mirror of
https://github.com/KusakabeShi/EtherGuard-VPN.git
synced 2025-08-17 12:17:15 +02:00
Static mode for supernode,dump packet, update readme, add code of concept
This commit is contained in:
2
.vscode/launch.json
vendored
2
.vscode/launch.json
vendored
@ -12,7 +12,7 @@
|
||||
"program": "${workspaceFolder}",
|
||||
"buildFlags": "-tags=vpp",
|
||||
"env": {"CGO_CFLAGS":"-I/usr/include/memif"},
|
||||
"args":["-config","tttttttttt.yaml","-mode","edge"/*,"-example"*/],
|
||||
"args":["-config","example_config/super_mode/s1.yaml","-mode","super"/*,"-example"*/],
|
||||
}
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
16
README.md
16
README.md
@ -4,13 +4,17 @@
|
||||
|
||||
A Full Mesh Layer2 VPN based on wireguard-go
|
||||
|
||||
[](code_of_conduct.md)
|
||||
|
||||
OSPF can find best route based on it's cost.
|
||||
But sometimes the lentancy are different in the packet goes and back.
|
||||
I'am thinking, is it possible to find the best route based on the **single-way latency**?
|
||||
For example, I have two routes A and B at node N1, both of them can reach my node N2. A goes fast, but B backs fast.
|
||||
My VPN can automatically send packet through route A at node N1, and the packet backs from route B.
|
||||
|
||||
Here is the solution. This VPN `Etherguard` can collect all the single-way lentancy from all nodes, and calculate the best route using [Floyd–Warshall algorithm](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Floyd%E2%80%93Warshall_algorithm).
|
||||
Here is the solution. This VPN `Etherguard` can collect all the single-way lentancy from all nodes, and calculate the best route using [Floyd–Warshall algorithm](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Floyd–Warshall_algorithm).
|
||||
|
||||
Wirried about the clock not match so that the measure result are not correct? It doesn't matter, here is the proof (Mandarin): [https://www.kskb.eu.org/2021/08/rootless-routerpart-3-etherguard.html](https://www.kskb.eu.org/2021/08/rootless-routerpart-3-etherguard.html)
|
||||
|
||||
## Usage
|
||||
|
||||
@ -18,7 +22,7 @@ Here is the solution. This VPN `Etherguard` can collect all the single-way lenta
|
||||
Usage of ./etherguard-go:
|
||||
-bind string
|
||||
UDP socket bind mode. [linux|std]
|
||||
You may need this if tou want to run Etherguard under WSL. (default "linux")
|
||||
You may need std mode if tou want to run Etherguard under WSL. (default "linux")
|
||||
-config string
|
||||
Config path.
|
||||
-example
|
||||
@ -68,7 +72,7 @@ Usage of ./etherguard-go:
|
||||
2. `kbdbg`: Keyboard debug mode.
|
||||
Let me construct Layer 2 header by ascii character only.
|
||||
So that I can track the packet flow with `loglevel` option.
|
||||
3. `noL2`: Remove all Layer 2 header
|
||||
3. `noL2`: Remove all Layer 2 header, all boardcast
|
||||
2. `nodeid`: NodeID. Must be unique in the whole Etherguard network.
|
||||
3. `nodename`: Node Name.
|
||||
4. `defaultttl`: Default TTL(etherguard layer. not affect ethernet layer)
|
||||
@ -85,8 +89,8 @@ Usage of ./etherguard-go:
|
||||
2. `dupchecktimeout`: Duplication chack timeout.
|
||||
3. `conntimeout`: Connection timeout.
|
||||
4. `savenewpeers`: Save peer info to local file.
|
||||
5. `supernode`: See [Super Mode](example_config/super_mode/README_zh.md)
|
||||
6. `p2p` See [P2P Mode](example_config/p2p_mode/README_zh.md)
|
||||
5. `supernode`: See [Super Mode](example_config/super_mode/README.md)
|
||||
6. `p2p` See [P2P Mode](example_config/p2p_mode/README.md)
|
||||
7. `ntpconfig`: NTP related settings
|
||||
1. `usentp`: USE NTP or not.
|
||||
2. `maxserveruse`: How many NTP servers should we use at once.
|
||||
@ -94,7 +98,7 @@ Usage of ./etherguard-go:
|
||||
3. `synctimeinterval`: NTP sync interval.
|
||||
4. `ntptimeout`: NTP timeout
|
||||
5. `servers`: NTP server list
|
||||
8. `nexthoptable`: Nexthop table。Only static mode use it. See [Static Mㄍㄟ](example_config/super_mode/README_zh.md)
|
||||
8. `nexthoptable`: Nexthop table。Only static mode use it. See [Static Mode](example_config/super_mode/README.md)
|
||||
9. `resetconninterval`: Reset the endpoint for peers. You may need this if that peer use DDNS.
|
||||
10. `peers`: Peer info.
|
||||
1. `nodeid`: Node ID.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -3,6 +3,8 @@
|
||||
|
||||
[English](README.md)
|
||||
|
||||
[](code_of_conduct.md)
|
||||
|
||||
一個從wireguard-go改來的Full Mesh Layer2 VPN.
|
||||
|
||||
OSPF能夠根據cost自動選路
|
||||
|
||||
133
code_of_conduct.md
Normal file
133
code_of_conduct.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,133 @@
|
||||
|
||||
# Contributor Covenant Code of Conduct
|
||||
|
||||
## Our Pledge
|
||||
|
||||
We as members, contributors, and leaders pledge to make participation in our
|
||||
community a harassment-free experience for everyone, regardless of age, body
|
||||
size, visible or invisible disability, ethnicity, sex characteristics, gender
|
||||
identity and expression, level of experience, education, socio-economic status,
|
||||
nationality, personal appearance, race, caste, color, religion, or sexual identity
|
||||
and orientation.
|
||||
|
||||
We pledge to act and interact in ways that contribute to an open, welcoming,
|
||||
diverse, inclusive, and healthy community.
|
||||
|
||||
## Our Standards
|
||||
|
||||
Examples of behavior that contributes to a positive environment for our
|
||||
community include:
|
||||
|
||||
* Demonstrating empathy and kindness toward other people
|
||||
* Being respectful of differing opinions, viewpoints, and experiences
|
||||
* Giving and gracefully accepting constructive feedback
|
||||
* Accepting responsibility and apologizing to those affected by our mistakes,
|
||||
and learning from the experience
|
||||
* Focusing on what is best not just for us as individuals, but for the
|
||||
overall community
|
||||
|
||||
Examples of unacceptable behavior include:
|
||||
|
||||
* The use of sexualized language or imagery, and sexual attention or
|
||||
advances of any kind
|
||||
* Trolling, insulting or derogatory comments, and personal or political attacks
|
||||
* Public or private harassment
|
||||
* Publishing others' private information, such as a physical or email
|
||||
address, without their explicit permission
|
||||
* Other conduct which could reasonably be considered inappropriate in a
|
||||
professional setting
|
||||
|
||||
## Enforcement Responsibilities
|
||||
|
||||
Community leaders are responsible for clarifying and enforcing our standards of
|
||||
acceptable behavior and will take appropriate and fair corrective action in
|
||||
response to any behavior that they deem inappropriate, threatening, offensive,
|
||||
or harmful.
|
||||
|
||||
Community leaders have the right and responsibility to remove, edit, or reject
|
||||
comments, commits, code, wiki edits, issues, and other contributions that are
|
||||
not aligned to this Code of Conduct, and will communicate reasons for moderation
|
||||
decisions when appropriate.
|
||||
|
||||
## Scope
|
||||
|
||||
This Code of Conduct applies within all community spaces, and also applies when
|
||||
an individual is officially representing the community in public spaces.
|
||||
Examples of representing our community include using an official e-mail address,
|
||||
posting via an official social media account, or acting as an appointed
|
||||
representative at an online or offline event.
|
||||
|
||||
## Enforcement
|
||||
|
||||
Instances of abusive, harassing, or otherwise unacceptable behavior may be
|
||||
reported to the community leaders responsible for enforcement at
|
||||
[INSERT CONTACT METHOD].
|
||||
All complaints will be reviewed and investigated promptly and fairly.
|
||||
|
||||
All community leaders are obligated to respect the privacy and security of the
|
||||
reporter of any incident.
|
||||
|
||||
## Enforcement Guidelines
|
||||
|
||||
Community leaders will follow these Community Impact Guidelines in determining
|
||||
the consequences for any action they deem in violation of this Code of Conduct:
|
||||
|
||||
### 1. Correction
|
||||
|
||||
**Community Impact**: Use of inappropriate language or other behavior deemed
|
||||
unprofessional or unwelcome in the community.
|
||||
|
||||
**Consequence**: A private, written warning from community leaders, providing
|
||||
clarity around the nature of the violation and an explanation of why the
|
||||
behavior was inappropriate. A public apology may be requested.
|
||||
|
||||
### 2. Warning
|
||||
|
||||
**Community Impact**: A violation through a single incident or series
|
||||
of actions.
|
||||
|
||||
**Consequence**: A warning with consequences for continued behavior. No
|
||||
interaction with the people involved, including unsolicited interaction with
|
||||
those enforcing the Code of Conduct, for a specified period of time. This
|
||||
includes avoiding interactions in community spaces as well as external channels
|
||||
like social media. Violating these terms may lead to a temporary or
|
||||
permanent ban.
|
||||
|
||||
### 3. Temporary Ban
|
||||
|
||||
**Community Impact**: A serious violation of community standards, including
|
||||
sustained inappropriate behavior.
|
||||
|
||||
**Consequence**: A temporary ban from any sort of interaction or public
|
||||
communication with the community for a specified period of time. No public or
|
||||
private interaction with the people involved, including unsolicited interaction
|
||||
with those enforcing the Code of Conduct, is allowed during this period.
|
||||
Violating these terms may lead to a permanent ban.
|
||||
|
||||
### 4. Permanent Ban
|
||||
|
||||
**Community Impact**: Demonstrating a pattern of violation of community
|
||||
standards, including sustained inappropriate behavior, harassment of an
|
||||
individual, or aggression toward or disparagement of classes of individuals.
|
||||
|
||||
**Consequence**: A permanent ban from any sort of public interaction within
|
||||
the community.
|
||||
|
||||
## Attribution
|
||||
|
||||
This Code of Conduct is adapted from the [Contributor Covenant][homepage],
|
||||
version 2.1, available at
|
||||
[https://www.contributor-covenant.org/version/2/1/code_of_conduct.html][v2.1].
|
||||
|
||||
Community Impact Guidelines were inspired by
|
||||
[Mozilla's code of conduct enforcement ladder][Mozilla CoC].
|
||||
|
||||
For answers to common questions about this code of conduct, see the FAQ at
|
||||
[https://www.contributor-covenant.org/faq][FAQ]. Translations are available
|
||||
at [https://www.contributor-covenant.org/translations][translations].
