Etherguard
Super mode
This mode is inspired by n2n. There 2 types of node: SuperNode and EdgeNode
EdgeNode must connect to SuperNode first,get connection info of other EdgeNode from the SuperNode
The SuperNode runs Floyd-Warshall Algorithm,and distribute the result to all other EdgeNodes.
Quick start
Edit the file gensuper.yaml based on your requirement first.
Config output dir: /tmp/eg_gen
Enable generated config overwrite: false # Allow overwrite while output the config
Add NodeID to the interface name: false # Add NodeID to the interface name in generated edge config
ConfigTemplate for super node: ""
ConfigTemplate for edge node: ""
Network name: eg_net
Super Node:
Listen port: 3456
EdgeAPI prefix: /eg_net/eg_api
Endpoint(IPv4)(optional): example.com
Endpoint(IPv6)(optional): example.com
Endpoint(EdgeAPI): http://example.com:3456/eg_net/eg_api
Edge Node:
Node IDs: "[1~10,11,19,23,29,31,55~66,88~99]"
MacAddress prefix: "" # Leave blank to generate randomly
IPv4 range: 192.168.76.0/24 # The IP part can be omitted
IPv6 range: fd95:71cb:a3df:e586::/64 #
IPv6 LL range: fe80::a3df:0/112 #
Then run this, and the required configuration file will be generated.
$ ./etherguard-go -mode gencfg -cfgmode super -config example_config/super_mode/gensuper.yaml
Run this in SuperNode
./etherguard-go -config [config path] -mode super
Run this in EdgeNode
./etherguard-go -config [config path] -mode edge
Documentation
This is the documentation of the super_mode of this example_config Before reading this, I'd like to suggest you read the static mode first.
In the super mode of the edge node, the NextHopTable and Peers section are useless. All infos are download from super node.
Meanwhile, super node will generate pre shared key for inter-edge communication(if UsePSKForInterEdge enabled).
SuperMsg
There are new type of DstID called SuperMsg(65534). All packets sends to and receive from super node are using this packet type.
This packet will not send to any other edge node, just like DstID == self.NodeID
Control Message
In Super mode, Beside Normal Packet. We introduce a new packet type called Control Message. In Super mode, we will not relay any control message. We just receive or send it to target directly.
We list all the control message we use in the super mode below.
Register
This control message works like this picture:
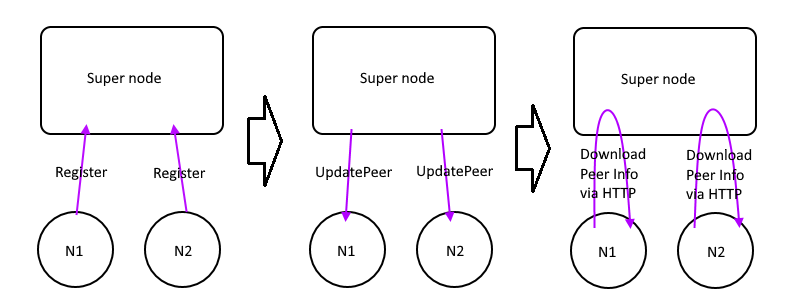
- EdgeNode send Register to the super node
- SuperNode knows it's external IP and port number
- Update it to database and distribute
UpdatePeerMsgto all edges - Other EdgeNodes get the notification, download the updated peer infos from SuperNode via HTTP API
Ping/Pong
While EdgeNodes get their peer info, they will trying to talk each other directly like this picture:
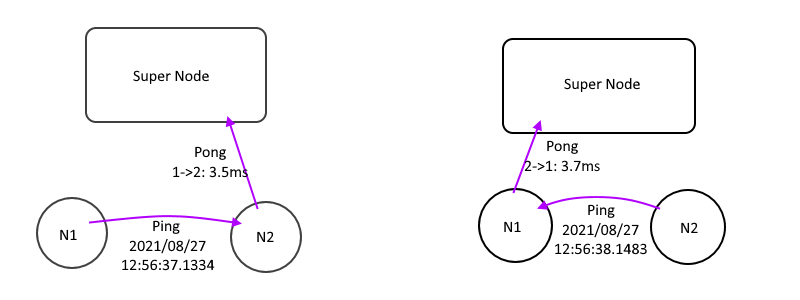
- Send
Pingto all other edges with local time with TTL=0 - Receive a
Ping, Subtract the peer time from local time, we get a single way latency. - Send a
Pongto SuperNode with single way latency, let SuperNode calculate the NextHopTable - Wait the SuperNode push
UpdateNhTablemessage and download it.
AdditionalCost
While we have all latency data of all nodes, AdditionalCost will be applied before Floyd-Warshall calculated.
Take the situation of this picture as an example:
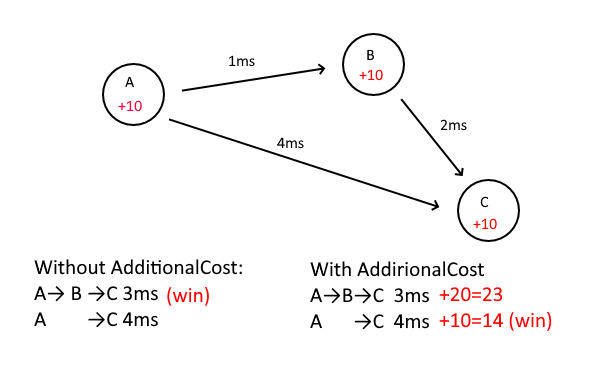
| Path | Latency | Cost | Win |
|---|---|---|---|
| A->B->C | 3ms | 3 | |
| A->C | 4ms | 4 | O |
In this situation, the difference between 3ms and 4ms is only 1ms It’s not worth to save this 1ms, and the forwarding itself takes time
With the AdditionalCost parameter, each node can set the additional cost of forwarding through this node
If ABC is all set to AdditionalCost=10
| Path | Latency | AdditionalCost | Cost | Win |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A->B->C | 3ms | 20 | 23 | |
| A->C | 4ms | 10 | 14 | O |
A->C will use direct connection instead of forward via B in order to save 1ms
Here AdditionalCost=10 can be interpreted as: It have to save 10ms to transfer by this Node.
