout | Experimental option, SuperNode offline timeout, switch to P2P mode<br>P2P mode needs to be enabled first<br>This option is useless while `UseP2P=false`<br>P2P mode has not been tested, stability is unknown, it is not recommended for production use
So like this, both V4 and V6 establish a session, so that both V4 and V6 can be taken care of at the same time.
## UDP hole punch reachability
For different NAT type, the UDP hole punch reachability can refer this table.([Origin](https://dh2i.com/kbs/kbs-2961448-understanding-different-nat-types-and-hole-punching/))
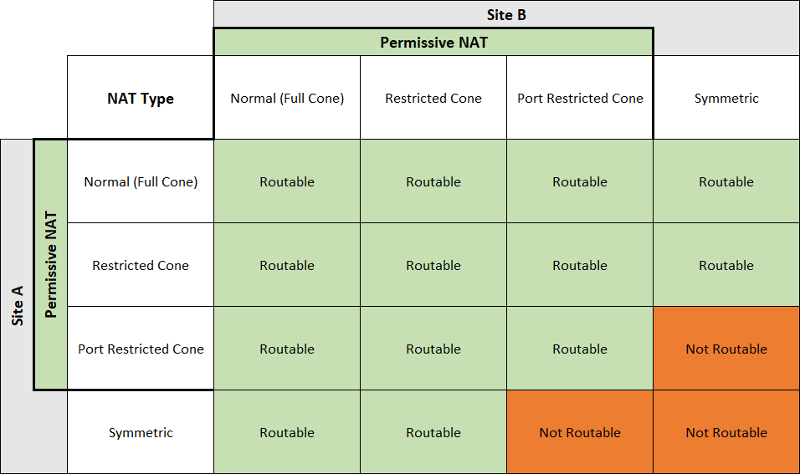
And if both sides are using ConeNAT, it's not gerenteed to punch success. It depends on the topology and the devices attributes.
Like the section 3.5 in [this article](https://bford.info/pub/net/p2pnat/#SECTION00035000000000000000), we can't punch success.
## Notice for Relay node
Unlike n2n, our supernode do not relay any packet for edges.
If the edge punch failed and no any route available, it's just unreachable. In this case we need to setup a relay node.
Relay node is a regular edge in public network, but `interface=dummy`.
And we have to note that **do not** use 127.0.0.1 to connect to supernode.
Because supernode well distribute the source IP of the nodes to all other edges. But 127.0.0.1 is not accessible from other edge.
Because it is in `stdio` mode, stdin will be read into the VPN network
Please type in one of the edge windows
```
b1aaaaaaaaaa
```
b1 will be converted into a 12byte layer 2 header, b is the broadcast address `FF:FF:FF:FF:FF:FF`, 1 is the ordinary MAC address `AA:BB:CC:DD:EE:01`, aaaaaaaaaa is the payload, and then feed it into the VPN
You should be able to see the string b1aaaaaaaaaa on another window. The first 12 bytes are converted back