|
||||
|
||||
[homepage]: https://www.contributor-covenant.org
|
||||
[v2.1]: https://www.contributor-covenant.org/version/2/1/code_of_conduct.html
|
||||
[Mozilla CoC]: https://github.com/mozilla/diversity
|
||||
[FAQ]: https://www.contributor-covenant.org/faq
|
||||
[translations]: https://www.contributor-covenant.org/translations
|
||||
@ -10,8 +10,8 @@ import (
|
||||
type Vertex uint16
|
||||
|
||||
const (
|
||||
Boardcast Vertex = math.MaxUint16 - iota // Normal boardcast, boardcast with route table
|
||||
ControlMessage Vertex = math.MaxUint16 - iota // p2p mode: boardcast to every know keer and prevent dup/ super mode: send to supernode
|
||||
Broadcast Vertex = math.MaxUint16 - iota // Normal boardcast, boardcast with route table
|
||||
ControlMessage Vertex = math.MaxUint16 - iota // p2p mode: boardcast to every know peer and prevent dup. super mode: send to supernode
|
||||
SuperNodeMessage Vertex = math.MaxUint16 - iota
|
||||
Special_NodeID Vertex = SuperNodeMessage
|
||||
)
|
||||
@ -39,7 +39,9 @@ type SuperConfig struct {
|
||||
RePushConfigInterval float64
|
||||
Passwords Passwords
|
||||
GraphRecalculateSetting GraphRecalculateSetting
|
||||
NextHopTable NextHopTable
|
||||
EdgeTemplate string
|
||||
UsePSKForInterEdge bool
|
||||
Peers []SuperPeerInfo
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
@ -86,7 +88,7 @@ type LoggerInfo struct {
|
||||
|
||||
func (v *Vertex) ToString() string {
|
||||
switch *v {
|
||||
case Boardcast:
|
||||
case Broadcast:
|
||||
return "Boardcast"
|
||||
case ControlMessage:
|
||||
return "Control"
|
||||
@ -135,6 +137,7 @@ type P2Pinfo struct {
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
type GraphRecalculateSetting struct {
|
||||
StaticMode bool
|
||||
JitterTolerance float64
|
||||
JitterToleranceMultiplier float64
|
||||
NodeReportTimeout float64
|
||||
|
||||
@ -16,6 +16,8 @@ import (
|
||||
"sync/atomic"
|
||||
"time"
|
||||
|
||||
"github.com/google/gopacket"
|
||||
"github.com/google/gopacket/layers"
|
||||
"golang.org/x/crypto/chacha20poly1305"
|
||||
|
||||
"github.com/KusakabeSi/EtherGuardVPN/config"
|
||||
@ -474,7 +476,7 @@ func (peer *Peer) RoutineSequentialReceiver() {
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
switch dst_nodeID {
|
||||
case config.Boardcast:
|
||||
case config.Broadcast:
|
||||
should_receive = true
|
||||
should_transfer = true
|
||||
case config.SuperNodeMessage:
|
||||
@ -492,7 +494,7 @@ func (peer *Peer) RoutineSequentialReceiver() {
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
case device.ID:
|
||||
if packet_type == path.NornalPacket {
|
||||
if packet_type == path.NormalPacket {
|
||||
should_receive = true
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
should_process = true
|
||||
@ -511,7 +513,7 @@ func (peer *Peer) RoutineSequentialReceiver() {
|
||||
device.log.Verbosef("TTL is 0 %v", dst_nodeID)
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
EgHeader.SetTTL(l2ttl - 1)
|
||||
if dst_nodeID == config.Boardcast { //Regular transfer algorithm
|
||||
if dst_nodeID == config.Broadcast { //Regular transfer algorithm
|
||||
device.TransitBoardcastPacket(src_nodeID, peer.ID, elem.Type, elem.packet, MessageTransportOffsetContent)
|
||||
} else if dst_nodeID == config.ControlMessage { // Control Message will try send to every know node regardless the connectivity
|
||||
skip_list := make(map[config.Vertex]bool)
|
||||
@ -535,7 +537,7 @@ func (peer *Peer) RoutineSequentialReceiver() {
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if should_process {
|
||||
if packet_type != path.NornalPacket {
|
||||
if packet_type != path.NormalPacket {
|
||||
if device.LogLevel.LogControl {
|
||||
if peer.GetEndpointDstStr() != "" {
|
||||
fmt.Println("Control: Received From:" + peer.GetEndpointDstStr() + " " + device.sprint_received(packet_type, elem.packet[path.EgHeaderLen:]))
|
||||
@ -549,14 +551,16 @@ func (peer *Peer) RoutineSequentialReceiver() {
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if should_receive { // Write message to tap device
|
||||
if packet_type == path.NornalPacket {
|
||||
if device.LogLevel.LogNormal {
|
||||
fmt.Println("Normal: Reveived Normal packet From:" + peer.GetEndpointDstStr() + " SrcID:" + src_nodeID.ToString() + " DstID:" + dst_nodeID.ToString() + " Len:" + strconv.Itoa(len(elem.packet)))
|
||||
}
|
||||
if packet_type == path.NormalPacket {
|
||||
if len(elem.packet) <= path.EgHeaderLen+12 {
|
||||
device.log.Errorf("Invalid normal packet from peer %v", peer.ID.ToString())
|
||||
goto skip
|
||||
}
|
||||
if device.LogLevel.LogNormal {
|
||||
fmt.Println("Normal: Reveived Normal packet From:" + peer.GetEndpointDstStr() + " SrcID:" + src_nodeID.ToString() + " DstID:" + dst_nodeID.ToString() + " Len:" + strconv.Itoa(len(elem.packet)))
|
||||
packet := gopacket.NewPacket(elem.packet[path.EgHeaderLen:], layers.LayerTypeEthernet, gopacket.Default)
|
||||
fmt.Println(packet.Dump())
|
||||
}
|
||||
src_macaddr := tap.GetSrcMacAddr(elem.packet[path.EgHeaderLen:])
|
||||
if !tap.IsNotUnicast(src_macaddr) {
|
||||
actual, loaded := device.l2fib.LoadOrStore(src_macaddr, src_nodeID)
|
||||
|
||||
@ -11,11 +11,14 @@ import (
|
||||
"net/http"
|
||||
"net/url"
|
||||
"strconv"
|
||||
"strings"
|
||||
"time"
|
||||
|
||||
"github.com/KusakabeSi/EtherGuardVPN/config"
|
||||
orderedmap "github.com/KusakabeSi/EtherGuardVPN/orderdmap"
|
||||
"github.com/KusakabeSi/EtherGuardVPN/path"
|
||||
"github.com/google/gopacket"
|
||||
"github.com/google/gopacket/layers"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
func (device *Device) SendPacket(peer *Peer, usage path.Usage, packet []byte, offset int) {
|
||||
@ -26,13 +29,15 @@ func (device *Device) SendPacket(peer *Peer, usage path.Usage, packet []byte, of
|
||||
}
|
||||
if device.LogLevel.LogNormal {
|
||||
EgHeader, _ := path.NewEgHeader(packet[:path.EgHeaderLen])
|
||||
if usage == path.NornalPacket {
|
||||
if usage == path.NormalPacket {
|
||||
dst_nodeID := EgHeader.GetDst()
|
||||
fmt.Println("Normal: Send Normal packet To:" + peer.GetEndpointDstStr() + " SrcID:" + device.ID.ToString() + " DstID:" + dst_nodeID.ToString() + " Len:" + strconv.Itoa(len(packet)))
|
||||
packet := gopacket.NewPacket(packet[path.EgHeaderLen:], layers.LayerTypeEthernet, gopacket.Default)
|
||||
fmt.Println(packet.Dump())
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
if device.LogLevel.LogControl {
|
||||
if usage != path.NornalPacket {
|
||||
if usage != path.NormalPacket {
|
||||
if peer.GetEndpointDstStr() != "" {
|
||||
fmt.Println("Control: Send To:" + peer.GetEndpointDstStr() + " " + device.sprint_received(usage, packet[path.EgHeaderLen:]))
|
||||
}
|
||||
@ -155,7 +160,7 @@ func (device *Device) process_received(msg_type path.Usage, peer *Peer, body []b
|
||||
if content, err := path.ParseQueryPeerMsg(body); err == nil {
|
||||
return device.process_RequestPeerMsg(content)
|
||||
}
|
||||
case path.BoardcastPeer:
|
||||
case path.BroadcastPeer:
|
||||
if content, err := path.ParseBoardcastPeerMsg(body); err == nil {
|
||||
return device.process_BoardcastPeerMsg(peer, content)
|
||||
}
|
||||
@ -203,7 +208,7 @@ func (device *Device) sprint_received(msg_type path.Usage, body []byte) string {
|
||||
return content.ToString()
|
||||
}
|
||||
return "QueryPeerMsg: Parse failed"
|
||||
case path.BoardcastPeer:
|
||||
case path.BroadcastPeer:
|
||||
if content, err := path.ParseBoardcastPeerMsg(body); err == nil {
|
||||
return content.ToString()
|
||||
}
|
||||
@ -213,6 +218,16 @@ func (device *Device) sprint_received(msg_type path.Usage, body []byte) string {
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func compareVersion(v1 string, v2 string) bool {
|
||||
if strings.Contains(v1, "-") {
|
||||
v1 = strings.Split(v1, "-")[0]
|
||||
}
|
||||
if strings.Contains(v2, "-") {
|
||||
v2 = strings.Split(v2, "-")[0]
|
||||
}
|
||||
return v1 == v2
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (device *Device) server_process_RegisterMsg(peer *Peer, content path.RegisterMsg) error {
|
||||
UpdateErrorMsg := path.UpdateErrorMsg{
|
||||
Node_id: peer.ID,
|
||||
@ -228,7 +243,7 @@ func (device *Device) server_process_RegisterMsg(peer *Peer, content path.Regist
|
||||
ErrorMsg: "Your node ID is not match with our registered nodeID",
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
if content.Version != device.Version {
|
||||
if compareVersion(content.Version, device.Version) == false {
|
||||
UpdateErrorMsg = path.UpdateErrorMsg{
|
||||
Node_id: peer.ID,
|
||||
Action: path.Shutdown,
|
||||
@ -297,11 +312,11 @@ func (device *Device) process_ping(peer *Peer, content path.PingMsg) error {
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (device *Device) SendPing(peer *Peer, times int, replies int, interval float32) {
|
||||
func (device *Device) SendPing(peer *Peer, times int, replies int, interval float64) {
|
||||
for i := 0; i < times; i++ {
|
||||
packet, usage, _ := device.GeneratePingPacket(device.ID, replies)
|
||||
device.SendPacket(peer, usage, packet, MessageTransportOffsetContent)
|
||||
time.Sleep(path.S2TD(float64(interval)))
|
||||
time.Sleep(path.S2TD(interval))
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
@ -657,7 +672,7 @@ func (device *Device) RoutineSpreadAllMyNeighbor() {
|
||||
}
|
||||
for {
|
||||
device.process_RequestPeerMsg(path.QueryPeerMsg{
|
||||
Request_ID: uint32(config.Boardcast),
|
||||
Request_ID: uint32(config.Broadcast),
|
||||
})
|
||||
time.Sleep(path.S2TD(device.DRoute.P2P.SendPeerInterval))
|
||||
}
|
||||
@ -737,7 +752,7 @@ func (device *Device) process_RequestPeerMsg(content path.QueryPeerMsg) error {
|
||||
header.SetSrc(device.ID)
|
||||
header.SetPacketLength(uint16(len(body)))
|
||||
copy(buf[path.EgHeaderLen:], body)
|
||||
device.SpreadPacket(make(map[config.Vertex]bool), path.BoardcastPeer, buf, MessageTransportOffsetContent)
|
||||
device.SpreadPacket(make(map[config.Vertex]bool), path.BroadcastPeer, buf, MessageTransportOffsetContent)
|
||||
}
|
||||
device.peers.RUnlock()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
@ -19,6 +19,8 @@ import (
|
||||
"github.com/KusakabeSi/EtherGuardVPN/config"
|
||||
"github.com/KusakabeSi/EtherGuardVPN/path"
|
||||
"github.com/KusakabeSi/EtherGuardVPN/tap"
|
||||
"github.com/google/gopacket"
|
||||
"github.com/google/gopacket/layers"
|
||||
"golang.org/x/crypto/chacha20poly1305"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
@ -254,9 +256,9 @@ func (device *Device) RoutineReadFromTUN() {
|
||||
dstMacAddr := tap.GetDstMacAddr(elem.packet[path.EgHeaderLen:])
|
||||
// lookup peer
|
||||
if tap.IsNotUnicast(dstMacAddr) {
|
||||
dst_nodeID = config.Boardcast
|
||||
dst_nodeID = config.Broadcast
|
||||
} else if val, ok := device.l2fib.Load(dstMacAddr); !ok { //Lookup failed
|
||||
dst_nodeID = config.Boardcast
|
||||
dst_nodeID = config.Broadcast
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
dst_nodeID = val.(config.Vertex)
|
||||
}
|
||||
@ -264,9 +266,9 @@ func (device *Device) RoutineReadFromTUN() {
|
||||
EgBody.SetDst(dst_nodeID)
|
||||
EgBody.SetPacketLength(uint16(len(elem.packet) - path.EgHeaderLen))
|
||||
EgBody.SetTTL(device.DefaultTTL)
|
||||
elem.Type = path.NornalPacket
|
||||
elem.Type = path.NormalPacket
|
||||
|
||||
if dst_nodeID != config.Boardcast {
|
||||
if dst_nodeID != config.Broadcast {
|
||||
var peer *Peer
|
||||
next_id := device.graph.Next(device.ID, dst_nodeID)
|
||||
if next_id != nil {
|
||||
@ -278,6 +280,8 @@ func (device *Device) RoutineReadFromTUN() {
|
||||
}
|
||||
if device.LogLevel.LogNormal {
|
||||
fmt.Println("Normal: Send Normal packet To:" + peer.GetEndpointDstStr() + " SrcID:" + device.ID.ToString() + " DstID:" + dst_nodeID.ToString() + " Len:" + strconv.Itoa(len(elem.packet)))
|
||||
packet := gopacket.NewPacket(elem.packet[path.EgHeaderLen:], layers.LayerTypeEthernet, gopacket.Default)
|
||||
fmt.Println(packet.Dump())
|
||||
}
|
||||
if peer.isRunning.Get() {
|
||||
peer.StagePacket(elem)
|
||||
|
||||
@ -62,6 +62,7 @@ P2P模式也有幾個參數
|
||||
1. sendpeerinterval: 廣播BoardcastPeer的間格
|
||||
1. peeralivetimeout: 每次收到封包就重置,超過時間沒收到就視為該peer離線
|
||||
1. graphrecalculatesetting: 一些和[Floyd-Warshall演算法](https://zh.wikipedia.org/zh-tw/Floyd-Warshall算法)相關的參數
|
||||
1. staticmode: 關閉Floyd-Warshall演算法,只使用一開始載入的nexthoptable。P2P單純用來打洞
|
||||
1. jittertolerance: 抖動容許誤差,收到Pong以後,一個37ms,一個39ms,不會觸發重新計算
|
||||
1. jittertolerancemultiplier: 一樣是抖動容許誤差,但是高ping的話允許更多誤差
|
||||
https://www.desmos.com/calculator/raoti16r5n
|
||||
@ -74,4 +75,4 @@ P2P模式下,PSK是禁用的。因為n個節點有n(n-1)/2的連線,每個
|
||||
也不像super mode,有中心伺服器統一分發
|
||||
每對peer要協商出一個PSK有難度,因此我設定禁用PSK了,只用wireguard原本的加密系統
|
||||
|
||||
**最後,P2P模式我還沒有大規模測試過,穩定性不知如何。PR is welecome**
|
||||
**最後,P2P模式我還沒有大規模測試過,穩定性不知如何。PR is welcome**
|
||||
@ -38,6 +38,7 @@ dynamicroute:
|
||||
usep2p: true
|
||||
sendpeerinterval: 20
|
||||
graphrecalculatesetting:
|
||||
staticmode: false
|
||||
jittertolerance: 20
|
||||
jittertolerancemultiplier: 1.1
|
||||
nodereporttimeout: 40
|
||||
|
||||
@ -38,6 +38,7 @@ dynamicroute:
|
||||
usep2p: true
|
||||
sendpeerinterval: 20
|
||||
graphrecalculatesetting:
|
||||
staticmode: false
|
||||
jittertolerance: 20
|
||||
jittertolerancemultiplier: 1.1
|
||||
nodereporttimeout: 40
|
||||
|
||||
@ -38,6 +38,7 @@ dynamicroute:
|
||||
usep2p: true
|
||||
sendpeerinterval: 20
|
||||
graphrecalculatesetting:
|
||||
staticmode: false
|
||||
jittertolerance: 20
|
||||
jittertolerancemultiplier: 1.1
|
||||
nodereporttimeout: 40
|
||||
|
||||
@ -38,6 +38,7 @@ dynamicroute:
|
||||
usep2p: true
|
||||
sendpeerinterval: 20
|
||||
graphrecalculatesetting:
|
||||
staticmode: false
|
||||
jittertolerance: 20
|
||||
jittertolerancemultiplier: 1.1
|
||||
nodereporttimeout: 40
|
||||
|
||||
@ -38,6 +38,7 @@ dynamicroute:
|
||||
usep2p: true
|
||||
sendpeerinterval: 20
|
||||
graphrecalculatesetting:
|
||||
staticmode: false
|
||||
jittertolerance: 20
|
||||
jittertolerancemultiplier: 1.1
|
||||
nodereporttimeout: 40
|
||||
|
||||
@ -38,6 +38,7 @@ dynamicroute:
|
||||
usep2p: true
|
||||
sendpeerinterval: 20
|
||||
graphrecalculatesetting:
|
||||
staticmode: false
|
||||
jittertolerance: 20
|
||||
jittertolerancemultiplier: 1.1
|
||||
nodereporttimeout: 40
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,4 +1,205 @@
|
||||
# Etherguard
|
||||
[中文版](README_zh.md)
|
||||
|
||||
WIP
|
||||
This is the documentation of the static_mode of this example_config
|
||||
|
||||
## Static mode
|
||||
|
||||
No dynamic routing, no handshake server.
|
||||
Similar to original wireguard , all things must be preconfigured.
|
||||
|
||||
But you need to setup an additional `Next hop table`, this table are share among all nodes.
|
||||
|
||||
The `nexthoptable` section is for this mode, and only works in this mode.
|
||||
|
||||
In this mode, there are no any Control Message, no connectivity check.
|
||||
Please maintains the predefined topology, otherwise if the relay node offline, part of this network will broken,
|
||||
|
||||
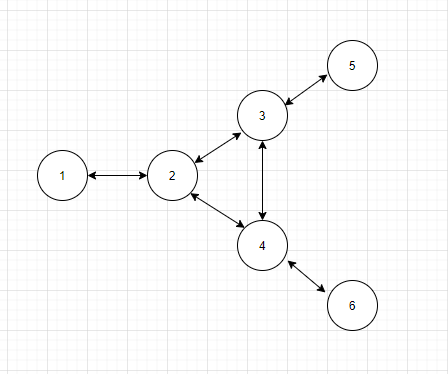
The topology of this [example_config](./):
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Before sending packet, We will set the SrcID to my NodeID. And the DstID will be found from l2fib table. If lookup failed or it's a Broadcast address, It will be set to `Broadcast(65535)`
|
||||
|
||||
While received packet, if the DstID==NodeID, or DstID==65535, it will receive the packet, and send to correspond tap device. And meanwhile, add the NodeID->SrcMacAddress to l2fib.
|
||||
If not, it will lookup from the `Next hop table`, to determine who will be sent of this packet.
|
||||
|
||||
Here is an example of the `Next hop table` in this example topology. A yaml formatted nested dictionary. `NhTable[SrcID][DstID]= Next hop ID`
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
nexthoptable:
|
||||
1:
|
||||
2: 2
|
||||
3: 2
|
||||
4: 2
|
||||
5: 2
|
||||
6: 2
|
||||
2:
|
||||
1: 1
|
||||
3: 3
|
||||
4: 4
|
||||
5: 3
|
||||
6: 4
|
||||
3:
|
||||
1: 2
|
||||
2: 2
|
||||
4: 4
|
||||
5: 5
|
||||
6: 4
|
||||
4:
|
||||
1: 2
|
||||
2: 2
|
||||
3: 3
|
||||
5: 3
|
||||
6: 6
|
||||
5:
|
||||
1: 3
|
||||
2: 3
|
||||
3: 3
|
||||
4: 3
|
||||
6: 3
|
||||
6:
|
||||
1: 4
|
||||
2: 4
|
||||
3: 4
|
||||
4: 4
|
||||
5: 4
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Broadcast
|
||||
Broadcast is a special case.
|
||||
|
||||
Today I am Node 4, and I received a `Src=1, dst=Broadcast`.
|
||||
I should send to Node 6 ONLY without sending it to Node 3.
|
||||
Cuz Node 3 should receive it from Node 2 Instead of me.
|
||||
|
||||
So if `dst=Broadcast`, I will check src to all my neighbors whether I am a required route of this packet.
|
||||
**1 -> 6** : [1 2 4 6] , I am a required route
|
||||
**1 -> 3** : [1 2 3] , I am not a required route
|
||||
**1 -> 3** : Skip check, packet is coming from it
|
||||
So I knows I should send this packet to Node 6 only.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### `Next Hop Table` calculator
|
||||
|
||||
This tool can also calculate `Next Hop Table` for you.
|
||||
|
||||
Prepare a `path.txt` first, mark all single way latency in it like this:
|
||||
```
|
||||
X 1 2 3 4 5 6
|
||||
1 0 0.5 Inf Inf Inf Inf
|
||||
2 0.5 0 0.5 0.5 Inf Inf
|
||||
3 Inf 0.5 0 0.5 0.5 Inf
|
||||
4 Inf 0.5 0.5 0 Inf 0.5
|
||||
5 Inf Inf 0.5 Inf 0 Inf
|
||||
6 Inf Inf Inf 0.5 Inf 0
|
||||
```
|
||||
`Inf` means unreachable.
|
||||
|
||||
Then use this command to calculate it.
|
||||
```
|
||||
./etherguard-go -config example_config/static_mode/path.txt -mode solve
|
||||
|
||||
NextHopTable:
|
||||
1:
|
||||
2: 2
|
||||
3: 2
|
||||
4: 2
|
||||
5: 2
|
||||
6: 2
|
||||
2:
|
||||
1: 1
|
||||
3: 3
|
||||
4: 4
|
||||
5: 3
|
||||
6: 4
|
||||
3:
|
||||
1: 2
|
||||
2: 2
|
||||
4: 4
|
||||
5: 5
|
||||
6: 4
|
||||
4:
|
||||
1: 2
|
||||
2: 2
|
||||
3: 3
|
||||
5: 3
|
||||
6: 6
|
||||
5:
|
||||
1: 3
|
||||
2: 3
|
||||
3: 3
|
||||
4: 3
|
||||
6: 3
|
||||
6:
|
||||
1: 4
|
||||
2: 4
|
||||
3: 4
|
||||
4: 4
|
||||
5: 4
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
There are some additional information of the calculation result.
|
||||
```
|
||||
Human readable:
|
||||
src dist path
|
||||
1 -> 2 0.500000 [1 2]
|
||||
1 -> 3 1.000000 [1 2 3]
|
||||
1 -> 4 1.000000 [1 2 4]
|
||||
1 -> 5 1.500000 [1 2 3 5]
|
||||
1 -> 6 1.500000 [1 2 4 6]
|
||||
2 -> 1 0.500000 [2 1]
|
||||
2 -> 3 0.500000 [2 3]
|
||||
2 -> 4 0.500000 [2 4]
|
||||
2 -> 5 1.000000 [2 3 5]
|
||||
2 -> 6 1.000000 [2 4 6]
|
||||
3 -> 1 1.000000 [3 2 1]
|
||||
3 -> 2 0.500000 [3 2]
|
||||
3 -> 4 0.500000 [3 4]
|
||||
3 -> 5 0.500000 [3 5]
|
||||
3 -> 6 1.000000 [3 4 6]
|
||||
4 -> 1 1.000000 [4 2 1]
|
||||
4 -> 2 0.500000 [4 2]
|
||||
4 -> 3 0.500000 [4 3]
|
||||
4 -> 5 1.000000 [4 3 5]
|
||||
4 -> 6 0.500000 [4 6]
|
||||
5 -> 1 1.500000 [5 3 2 1]
|
||||
5 -> 2 1.000000 [5 3 2]
|
||||
5 -> 3 0.500000 [5 3]
|
||||
5 -> 4 1.000000 [5 3 4]
|
||||
5 -> 6 1.500000 [5 3 4 6]
|
||||
6 -> 1 1.500000 [6 4 2 1]
|
||||
6 -> 2 1.000000 [6 4 2]
|
||||
6 -> 3 1.000000 [6 4 3]
|
||||
6 -> 4 0.500000 [6 4]
|
||||
6 -> 5 1.500000 [6 4 3 5]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Quick start
|
||||
|
||||
#### Run example config
|
||||
|
||||
Execute following command in **Different Terminal**
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
./etherguard-go -config example_config/super_mode/n1.yaml -mode edge
|
||||
./etherguard-go -config example_config/super_mode/n2.yaml -mode edge
|
||||
./etherguard-go -config example_config/super_mode/n3.yaml -mode edge
|
||||
./etherguard-go -config example_config/super_mode/n4.yaml -mode edge
|
||||
./etherguard-go -config example_config/super_mode/n5.yaml -mode edge
|
||||
./etherguard-go -config example_config/super_mode/n6.yaml -mode edge
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The iface type of this example config is `stdio` (keyboard debug), so it will read data from stdin.
|
||||
Then input following text in the terminal
|
||||
```
|
||||
b1message
|
||||
```
|
||||
The `l2headermode` is `kbdbg`, means `Keyboard debug`. So that the first two byte will be convert to `FF:FF:FF:FF:FF:FF`, and `AA:BB:CC:DD:EE:01`. And the `message` is the real payload.
|
||||
|
||||
With other debug message, you should be able to see the message in other terminal.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Use it in real world
|
||||
|
||||
Please modify the `itype` to `tap`, and modify the pubkey and privkey, close unnecessary logging , and deploy to all nodes.
|
||||
|
||||
## Next: [Super Mode](../super_mode/README.md)
|
||||
@ -31,7 +31,7 @@ Static Mode的[範例配置檔](./)的說明文件
|
||||
轉發/發送封包時,直接查詢 `NhTable[起點][終點]=下一跳`
|
||||
就知道下面一個封包要轉給誰了
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
nexthoptable:
|
||||
1:
|
||||
2: 2
|
||||
@ -182,4 +182,32 @@ src dist path
|
||||
6 -> 5 1.500000 [6 4 3 5]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
接下來你就能了解一下[Super Mode的運作](../super_mode/README_zh.md)
|
||||
### Quick start
|
||||
|
||||
#### Run example config
|
||||
|
||||
在**不同terminal**分別執行以下命令
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
./etherguard-go -config example_config/super_mode/n1.yaml -mode edge
|
||||
./etherguard-go -config example_config/super_mode/n2.yaml -mode edge
|
||||
./etherguard-go -config example_config/super_mode/n3.yaml -mode edge
|
||||
./etherguard-go -config example_config/super_mode/n4.yaml -mode edge
|
||||
./etherguard-go -config example_config/super_mode/n5.yaml -mode edge
|
||||
./etherguard-go -config example_config/super_mode/n6.yaml -mode edge
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
因為本範例配置是stdio的kbdbg模式,stdin會讀入VPN網路
|
||||
請在其中一個edge視窗中鍵入
|
||||
```
|
||||
b1message
|
||||
```
|
||||
因為`l2headermode`是`kbdbg`,所以b1會被轉換成 12byte 的layer 2 header,b是廣播地址`FF:FF:FF:FF:FF:FF`,1是普通地址`AA:BB:CC:DD:EE:01`,message是後面的payload,然後再丟入VPN
|
||||
此時應該要能夠在另一個視窗上看見字串b1message。前12byte被轉換回來了
|
||||
|
||||
#### Run your own etherguard
|
||||
|
||||
要正式使用,請將itype改成`tap`,並且修改各節點的公鑰私鑰和連線地址
|
||||
再關閉不必要的log增加性能,最後部屬到不同節點即可
|
||||
|
||||
## 下一篇: [Super Mode的運作](../super_mode/README_zh.md)
|
||||
@ -38,6 +38,7 @@ dynamicroute:
|
||||
usep2p: false
|
||||
sendpeerinterval: 20
|
||||
graphrecalculatesetting:
|
||||
staticmode: false
|
||||
jittertolerance: 20
|
||||
jittertolerancemultiplier: 1.1
|
||||
nodereporttimeout: 40
|
||||
|
||||
@ -38,6 +38,7 @@ dynamicroute:
|
||||
usep2p: false
|
||||
sendpeerinterval: 20
|
||||
graphrecalculatesetting:
|
||||
staticmode: false
|
||||
jittertolerance: 20
|
||||
jittertolerancemultiplier: 1.1
|
||||
nodereporttimeout: 40
|
||||
|
||||
@ -38,6 +38,7 @@ dynamicroute:
|
||||
usep2p: false
|
||||
sendpeerinterval: 20
|
||||
graphrecalculatesetting:
|
||||
staticmode: false
|
||||
jittertolerance: 20
|
||||
jittertolerancemultiplier: 1.1
|
||||
nodereporttimeout: 40
|
||||
|
||||
@ -38,6 +38,7 @@ dynamicroute:
|
||||
usep2p: false
|
||||
sendpeerinterval: 20
|
||||
graphrecalculatesetting:
|
||||
staticmode: false
|
||||
jittertolerance: 20
|
||||
jittertolerancemultiplier: 1.1
|
||||
nodereporttimeout: 40
|
||||
|
||||
@ -38,6 +38,7 @@ dynamicroute:
|
||||
usep2p: false
|
||||
sendpeerinterval: 20
|
||||
graphrecalculatesetting:
|
||||
staticmode: false
|
||||
jittertolerance: 20
|
||||
jittertolerancemultiplier: 1.1
|
||||
nodereporttimeout: 40
|
||||
|
||||
@ -38,6 +38,7 @@ dynamicroute:
|
||||
usep2p: false
|
||||
sendpeerinterval: 20
|
||||
graphrecalculatesetting:
|
||||
staticmode: false
|
||||
jittertolerance: 20
|
||||
jittertolerancemultiplier: 1.1
|
||||
nodereporttimeout: 40
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,4 +1,487 @@
|
||||
# Etherguard
|
||||
[中文版](README_zh.md)
|
||||
|
||||
WIP
|
||||
This is the documentation of the super_mode of this example_config
|
||||
Before reading this, I'd like to suggest you read the [static mode](../static_mode/README.md) first.
|
||||
|
||||
## Super mode
|
||||
|
||||
Super mode are inspired by [n2n](https://github.com/ntop/n2n)
|
||||
We have two types of node, we called it super node and edge node.
|
||||
|
||||
All edge nodes have to connect to super node, exchange data and UDP hole punch each other by super node.
|
||||
The super node runs the [Floyd-Warshall Algorithm](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Floyd–Warshall_algorithm), and distribute the result to all edge node.
|
||||
|
||||
In the super mode of the edge node, the `nexthoptable` and `peers` section are useless. All infos are download from super node.
|
||||
Meanwhile, super node will generate pre shared key for inter-edge communication(if `usepskforinteredge` enabled).
|
||||
```golang
|
||||
psk = shs256("PubkeyPeerA" + "PubkeyPeerB" + "Chef Special and Featured in the season see salt")[:32]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### SuperMsg
|
||||
There are new type of DstID called `SuperMsg`(65534). All packets sends to and receive from super node are using this packet type.
|
||||
This packet will not send to any other edge node, just like `DstID == self.NodeID`
|
||||
|
||||
## Control Message
|
||||
In Super mode, Beside `Normal Packet`. We introduce a new packet type called `Control Message`. In Super mode, we will not relay any control message. We just receive or send it to target directly.
|
||||
We list all the control message we use in the super mode below.
|
||||
|
||||
### Register
|
||||
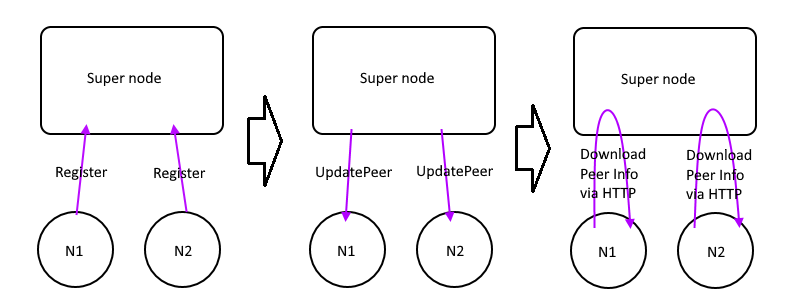
This control message works like this picture:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
1. edge node send Register to the super node
|
||||
2. Supernode knows it's external IP and port number
|
||||
3. Update it to database and distribute `UpdatePeerMsg` to all edges
|
||||
4. Other edges get the notification, download the updated peer infos from supernode via HTTP API
|
||||
|
||||
### Ping/Pong
|
||||
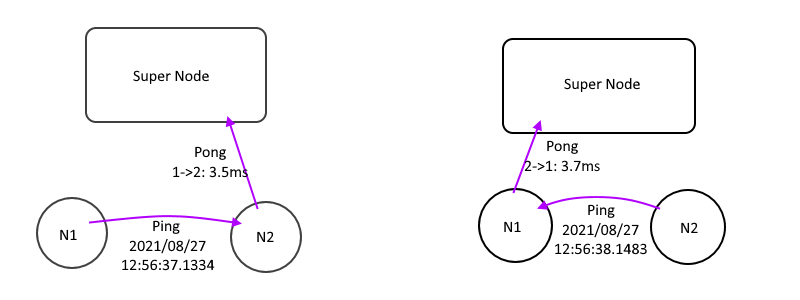
While edges get the peer infos, edges will start trying to talk each other directly like this picture:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
1. Send `Ping` to all other edges with local time with TTL=0
|
||||
2. Received a `Ping`, Subtract the peer time from local time, we get a single way latency.
|
||||
3. Send a `Pong` to supernode, let supernode calculate the NextHopTable
|
||||
4. Wait the supernode push `UpdateNhTable` message and download it.
|
||||
|
||||
### UpdateNhTable
|
||||
While supernode get a `Pong` message, it will run the [Floyd-Warshall Algorithm](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Floyd–Warshall_algorithm) to calculate the NextHopTable
|
||||
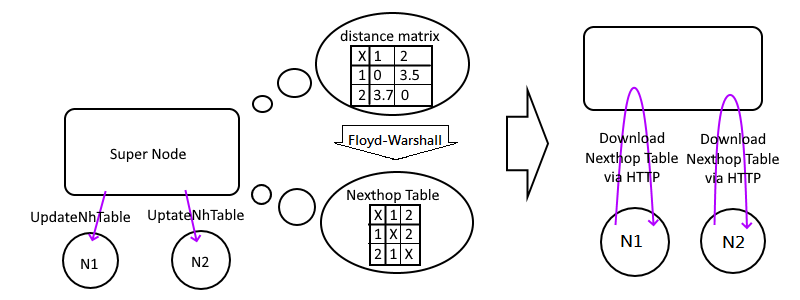
|
||||
If there are any changes of this table, it will distribute `UpdateNhTable` to all edges to till then download the latest NextHopTable via HTTP API as soon as possible.
|
||||
|
||||
### UpdateError
|
||||
Notify edges that an error has occurred, and close the edge
|
||||
It occurs when the version number is not match with supernode, or the NodeID of the edge is configured incorrectly, or the edge is deleted.
|
||||
|
||||
### HTTP API
|
||||
Why we use HTTP API instead of pack all information in the `UpdateXXX`?
|
||||
Because UDP is an unreliable protocol, there is an limit on the amount of content that can be carried.
|
||||
But the peer list contains all the peer information, the length is not fixed, it may exceed
|
||||
So we use `UpdateXXX` to tell we have a update, please download the latest information from supernode via HTTP API as soon as possible.
|
||||
And `UpdateXXX` itself is not reliable, maybe it didn't reach the edge node at all.
|
||||
So the information of `UpdateXXX` carries the `state hash`. Bring it when with HTTP API. When the super node receives the HTTP API and sees the `state hash`, it knows that the edge node has received the `UpdateXXX`.
|
||||
Otherwise, it will send `UpdateXXX` to the node again after few seconds.
|
||||
|
||||
## HTTP Guest API
|
||||
HTTP also has some APIs for the front-end to help manage the entire network
|
||||
|
||||
### peerstate
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:3000/api/peerstate?Password=passwd"
|
||||
```
|
||||
It can show some information such as single way latency or last seen time.
|
||||
We can visualize it by Force-directed graph drawing.
|
||||
|
||||
There is an `Infinity` section in the json response. It should be 9999. It means infinity if the number larger than it.
|
||||
Cuz json can't present infinity so that I use this trick.
|
||||
While we see the latency larger than this, we doesn't need to draw lines in this two nodes.
|
||||
|
||||
Example return value:
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"PeerInfo": {
|
||||
"1": {
|
||||
"Name": "hk",
|
||||
"LastSeen": "2021-09-29 11:23:22.854700559 +0000 UTC m=+28740.116476977"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"1001": {
|
||||
"Name": "relay_kr",
|
||||
"LastSeen": "2021-09-29 11:23:21.277417897 +0000 UTC m=+28738.539194315"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"121": {
|
||||
"Name": "za_north",
|
||||
"LastSeen": "0001-01-01 00:00:00 +0000 UTC"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"33": {
|
||||
"Name": "us_west",
|
||||
"LastSeen": "2021-09-29 11:23:13.257033252 +0000 UTC m=+28730.518809670"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"49": {
|
||||
"Name": "us_east",
|
||||
"LastSeen": "2021-09-29 11:23:16.606165241 +0000 UTC m=+28733.867941659"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"51": {
|
||||
"Name": "ca_central",
|
||||
"LastSeen": "0001-01-01 00:00:00 +0000 UTC"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"65": {
|
||||
"Name": "fr",
|
||||
"LastSeen": "2021-09-29 11:23:19.4084596 +0000 UTC m=+28736.670236018"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"81": {
|
||||
"Name": "au_central",
|
||||
"LastSeen": "0001-01-01 00:00:00 +0000 UTC"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"89": {
|
||||
"Name": "uae_north",
|
||||
"LastSeen": "0001-01-01 00:00:00 +0000 UTC"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"9": {
|
||||
"Name": "jp_east",
|
||||
"LastSeen": "2021-09-29 11:23:16.669505147 +0000 UTC m=+28733.931281565"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"97": {
|
||||
"Name": "br_south",
|
||||
"LastSeen": "0001-01-01 00:00:00 +0000 UTC"
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"Infinity": 99999,
|
||||
"Edges": {
|
||||
"1": {
|
||||
"1001": 0.033121187,
|
||||
"33": 0.075653164,
|
||||
"49": 0.100471502,
|
||||
"65": 0.065714769,
|
||||
"9": 0.022864241
|
||||
},
|
||||
"1001": {
|
||||
"1": 0.018561948,
|
||||
"33": 0.064077348,
|
||||
"49": 0.094459818,
|
||||
"65": 0.079481599,
|
||||
"9": 0.011163433
|
||||
},
|
||||
"33": {
|
||||
"1": 0.075263428,
|
||||
"1001": 0.070029457,
|
||||
"49": 0.032631349,
|
||||
"65": 0.045575061,
|
||||
"9": 0.050444255
|
||||
},
|
||||
"49": {
|
||||
"1": 0.100271358,
|
||||
"1001": 0.100182834,
|
||||
"33": 0.034563118,
|
||||
"65": 0.017950046,
|
||||
"9": 0.07510982
|
||||
},
|
||||
"65": {
|
||||
"1": 0.114219741,
|
||||
"1001": 0.132759205,
|
||||
"33": 0.095265063,
|
||||
"49": 0.067413235,
|
||||
"9": 0.127562362
|
||||
},
|
||||
"9": {
|
||||
"1": 0.026909699,
|
||||
"1001": 0.022555855,
|
||||
"33": 0.056469043,
|
||||
"49": 0.090400723,
|
||||
"65": 0.08525314
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"NhTable": {
|
||||
"1": {
|
||||
"1001": 1001,
|
||||
"33": 33,
|
||||
"49": 49,
|
||||
"65": 65,
|
||||
"9": 9
|
||||
},
|
||||
"1001": {
|
||||
"1": 1,
|
||||
"33": 33,
|
||||
"49": 49,
|
||||
"65": 65,
|
||||
"9": 9
|
||||
},
|
||||
"33": {
|
||||
"1": 1,
|
||||
"1001": 1001,
|
||||
"49": 49,
|
||||
"65": 65,
|
||||
"9": 9
|
||||
},
|
||||
"49": {
|
||||
"1": 1,
|
||||
"1001": 9,
|
||||
"33": 33,
|
||||
"65": 65,
|
||||
"9": 9
|
||||
},
|
||||
"65": {
|
||||
"1": 1,
|
||||
"1001": 1001,
|
||||
"33": 33,
|
||||
"49": 49,
|
||||
"9": 9
|
||||
},
|
||||
"9": {
|
||||
"1": 1,
|
||||
"1001": 1001,
|
||||
"33": 33,
|
||||
"49": 33,
|
||||
"65": 65
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"Dist": {
|
||||
"1": {
|
||||
"1": 0,
|
||||
"1001": 0.033121187,
|
||||
"33": 0.075119328,
|
||||
"49": 0.102236885,
|
||||
"65": 0.074688856,
|
||||
"9": 0.022473723
|
||||
},
|
||||
"1001": {
|
||||
"1": 0.018561948,
|
||||
"1001": 0,
|
||||
"33": 0.064077348,
|
||||
"49": 0.094459818,
|
||||
"65": 0.079481599,
|
||||
"9": 0.011163433
|
||||
},
|
||||
"33": {
|
||||
"1": 0.075263428,
|
||||
"1001": 0.070029457,
|
||||
"33": 0,
|
||||
"49": 0.032631349,
|
||||
"65": 0.045575061,
|
||||
"9": 0.050444255
|
||||
},
|
||||
"49": {
|
||||
"1": 0.100271358,
|
||||
"1001": 0.097665675,
|
||||
"33": 0.034563118,
|
||||
"49": 0,
|
||||
"65": 0.017950046,
|
||||
"9": 0.07510982
|
||||
},
|
||||
"65": {
|
||||
"1": 0.114219741,
|
||||
"1001": 0.132759205,
|
||||
"33": 0.095265063,
|
||||
"49": 0.067413235,
|
||||
"65": 0,
|
||||
"9": 0.127562362
|
||||
},
|
||||
"9": {
|
||||
"1": 0.026909699,
|
||||
"1001": 0.022555855,
|
||||
"33": 0.056469043,
|
||||
"49": 0.089100392,
|
||||
"65": 0.08525314,
|
||||
"9": 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Section meaning:
|
||||
1. PeerInfo: NodeID,Name,LastSeen
|
||||
2. Edges: The **Single way latency**,9999 or missing means unreachable(UDP hole punching failed)
|
||||
3. NhTable: Calculate result.
|
||||
4. Dist: The latency of **packet through Etherguard**
|
||||
|
||||
### peeradd
|
||||
We can add new edges with this API without restart the supernode
|
||||
|
||||
Exanple:
|
||||
```
|
||||
curl -X POST "http://127.0.0.1:3000/api/peer/add?Password=passwd_addpeer" \
|
||||
-H "Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded" \
|
||||
-d "nodeid=100&name=Node_100&pubkey=6SuqwPH9pxGigtZDNp3PABZYfSEzDaBSwuThsUUAcyM="
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Parameter:
|
||||
1. URL query: Password: Password. Configured in the config file.
|
||||
1. Post body:
|
||||
1. nodeid: Node ID
|
||||
1. pubkey: Public Key
|
||||
1. pskey: Pre shared Key
|
||||
|
||||
Return value:
|
||||
1. http code != 200: Error reason
|
||||
2. http code == 200,An example edge config.
|
||||
* generate by contents in `edgetemplate` with custom data (nodeid/name/pubkey)
|
||||
* Convenient for users to copy and paste
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
interface:
|
||||
itype: stdio
|
||||
name: tap1
|
||||
vppifaceid: 1
|
||||
vppbridgeid: 4242
|
||||
macaddrprefix: AA:BB:CC:DD
|
||||
mtu: 1416
|
||||
recvaddr: 127.0.0.1:4001
|
||||
sendaddr: 127.0.0.1:5001
|
||||
l2headermode: kbdbg
|
||||
nodeid: 100
|
||||
nodename: Node_100
|
||||
defaultttl: 200
|
||||
privkey: Your_Private_Key
|
||||
listenport: 3001
|
||||
loglevel:
|
||||
loglevel: normal
|
||||
logtransit: true
|
||||
logcontrol: true
|
||||
lognormal: true
|
||||
logntp: true
|
||||
dynamicroute:
|
||||
sendpinginterval: 16
|
||||
peeralivetimeout: 30
|
||||
dupchecktimeout: 40
|
||||
conntimeout: 30
|
||||
connnexttry: 5
|
||||
savenewpeers: true
|
||||
supernode:
|
||||
usesupernode: true
|
||||
pskey: ""
|
||||
connurlv4: 127.0.0.1:3000
|
||||
pubkeyv4: LJ8KKacUcIoACTGB/9Ed9w0osrJ3WWeelzpL2u4oUic=
|
||||
connurlv6: ""
|
||||
pubkeyv6: HCfL6YJtpJEGHTlJ2LgVXIWKB/K95P57LHTJ42ZG8VI=
|
||||
apiurl: http://127.0.0.1:3000/api
|
||||
supernodeinfotimeout: 50
|
||||
p2p:
|
||||
usep2p: false
|
||||
sendpeerinterval: 20
|
||||
graphrecalculatesetting:
|
||||
jittertolerance: 20
|
||||
jittertolerancemultiplier: 1.1
|
||||
nodereporttimeout: 40
|
||||
recalculatecooldown: 5
|
||||
ntpconfig:
|
||||
usentp: true
|
||||
maxserveruse: 8
|
||||
synctimeinterval: 3600
|
||||
ntptimeout: 3
|
||||
servers:
|
||||
- time.google.com
|
||||
- time1.google.com
|
||||
- time2.google.com
|
||||
- time3.google.com
|
||||
- time4.google.com
|
||||
- time1.facebook.com
|
||||
- time2.facebook.com
|
||||
- time3.facebook.com
|
||||
- time4.facebook.com
|
||||
- time5.facebook.com
|
||||
- time.cloudflare.com
|
||||
- time.apple.com
|
||||
- time.asia.apple.com
|
||||
- time.euro.apple.com
|
||||
- time.windows.com
|
||||
nexthoptable: {}
|
||||
resetconninterval: 86400
|
||||
peers: []
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### peerdel
|
||||
Delete peer
|
||||
|
||||
There are two deletion modes, namely password deletion and private key deletion.
|
||||
Designed to be used by administrators, or for people who join the network and want to leave the network.
|
||||
|
||||
Use Password to delete any node. Take the newly added node above as an example, use this API to delete the node
|
||||
```
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:3000/api/peer/del?Password=passwd_delpeer&nodeid=100"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
We can also use privkey to delete, the same as above, but use privkey parameter only.
|
||||
```
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:3000/api/peer/del?privkey=IJtpnkm9ytbuCukx4VBMENJKuLngo9KSsS1D60BqonQ="
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Parameter:
|
||||
1. URL query:
|
||||
1. Password: Password: Password. Configured in the config file.
|
||||
1. nodeid: Node ID that you want to delete
|
||||
1. privkey: The private key of the edge
|
||||
|
||||
Return value:
|
||||
1. http code != 200: Error reason
|
||||
2. http code == 200: Success message
|
||||
|
||||
## Config Parameters
|
||||
|
||||
### Super mode of edge node
|
||||
1. `usesupernode`: Whether to enable Super mode
|
||||
1. `pskey`: Pre shared Key used to establish connection with supernode
|
||||
1. `connurlv4`: IPv4 connection address of the Super node
|
||||
1. `pubkeyv4`: IPv4 key of Super node
|
||||
1. `connurlv6`: IPv6 connection address of the Super node
|
||||
1. `pubkeyv6`: IPv6 key of Super node
|
||||
1. `apiurl`: HTTP(S) API connection address of Super node
|
||||
1. `supernodeinfotimeout`: Supernode Timeout
|
||||
|
||||
### Super node it self
|
||||
|
||||
1. nodename: node name
|
||||
1. privkeyv4: private key for ipv4
|
||||
1. privkeyv6: private key for ipv6
|
||||
1. listenport: listen udp port number
|
||||
1. loglevel: Refer to [README.md](../README.md)
|
||||
1. repushconfiginterval: re-push interval of `UpdateXXX` messages
|
||||
1. passwords: HTTP API password
|
||||
1. showstate: node information
|
||||
1. addpeer: add peer
|
||||
1. delpeer: delete peer
|
||||
1. graphrecalculatesetting: Some parameters related to [Floyd-Warshall algorithm](https://zh.wikipedia.org/zh-tw/Floyd-Warshall algorithm)
|
||||
1. staticmode: Disable the Floyd-Warshall algorithm and only use the nexthoptable loaded at the beginning.
|
||||
Supernode is only used to assist hole punching
|
||||
1. recalculatecooldown: Floyd-Warshal is O(n^3) time complexity algorithm, which cannot be calculated too often. Set a cooling time
|
||||
1. jittertolerance: jitter tolerance, after receiving Pong, one 37ms and one 39ms will not trigger recalculation
|
||||
1. jittertolerancemultiplier: the same is the jitter tolerance, but high ping allows more errors
|
||||
https://www.desmos.com/calculator/raoti16r5n
|
||||
1. nodereporttimeout: The timeout of the received `Pong` packet. Change back to Infinity after timeout.
|
||||
1. nexthoptable: only works in `staticmode==true`, set nexthoptable manually
|
||||
1. edgetemplate: for `addpeer` API. Refer to this configuration file and show a sample configuration file of the edge to the user
|
||||
1. usepskforinteredge: Whether to enable pre-share key communication between edges. If enabled, supernode will generate PSKs for edges automatically
|
||||
1. peers: Peer list, refer to [README.md](../README.md)
|
||||
1. nodeid: Peer's node ID
|
||||
1. name: Peer name (displayed on the front end)
|
||||
1. pubkey: peer public key
|
||||
1. pskey: preshared key The PSK that this peer connects to this Supernode
|
||||
|
||||
## V4 V6 Two Keys
|
||||
Why we split IPv4 and IPv6 into two session?
|
||||
Because of this situation
|
||||
|
||||
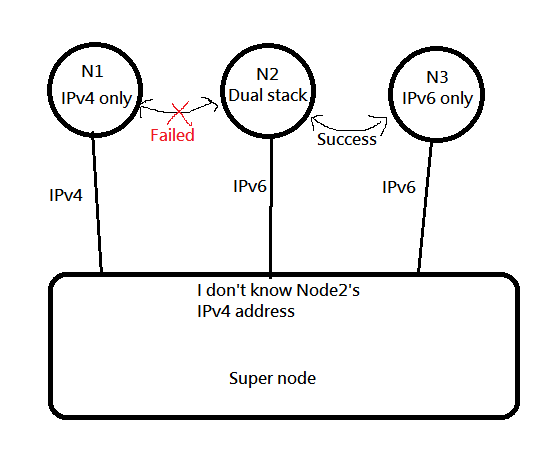
|
||||
|
||||
In this case, SuperNode does not know the external ipv4 address of Node02 and cannot help Node1 and Node2 to UDP hole punch.
|
||||
|
||||
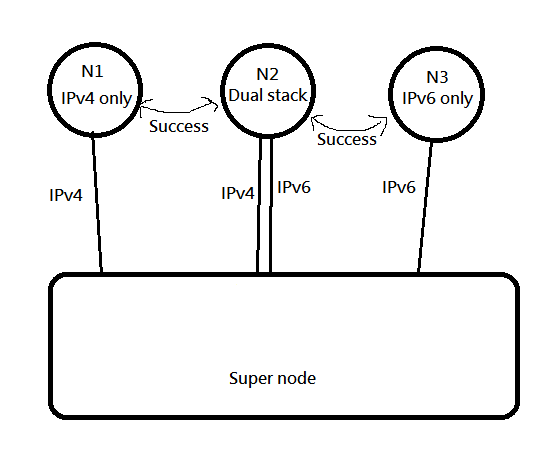
|
||||
|
||||
So like this, both V4 and V6 establish a session, so that both V4 and V6 can be taken care of at the same time.
|
||||
|
||||
## UDP hole punch reachability
|
||||
For different NAT type, the UDP hole punch reachability can refer this table.([Origin](https://dh2i.com/kbs/kbs-2961448-understanding-different-nat-types-and-hole-punching/))
|
||||
|
||||
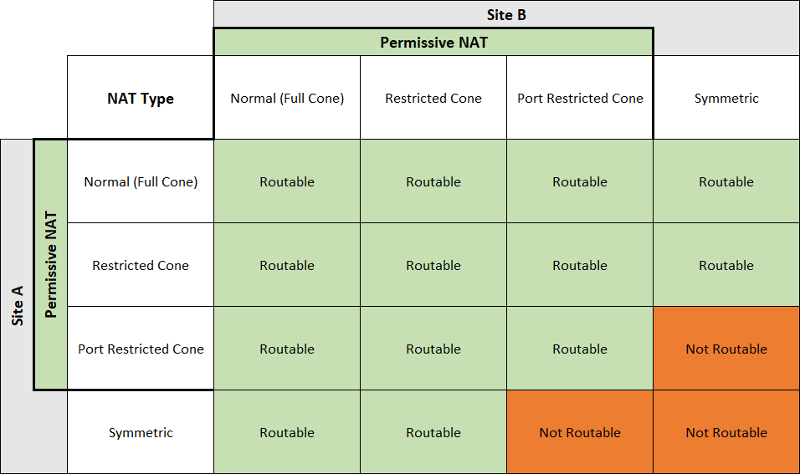
|
||||
|
||||
And if both sides are using ConeNAT, it's not gerenteed to punch success. It depends on the topology and the devices attributes.
|
||||
Like the section 3.5 in [this article](https://bford.info/pub/net/p2pnat/#SECTION00035000000000000000), we can't punch success.
|
||||
|
||||
## Notice for Relay node
|
||||
Unlike n2n, our supernode do not relay any packet for edges.
|
||||
If the edge punch failed and no any route available, it's just unreachable. In this case we need to setup a relay node.
|
||||
|
||||
Relay node is a regular edge in public network, but `interface=dummy`.
|
||||
|
||||
And we have to note that **do not** use 127.0.0.1 to connect to supernode.
|
||||
Because supernode well distribute the source IP of the nodes to all other edges. But 127.0.0.1 is not accessible from other edge.
|
||||
|
||||
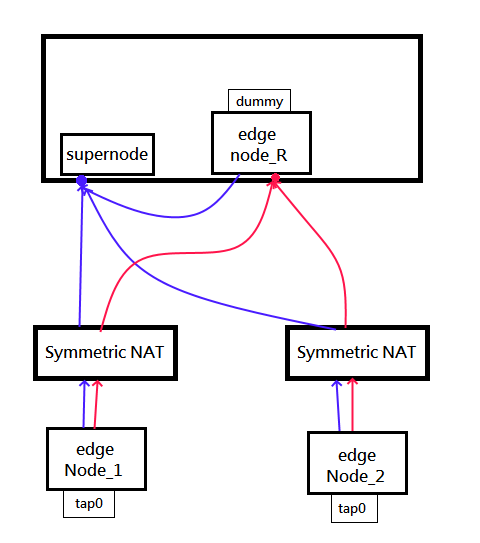
|
||||
|
||||
To avoid this issue, please use the external IP of the supernode in the edge config.
|
||||
|
||||
## Quick start
|
||||
Run this example_config (please open three terminals):
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
./etherguard-go -config example_config/super_mode/s1.yaml -mode super
|
||||
./etherguard-go -config example_config/super_mode/n1.yaml -mode edge
|
||||
./etherguard-go -config example_config/super_mode/n2.yaml -mode edge
|
||||
```
|
||||
Because it is in `stdio` mode, stdin will be read into the VPN network
|
||||
Please type in one of the edge windows
|
||||
```
|
||||
b1aaaaaaaaaa
|
||||
```
|
||||
b1 will be converted into a 12byte layer 2 header, b is the broadcast address `FF:FF:FF:FF:FF:FF`, 1 is the ordinary MAC address `AA:BB:CC:DD:EE:01`, aaaaaaaaaa is the payload, and then feed it into the VPN
|
||||
You should be able to see the string b1aaaaaaaaaa on another window. The first 12 bytes are converted back
|
||||
|
||||
## Next: [P2P Mode](../p2p_mode/README.md)
|
||||
@ -13,27 +13,30 @@ Super Mode是受到[n2n](https://github.com/ntop/n2n)的啟發
|
||||
藉由supernode交換其他節點的資訊,以及udp打洞
|
||||
由supernode執行[Floyd-Warshall演算法](https://zh.wikipedia.org/zh-tw/Floyd-Warshall算法),並把計算結果分發給全部edge node
|
||||
|
||||
在super mode模式下,設定檔裡面的`nexthoptable`以及`peers`是無效的。
|
||||
在edge node的super模式下,設定檔裡面的`nexthoptable`以及`peers`是無效的。
|
||||
這些資訊都是從super node上面下載
|
||||
同時,supernode會幫每個連線生成Preshared Key,分發給edge使用。
|
||||
同時,supernode會幫每個連線生成Preshared Key,分發給edge使用(如果`usepskforinteredge`有啟用的話)。
|
||||
```golang
|
||||
psk = shs256("PubkeyPeerA" + "PubkeyPeerB" + "主廚特調當季精選海鹽")[:32]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### SuperMsg
|
||||
|
||||
但是比起Static mode,Super mode引入了一種新的 `終點ID` 叫做 `SuperMsg`。
|
||||
所有送往Super node的封包都會是這種類型。
|
||||
這種封包不會在edge node之間傳播,收到也會不會轉給任何人,如同`終點ID == 自己`一般
|
||||
|
||||
### Register
|
||||
## Control Message
|
||||
從Super mode開始,我們有了Static mode不存在的Control Message。他會控制EtherGuard一些行為
|
||||
在Super mode下,我們不會轉發任何控制消息。 我們只會直接接收或發送給目標。
|
||||
下面列出Super Mode會出現的Control message
|
||||
|
||||
### Register
|
||||
具體運作方式類似這張圖
|
||||

|
||||
首先edge node發送regiater給super node
|
||||
super node收到以後就知道這個edge的endpoint IP和埠號。
|
||||
更新進資料庫以後發布`UpdatePeerMsg`。
|
||||
其他edge node收到以後就用HTTP API去下載完整的peer list。並且把自己沒有的peer通通加到本地
|
||||

|
||||
1. edge node發送`Register`給super node
|
||||
2. super node收到以後就知道這個edge的endpoint IP和埠號。
|
||||
3. 更新進資料庫以後發布`UpdatePeerMsg`。
|
||||
4. 其他edge node收到以後就用HTTP API去下載完整的peer list。並且把自己沒有的peer通通加到本地
|
||||
|
||||
### Ping/Pong
|
||||
有了peer list以後,接下來的運作方式類似這張圖
|
||||
@ -43,13 +46,17 @@ Edge node 會嘗試向其他所有peer發送`Ping`,裡面會攜帶節點自己
|
||||
收到`Ping`,就會產生一個`Pong`,並攜帶時間差。這個時間就是單向延遲
|
||||
但是他不會把`Pong`送回給原節點,而是送給Super node
|
||||
|
||||
### 轉發表
|
||||
### UpdateNhTable
|
||||
Super node收到節點們傳來的Pong以後,就知道他們的單向延遲了。接下來的運作方式類似這張圖
|
||||

|
||||
Super node收到Pong以後,就會更新它裡面的`Distance matrix`,並且重新計算轉發表
|
||||
如果有變動,就發布`UpdateNhTableMsg`
|
||||
其他edge node收到以後就用HTTP API去下載完整的轉發表
|
||||
|
||||
### UpdateError
|
||||
通知edges有錯誤發生,關閉egde端程式
|
||||
發生在版本號不匹被,該edge的NodeID配置錯誤,還有該Edge被刪除時觸發
|
||||
|
||||
### HTTP API
|
||||
為什麼要用HTTP額外下載呢?直接`UpdateXXX`夾帶資訊不好嗎?
|
||||
因為udp是不可靠協議,能攜帶的內容量也有上限。
|
||||
@ -61,15 +68,18 @@ Super node收到Pong以後,就會更新它裡面的`Distance matrix`,並且
|
||||
這樣super node收到HTTP API看到`state hash`就知道這個edge node確實有收到`UpdateXXX`了。
|
||||
不然每隔一段時間就會重新發送`UpdateXXX`給該節點
|
||||
|
||||
## HTTP Guest API
|
||||
HTTP還有一些個API,給前端使用,幫助管理整個網路
|
||||
|
||||
### peerstate
|
||||
HTTP還有三個個API,首先是這個peerstate
|
||||
```
|
||||
http://127.0.0.1:3000/api/peerstate?Password=passwd
|
||||
首先是這個peerstate
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:3000/api/peerstate?Password=passwd"
|
||||
```
|
||||
可以給前端看的,用來顯示現在各節點之間的單向延遲狀況
|
||||
之後可以用來畫力導向圖。
|
||||
|
||||
這個json下載下來有一個叫做`infinity`的欄位,值應該永遠是99999
|
||||
這個json下載下來有一個叫做`infinity`的欄位,值應該永遠是9999
|
||||
因為json沒辦法表達無限大。所以大於這個數值的就是無限大,不可達的意思
|
||||
這個數值是編譯時決定的,一般不會動。但保留變更的彈性
|
||||
所以有這個欄位,前端顯示時看到數值大於這個,就視為不可達,不用畫線了
|
||||
@ -386,10 +396,10 @@ curl "http://127.0.0.1:3000/api/peer/del?privkey=IJtpnkm9ytbuCukx4VBMENJKuLngo9K
|
||||
1. privkey: 該節點的私鑰
|
||||
|
||||
返回值:
|
||||
1. http code != 200: 被刪除的nodeID
|
||||
2. http code == 200: 空字串,表示成功
|
||||
1. http code != 200: 錯誤訊息
|
||||
2. http code == 200: 被刪除的nodeID
|
||||
|
||||
## Config Paramaters
|
||||
## Config Parameters
|
||||
|
||||
### Super mode的edge node有幾個參數
|
||||
1. `usesupernode`: 是否啟用Super mode
|
||||
@ -407,40 +417,28 @@ curl "http://127.0.0.1:3000/api/peer/del?privkey=IJtpnkm9ytbuCukx4VBMENJKuLngo9K
|
||||
1. privkeyv4: ipv4用的私鑰
|
||||
1. privkeyv6: ipv6用的私鑰
|
||||
1. listenport: 監聽udp埠號
|
||||
1. statepassword: Guest API 的密碼
|
||||
1. loglevel: 參考 [README_zh.md](../README_zh.md)
|
||||
1. repushconfiginterval: 重新push`UpdateXXX`的間格
|
||||
1. passwords: HTTP API 密碼
|
||||
1. showstate: 節點資訊
|
||||
1. addpeer: 新增peer
|
||||
1. delpeer: 刪除peer
|
||||
1. graphrecalculatesetting:
|
||||
1. graphrecalculatesetting: 一些和[Floyd-Warshall演算法](https://zh.wikipedia.org/zh-tw/Floyd-Warshall算法)相關的參數
|
||||
1. staticmode: 關閉Floyd-Warshall演算法,只使用一開始載入的nexthoptable。Supernode單純用來輔助打洞
|
||||
1. recalculatecooldown: Floyd-Warshal是O(n^3)時間複雜度,不能太常算。設個冷卻時間
|
||||
1. jittertolerance: 抖動容許誤差,收到Pong以後,一個37ms,一個39ms,不會觸發重新計算
|
||||
1. jittertolerancemultiplier: 一樣是抖動容許誤差,但是高ping的話允許更多誤差
|
||||
https://www.desmos.com/calculator/raoti16r5n
|
||||
1. nodereporttimeout: 收到的`Pong`封包的有效期限。太久沒收到就變回Infinity
|
||||
1. recalculatecooldown: Floyd-Warshal是O(n^3)時間複雜度,不能太頻繁計算。設個冷卻時間
|
||||
1. nexthoptable: 僅在`staticmode==true` 有效,手動設定的nexthoptable
|
||||
1. edgetemplate: 給`addpeer`API用的。參考這個設定檔,顯示一個範例設定檔給edge
|
||||
1. usepskforinteredge: 是否啟用edge間pre shares key通信。若啟用則幫edge們自動生成PSK
|
||||
1. peers: Peer列表,參考 [README_zh.md](../README_zh.md)
|
||||
1. nodeid: Peer的節點ID
|
||||
1. name: Peer名稱(顯示在前端)
|
||||
1. pubkey: peer 公鑰
|
||||
1. pskey: preshared key 該peer和本Supernode連線的PSK
|
||||
|
||||
##
|
||||
執行此範例設定檔(請開三個terminal):
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
./etherguard-go -config example_config/super_mode/s1.yaml -mode super
|
||||
./etherguard-go -config example_config/super_mode/n1.yaml -mode edge
|
||||
./etherguard-go -config example_config/super_mode/n2.yaml -mode edge
|
||||
```
|
||||
因為是stdio模式,stdin會讀入VPN網路
|
||||
請在其中一個edge視窗中鍵入
|
||||
```
|
||||
b1aaaaaaaaaa
|
||||
```
|
||||
b1會被轉換成 12byte 的layer 2 header,b是廣播地址`FF:FF:FF:FF:FF:FF`,1是普通地址`AA:BB:CC:DD:EE:01`,aaaaaaaaaa是後面的payload,然後再丟入VPN
|
||||
此時應該要能夠在另一個視窗上看見字串b1aaaaaaaaaa。前12byte被轉換回來了
|
||||
|
||||
## V4 V6 兩個公鑰
|
||||
為什麼要分開IPv4和IPv6呢?
|
||||
@ -457,7 +455,7 @@ b1會被轉換成 12byte 的layer 2 header,b是廣播地址`FF:FF:FF:FF:FF:FF`
|
||||
## 打洞可行性
|
||||
對於不同的NAT type,打洞的可行性可以參考這張圖([出處](https://dh2i.com/kbs/kbs-2961448-understanding-different-nat-types-and-hole-punching/))
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
還有,就算雙方都是ConeNAT,也不保證100%成功。
|
||||
還得看NAT設備的支援情況,詳見[此文](https://bford.info/pub/net/p2pnat/#SECTION00035000000000000000),裡面3.5章節描述的情況,也無法打洞成功
|
||||
@ -473,6 +471,19 @@ Relay node其實也是一個edge node,只不過被設定成為interface=dummy
|
||||
因為如果用127.0.0.1連接supernode,supernode看到封包的src IP就是127.0.0.1,就會把127.0.0.1分發給`Node_1`和`Node_2`
|
||||
`Node_1`和`Node_2`看到`Node_R`的連線地址是`127.0.0.1`,就連不上了
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Quick start
|
||||
執行此範例設定檔(請開三個terminal):
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
./etherguard-go -config example_config/super_mode/s1.yaml -mode super
|
||||
./etherguard-go -config example_config/super_mode/n1.yaml -mode edge
|
||||
./etherguard-go -config example_config/super_mode/n2.yaml -mode edge
|
||||
```
|
||||
因為是stdio模式,stdin會讀入VPN網路
|
||||
請在其中一個edge視窗中鍵入
|
||||
```
|
||||
b1aaaaaaaaaa
|
||||
```
|
||||
b1會被轉換成 12byte 的layer 2 header,b是廣播地址`FF:FF:FF:FF:FF:FF`,1是普通地址`AA:BB:CC:DD:EE:01`,aaaaaaaaaa是後面的payload,然後再丟入VPN
|
||||
此時應該要能夠在另一個視窗上看見字串b1aaaaaaaaaa。前12byte被轉換回來了
|
||||
|
||||
看完本章捷,接下來你就能了解一下[P2P Mode的運作](../p2p_mode/README_zh.md)
|
||||
|
||||
@ -39,6 +39,7 @@ dynamicroute:
|
||||
usep2p: false
|
||||
sendpeerinterval: 20
|
||||
graphrecalculatesetting:
|
||||
staticmode: false
|
||||
jittertolerance: 20
|
||||
jittertolerancemultiplier: 1.1
|
||||
nodereporttimeout: 40
|
||||
|
||||
@ -39,6 +39,7 @@ dynamicroute:
|
||||
usep2p: false
|
||||
sendpeerinterval: 20
|
||||
graphrecalculatesetting:
|
||||
staticmode: false
|
||||
jittertolerance: 20
|
||||
jittertolerancemultiplier: 1.1
|
||||
nodereporttimeout: 40
|
||||
|
||||
@ -14,17 +14,23 @@ passwords:
|
||||
addpeer: passwd_addpeer
|
||||
delpeer: passwd_delpeer
|
||||
graphrecalculatesetting:
|
||||
staticmode: false
|
||||
jittertolerance: 5
|
||||
jittertolerancemultiplier: 1.01
|
||||
nodereporttimeout: 50
|
||||
recalculatecooldown: 5
|
||||
nexthoptable:
|
||||
1:
|
||||
2: 2
|
||||
2:
|
||||
1: 1
|
||||
edgetemplate: example_config/super_mode/n1.yaml
|
||||
peers:
|
||||
- nodeid: 2
|
||||
name: Node_02
|
||||
pubkey: dHeWQtlTPQGy87WdbUARS4CtwVaR2y7IQ1qcX4GKSXk=
|
||||
pskey: juJMQaGAaeSy8aDsXSKNsPZv/nFiPj4h/1G70tGYygs=
|
||||
- nodeid: 1
|
||||
name: Node_01
|
||||
pubkey: ZqzLVSbXzjppERslwbf2QziWruW3V/UIx9oqwU8Fn3I=
|
||||
pskey: iPM8FXfnHVzwjguZHRW9bLNY+h7+B1O2oTJtktptQkI=
|
||||
- nodeid: 2
|
||||
name: Node_02
|
||||
pubkey: dHeWQtlTPQGy87WdbUARS4CtwVaR2y7IQ1qcX4GKSXk=
|
||||
pskey: juJMQaGAaeSy8aDsXSKNsPZv/nFiPj4h/1G70tGYygs=
|
||||
|
||||
13
go.mod
13
go.mod
@ -3,12 +3,13 @@ module github.com/KusakabeSi/EtherGuardVPN
|
||||
go 1.16
|
||||
|
||||
require (
|
||||
git.fd.io/govpp.git v0.3.6-0.20210810100027-c0da1f2999a6
|
||||
git.fd.io/govpp.git/extras v0.0.0-20210810100027-c0da1f2999a6
|
||||
git.fd.io/govpp.git v0.3.6-0.20210927044411-385ccc0d8ba9
|
||||
git.fd.io/govpp.git/extras v0.0.0-20210927044411-385ccc0d8ba9
|
||||
github.com/KusakabeSi/go-cache v0.0.0-20210823132304-22b5b1d22b41
|
||||
github.com/beevik/ntp v0.3.0
|
||||
github.com/sirupsen/logrus v1.8.1
|
||||
golang.org/x/crypto v0.0.0-20210322153248-0c34fe9e7dc2
|
||||
golang.org/x/sys v0.0.0-20210403161142-5e06dd20ab57
|
||||
gopkg.in/yaml.v2 v2.4.0
|
||||
github.com/google/gopacket v1.1.19
|
||||
github.com/sirupsen/logrus v1.6.0
|
||||
golang.org/x/crypto v0.0.0-20210921155107-089bfa567519
|
||||
golang.org/x/sys v0.0.0-20210615035016-665e8c7367d1
|
||||
gopkg.in/yaml.v2 v2.2.2
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
2
main.go
2
main.go
@ -47,7 +47,7 @@ var (
|
||||
tconfig = flag.String("config", "", "Config path for the interface.")
|
||||
mode = flag.String("mode", "", "Running mode. [super|edge|solve]")
|
||||
printExample = flag.Bool("example", false, "Print example config")
|
||||
bind = flag.String("bind", "linux", "UDP socket bind mode. [linux|std]\nYou may need this if tou want to run Etherguard under WSL.")
|
||||
bind = flag.String("bind", "linux", "UDP socket bind mode. [linux|std]\nYou may need std mode if you want to run Etherguard under WSL.")
|
||||
nouapi = flag.Bool("no-uapi", false, "Disable UAPI\nWith UAPI, you can check etherguard status by \"wg\" command")
|
||||
version = flag.Bool("version", false, "Show version")
|
||||
help = flag.Bool("help", false, "Show this help")
|
||||
|
||||
35
main_edge.go
35
main_edge.go
@ -25,20 +25,24 @@ import (
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
func printExampleEdgeConf() {
|
||||
v1 := config.Vertex(1)
|
||||
v2 := config.Vertex(2)
|
||||
tconfig := config.EdgeConfig{
|
||||
Interface: config.InterfaceConf{
|
||||
Itype: "stdio",
|
||||
VPPIfaceID: 5,
|
||||
Name: "tap1",
|
||||
MacAddrPrefix: "AA:BB:CC:DD:EE:FF",
|
||||
MTU: 1400,
|
||||
VPPIfaceID: 5,
|
||||
VPPBridgeID: 4242,
|
||||
MacAddrPrefix: "AA:BB:CC:DD",
|
||||
MTU: 1416,
|
||||
RecvAddr: "127.0.0.1:4001",
|
||||
SendAddr: "127.0.0.1:5001",
|
||||
L2HeaderMode: "nochg",
|
||||
},
|
||||
NodeID: 1,
|
||||
NodeName: "Node01",
|
||||
PrivKey: "SM8pGjT0r8njy1/7ffN4wMwF7nnJ8UYSjGRWpCqo3ng=",
|
||||
DefaultTTL: 200,
|
||||
PrivKey: "6GyDagZKhbm5WNqMiRHhkf43RlbMJ34IieTlIuvfJ1M=",
|
||||
ListenPort: 3001,
|
||||
LogLevel: config.LoggerInfo{
|
||||
LogLevel: "normal",
|
||||
@ -52,20 +56,23 @@ func printExampleEdgeConf() {
|
||||
PeerAliveTimeout: 30,
|
||||
DupCheckTimeout: 40,
|
||||
ConnTimeOut: 30,
|
||||
ConnNextTry: 5,
|
||||
SaveNewPeers: true,
|
||||
SuperNode: config.SuperInfo{
|
||||
UseSuperNode: true,
|
||||
PSKey: "iPM8FXfnHVzwjguZHRW9bLNY+h7+B1O2oTJtktptQkI=",
|
||||
ConnURLV4: "127.0.0.1:3000",
|
||||
PubKeyV4: "LJ8KKacUcIoACTGB/9Ed9w0osrJ3WWeelzpL2u4oUic=",
|
||||
ConnURLV6: "[::1]:3000",
|
||||
PubKeyV6: "HCfL6YJtpJEGHTlJ2LgVXIWKB/K95P57LHTJ42ZG8VI=",
|
||||
APIUrl: "http://127.0.0.1:3000/api",
|
||||
SuperNodeInfoTimeout: 40,
|
||||
SuperNodeInfoTimeout: 50,
|
||||
},
|
||||
P2P: config.P2Pinfo{
|
||||
UseP2P: true,
|
||||
SendPeerInterval: 20,
|
||||
GraphRecalculateSetting: config.GraphRecalculateSetting{
|
||||
StaticMode: false,
|
||||
JitterTolerance: 20,
|
||||
JitterToleranceMultiplier: 1.1,
|
||||
NodeReportTimeout: 40,
|
||||
@ -76,7 +83,7 @@ func printExampleEdgeConf() {
|
||||
UseNTP: true,
|
||||
MaxServerUse: 5,
|
||||
SyncTimeInterval: 3600,
|
||||
NTPTimeout: 10,
|
||||
NTPTimeout: 3,
|
||||
Servers: []string{"time.google.com",
|
||||
"time1.google.com",
|
||||
"time2.google.com",
|
||||
@ -94,18 +101,20 @@ func printExampleEdgeConf() {
|
||||
"time.windows.com"},
|
||||
},
|
||||
},
|
||||
NextHopTable: config.NextHopTable{},
|
||||
NextHopTable: config.NextHopTable{
|
||||
config.Vertex(1): {
|
||||
config.Vertex(2): &v2,
|
||||
},
|
||||
config.Vertex(2): {
|
||||
config.Vertex(1): &v1,
|
||||
},
|
||||
},
|
||||
ResetConnInterval: 86400,
|
||||
Peers: []config.PeerInfo{
|
||||
{
|
||||
NodeID: 2,
|
||||
PubKey: "ZqzLVSbXzjppERslwbf2QziWruW3V/UIx9oqwU8Fn3I=",
|
||||
EndPoint: "127.0.0.1:3001",
|
||||
Static: true,
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
NodeID: 2,
|
||||
PubKey: "dHeWQtlTPQGy87WdbUARS4CtwVaR2y7IQ1qcX4GKSXk=",
|
||||
PSKey: "juJMQaGAaeSy8aDsXSKNsPZv/nFiPj4h/1G70tGYygs=",
|
||||
EndPoint: "127.0.0.1:3002",
|
||||
Static: true,
|
||||
},
|
||||
|
||||
@ -159,6 +159,7 @@ func get_peerinfo(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
|
||||
http_PeerInfo_2peer := make(config.API_Peers)
|
||||
|
||||
for PeerPubKey, peerinfo := range http_PeerInfo {
|
||||
if http_sconfig.UsePSKForInterEdge {
|
||||
h := sha256.New()
|
||||
if NodeID > peerinfo.NodeID {
|
||||
h.Write([]byte(PubKey))
|
||||
@ -174,6 +175,9 @@ func get_peerinfo(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
|
||||
var psk device.NoisePresharedKey
|
||||
copy(psk[:], bs[:])
|
||||
peerinfo.PSKey = psk.ToString()
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
peerinfo.PSKey = ""
|
||||
}
|
||||
http_PeerInfo_2peer[PeerPubKey] = peerinfo
|
||||
}
|
||||
api_peerinfo_str_byte, _ := json.Marshal(&http_PeerInfo_2peer)
|
||||
@ -321,21 +325,48 @@ func peeradd(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) { //Waiting for test
|
||||
}
|
||||
for _, peerinfo := range http_sconfig.Peers {
|
||||
if peerinfo.NodeID == NodeID {
|
||||
w.WriteHeader(http.StatusNotFound)
|
||||
w.WriteHeader(http.StatusConflict)
|
||||
w.Write([]byte("NodeID exists"))
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
if peerinfo.Name == Name {
|
||||
w.WriteHeader(http.StatusNotFound)
|
||||
w.WriteHeader(http.StatusConflict)
|
||||
w.Write([]byte("Node name exists"))
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
if peerinfo.PubKey == PubKey {
|
||||
w.WriteHeader(http.StatusNotFound)
|
||||
w.WriteHeader(http.StatusConflict)
|
||||
w.Write([]byte("PubKey exists"))
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
if http_sconfig.GraphRecalculateSetting.StaticMode == false {
|
||||
NhTableStr := r.Form.Get("nexthoptable")
|
||||
if NhTableStr == "" {
|
||||
w.WriteHeader(http.StatusExpectationFailed)
|
||||
w.Write([]byte("Your NextHopTable is in static mode.\nPlease provide your new NextHopTable in \"nexthoptable\" parmater in json format"))
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
var NewNhTable config.NextHopTable
|
||||
err := json.Unmarshal([]byte(NhTableStr), &NewNhTable)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
w.WriteHeader(http.StatusExpectationFailed)
|
||||
w.Write([]byte(fmt.Sprintf("%v", err)))
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
err = checkNhTable(NewNhTable, append(http_sconfig.Peers, config.SuperPeerInfo{
|
||||
NodeID: NodeID,
|
||||
Name: Name,
|
||||
PubKey: PubKey,
|
||||
PSKey: PSKey,
|
||||
}))
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
w.WriteHeader(http.StatusExpectationFailed)
|
||||
w.Write([]byte(fmt.Sprintf("%v", err)))
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
http_graph.SetNHTable(NewNhTable, [32]byte{})
|
||||
}
|
||||
super_peeradd(config.SuperPeerInfo{
|
||||
NodeID: NodeID,
|
||||
Name: Name,
|
||||
@ -362,7 +393,7 @@ func peeradd(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) { //Waiting for test
|
||||
|
||||
func peerdel(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) { //Waiting for test
|
||||
params := r.URL.Query()
|
||||
toDelete := config.Boardcast
|
||||
toDelete := config.Broadcast
|
||||
|
||||
PasswordA, has := params["Password"]
|
||||
PubKey := ""
|
||||
@ -402,9 +433,8 @@ func peerdel(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) { //Waiting for test
|
||||
toDelete = peerinfo.NodeID
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
if toDelete == config.Boardcast {
|
||||
if toDelete == config.Broadcast {
|
||||
w.WriteHeader(http.StatusUnauthorized)
|
||||
w.Write([]byte("Wrong password"))
|
||||
return
|
||||
@ -418,6 +448,7 @@ func peerdel(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) { //Waiting for test
|
||||
peers_new = append(peers_new, peerinfo)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
http_sconfig.Peers = peers_new
|
||||
configbytes, _ := yaml.Marshal(http_sconfig)
|
||||
ioutil.WriteFile(http_sconfig_path, configbytes, 0644)
|
||||
|
||||
@ -30,7 +30,40 @@ import (
|
||||
yaml "gopkg.in/yaml.v2"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
func checkNhTable(NhTable config.NextHopTable, peers []config.SuperPeerInfo) error {
|
||||
allpeer := make(map[config.Vertex]bool, len(peers))
|
||||
for _, peer1 := range peers {
|
||||
allpeer[peer1.NodeID] = true
|
||||
}
|
||||
for _, peer1 := range peers {
|
||||
for _, peer2 := range peers {
|
||||
if peer1.NodeID == peer2.NodeID {
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
id1 := peer1.NodeID
|
||||
id2 := peer2.NodeID
|
||||
if dst, has := NhTable[id1]; has {
|
||||
if next, has2 := dst[id2]; has2 {
|
||||
if _, hasa := allpeer[*next]; hasa {
|
||||
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
return errors.New(fmt.Sprintf("NextHopTable[%v][%v]=%v which is not in the peer list", id1, id2, next))
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
return errors.New(fmt.Sprintf("NextHopTable[%v][%v] not found", id1, id2))
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
return errors.New(fmt.Sprintf("NextHopTable[%v] not found", id1))
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func printExampleSuperConf() {
|
||||
v1 := config.Vertex(1)
|
||||
v2 := config.Vertex(2)
|
||||
|
||||
sconfig := config.SuperConfig{
|
||||
NodeName: "NodeSuper",
|
||||
PrivKeyV4: "mL5IW0GuqbjgDeOJuPHBU2iJzBPNKhaNEXbIGwwYWWk=",
|
||||
@ -42,24 +75,46 @@ func printExampleSuperConf() {
|
||||
LogControl: true,
|
||||
},
|
||||
RePushConfigInterval: 30,
|
||||
Peers: []config.SuperPeerInfo{
|
||||
{
|
||||
NodeID: 2,
|
||||
Name: "Node02",
|
||||
PubKey: "NuYJ/3Ght+C4HovFq5Te/BrIazo6zwDJ8Bdu4rQCz0o=",
|
||||
PSKey: "NuYJ/3Ght+C4HovFq5Te/BrIazo6zwDJ8Bdu4rQCz0o=",
|
||||
},
|
||||
Passwords: config.Passwords{
|
||||
ShowState: "passwd",
|
||||
AddPeer: "passwd_addpeer",
|
||||
DelPeer: "passwd_delpeer",
|
||||
},
|
||||
GraphRecalculateSetting: config.GraphRecalculateSetting{
|
||||
StaticMode: false,
|
||||
JitterTolerance: 5,
|
||||
JitterToleranceMultiplier: 1.01,
|
||||
NodeReportTimeout: 40,
|
||||
RecalculateCoolDown: 5,
|
||||
},
|
||||
NextHopTable: config.NextHopTable{
|
||||
config.Vertex(1): {
|
||||
config.Vertex(2): &v2,
|
||||
},
|
||||
config.Vertex(2): {
|
||||
config.Vertex(1): &v1,
|
||||
},
|
||||
},
|
||||
EdgeTemplate: "example_config/super_mode/n1.yaml",
|
||||
UsePSKForInterEdge: true,
|
||||
Peers: []config.SuperPeerInfo{
|
||||
{
|
||||
NodeID: 1,
|
||||
Name: "Node_01",
|
||||
PubKey: "ZqzLVSbXzjppERslwbf2QziWruW3V/UIx9oqwU8Fn3I=",
|
||||
PSKey: "iPM8FXfnHVzwjguZHRW9bLNY+h7+B1O2oTJtktptQkI=",
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
NodeID: 2,
|
||||
Name: "Node_02",
|
||||
PubKey: "dHeWQtlTPQGy87WdbUARS4CtwVaR2y7IQ1qcX4GKSXk=",
|
||||
PSKey: "juJMQaGAaeSy8aDsXSKNsPZv/nFiPj4h/1G70tGYygs=",
|
||||
},
|
||||
},
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
soprint, _ := yaml.Marshal(sconfig)
|
||||
fmt.Print(string(soprint))
|
||||
scprint, _ := yaml.Marshal(sconfig)
|
||||
fmt.Print(string(scprint))
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
@ -120,7 +175,13 @@ func Super(configPath string, useUAPI bool, printExample bool, bindmode string)
|
||||
Event_server_NhTable_changed: make(chan struct{}, 1<<4),
|
||||
}
|
||||
http_graph = path.NewGraph(3, true, sconfig.GraphRecalculateSetting, config.NTPinfo{}, sconfig.LogLevel.LogNTP)
|
||||
|
||||
http_graph.SetNHTable(http_sconfig.NextHopTable, [32]byte{})
|
||||
if sconfig.GraphRecalculateSetting.StaticMode {
|
||||
err = checkNhTable(http_sconfig.NextHopTable, sconfig.Peers)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
thetap4, _ := tap.CreateDummyTAP()
|
||||
http_device4 = device.NewDevice(thetap4, config.SuperNodeMessage, conn.NewDefaultBind(true, false, bindmode), logger4, http_graph, true, configPath, nil, &sconfig, &super_chains, Version)
|
||||
defer http_device4.Close()
|
||||
@ -140,7 +201,6 @@ func Super(configPath string, useUAPI bool, printExample bool, bindmode string)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if sconfig.PrivKeyV6 != "" {
|
||||
|
||||
pk6, err := device.Str2PriKey(sconfig.PrivKeyV6)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
fmt.Println("Error decode base64 ", err)
|
||||
@ -316,6 +376,7 @@ func Event_server_event_hendler(graph *path.IG, events path.SUPER_Events) {
|
||||
new_hash_str := hex.EncodeToString(md5_hash_raw[:])
|
||||
new_hash_str_byte := []byte(new_hash_str)
|
||||
copy(http_NhTable_Hash[:], new_hash_str_byte)
|
||||
copy(graph.NhTableHash[:], new_hash_str_byte)
|
||||
http_NhTableStr = NhTablestr
|
||||
PushNhTable()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
@ -21,7 +21,7 @@ const (
|
||||
MessageCookieReplyType
|
||||
MessageTransportType
|
||||
|
||||
NornalPacket
|
||||
NormalPacket
|
||||
Register //Register to server
|
||||
|
||||
UpdatePeer //Comes from server
|
||||
@ -31,7 +31,7 @@ const (
|
||||
PingPacket //Comes from other peer
|
||||
PongPacket //Send to everyone, include server
|
||||
QueryPeer
|
||||
BoardcastPeer
|
||||
BroadcastPeer
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
func NewEgHeader(pac []byte) (e EgHeader, err error) {
|
||||
|
||||
10
path/path.go
10
path/path.go
@ -1,6 +1,7 @@
|
||||
package path
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"bytes"
|
||||
"fmt"
|
||||
"io/ioutil"
|
||||
"math"
|
||||
@ -43,6 +44,7 @@ type IG struct {
|
||||
Vert map[config.Vertex]bool
|
||||
edges map[config.Vertex]map[config.Vertex]Latency
|
||||
edgelock *sync.RWMutex
|
||||
StaticMode bool
|
||||
JitterTolerance float64
|
||||
JitterToleranceMultiplier float64
|
||||
NodeReportTimeout time.Duration
|
||||
@ -69,6 +71,7 @@ func S2TD(secs float64) time.Duration {
|
||||
func NewGraph(num_node int, IsSuperMode bool, theconfig config.GraphRecalculateSetting, ntpinfo config.NTPinfo, logntp bool) *IG {
|
||||
g := IG{
|
||||
edgelock: &sync.RWMutex{},
|
||||
StaticMode: theconfig.StaticMode,
|
||||
JitterTolerance: theconfig.JitterTolerance,
|
||||
JitterToleranceMultiplier: theconfig.JitterToleranceMultiplier,
|
||||
NodeReportTimeout: S2TD(theconfig.NodeReportTimeout),
|
||||
@ -112,6 +115,12 @@ func (g *IG) ShouldUpdate(u config.Vertex, v config.Vertex, newval float64) bool
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (g *IG) RecalculateNhTable(checkchange bool) (changed bool) {
|
||||
if g.StaticMode {
|
||||
if bytes.Equal(g.NhTableHash[:], make([]byte, 32)) {
|
||||
changed = checkchange
|
||||
}
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
if g.recalculateTime.Add(g.RecalculateCoolDown).Before(time.Now()) {
|
||||
dist, next := FloydWarshall(g)
|
||||
changed = false
|
||||
@ -147,6 +156,7 @@ func (g *IG) RemoveVirt(v config.Vertex, recalculate bool, checkchange bool) (ch
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
g.edgelock.Unlock()
|
||||
g.NhTableHash = [32]byte{}
|
||||
if recalculate {
|
||||
changed = g.RecalculateNhTable(checkchange)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
@ -39,7 +39,7 @@ func Charform2mac(b byte) MacAddress {
|
||||
if b == 'b' {
|
||||
return MacAddress{0xff, 0xff, 0xff, 0xff, 0xff, 0xff}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return MacAddress{0x00, 0x11, 0xff, 0xff, 0xff, b - 48}
|
||||
return MacAddress{0xaa, 0xbb, 0xcc, 0xdd, 0xee, b - 48}
|
||||
}
|
||||
func Mac2charForm(m []byte) byte {
|
||||
var M MacAddress
|
||||
|
||||
Reference in New Issue
Block a user