UpdateNhTable
While supernode get a Pong message, it will update the Distance matrix and run the Floyd-Warshall Algorithm to calculate the NextHopTable.
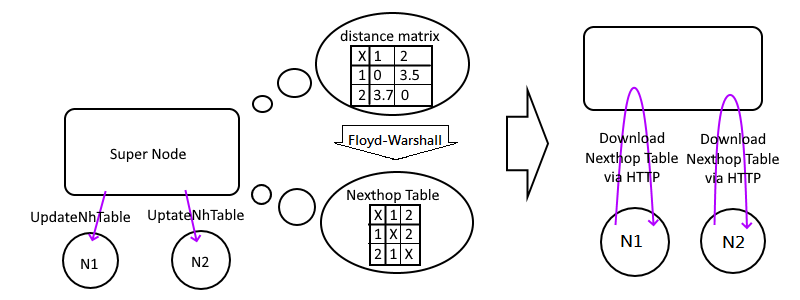
If there are any changes of this table, it will distribute UpdateNhTable to all edges to till then download the latest NextHopTable via HTTP API as soon as possible.
ServerUpdate
Send message to EdgeMode from SuperNode
- Turn off EdgeNode
- Version Not match
- Wrong NodeID
- Deleted by SuperNode
- Notify EdgeNode there are something new
- UpdateNhTable
- UpdatePeer
- UpdateSuperParams
HTTP EdgeAPI
Why we use HTTP API instead of pack all information in the UpdateXXX?
Because UDP is an unreliable protocol, there is an limit on the amount of content that can be carried.
But the peer list contains all the peer information, the length is not fixed, it may exceed
So we use UpdateXXX to tell we have a update, please download the latest information from SuperNode via HTTP API as soon as possible.
And UpdateXXX itself is not reliable, maybe it didn't reach the edge node at all.
So the information of UpdateXXX carries the state hash. Bring it when with HTTP API. When the super node receives the HTTP API and sees the state hash, it knows that the edge node has received the UpdateXXX.
Otherwise, it will send UpdateXXX to the node again after few seconds.
The default configuration is to use HTTP. But for the sake of your security, it is recommended to use an reverse-proxy ot convert it into https I have thought about the development of SuperNode to natively support https, but the dynamic update of the certificate costs me too much time.
HTTP Manage API
HTTP also has some APIs for the front-end to help manage the entire network
super/state
curl "http://127.0.0.1:3456/eg_net/eg_api/manage/super/state?Password=passwd_showstate"
It can show some information such as single way latency or last seen time.
We can visualize it by Force-directed graph drawing.
There is an Infinity section in the json response. It should be 9999. It means infinity if the number larger than it.
Cuz json can't present infinity so that I use this trick.
While we see the latency larger than this, we doesn't need to draw lines in this two nodes.
Example return value:
{
"PeerInfo": {
"1": {
"Name": "Node_01",
"LastSeen": "2021-12-05 21:21:56.039750832 +0000 UTC m=+23.401193649"
},
"2": {
"Name": "Node_02",
"LastSeen": "2021-12-05 21:21:57.711616169 +0000 UTC m=+25.073058986"
}
},
"Infinity": 99999,
"Edges": {
"1": {
"2": 0.002179297
},
"2": {
"1": -0.00030252
}
},
"Edges_Nh": {
"1": {
"2": 0.012179297
},
"2": {
"1": 0.00969748
}
},
"NhTable": {
"1": {
"2": 2
},
"2": {
"1": 1
}
},
"Dist": {
"1": {
"1": 0,
"2": 0.012179297
},
"2": {
"1": 0.00969748,
"2": 0
}
}
}
Section meaning:
- PeerInfo: NodeID,Name,LastSeen
- Edges: The Single way latency,99999 or missing means unreachable(UDP hole punching failed)
- Edges_Nh: Edges with AdditionalCost
- NhTable: Calculate result.
- Dist: The latency of packet through Etherguard
peer/add
We can add new edges with this API without restart the SuperNode
Exanple:
curl -X POST "http://127.0.0.1:3456/eg_net/eg_api/manage/peer/add?Password=passwd_addpeer" \
-H "Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded" \
-d "NodeID=100&Name=Node_100&PubKey=DG%2FLq1bFpE%2F6109emAoO3iaC%2BshgWtdRaGBhW3soiSI%3D&AdditionalCost=1000&PSKey=w5t64vFEoyNk%2FiKJP3oeSi9eiGEiPteZmf2o0oI2q2U%3D&SkipLocalIP=false"
Parameter:
- URL query: Password: Password. Configured in the config file.
- Post body:
- NodeID: Node ID
- Name: Name
- PubKey: Public Key
- PSKey: Pre shared Key
- AdditionalCost: Additional cost for packet transfer. Unit: ms
- SkipLocalIP: Skip local IP reported by the node
- nexthoptable: If the
graphrecalculatesettingof your super node is in static mode, you need to provide a newNextHopTablein json format in this parameter.
Return value:
- http code != 200: Error reason
- http code == 200,An example edge config.
- generate by contents in
edgetemplatewith custom data (nodeid/name/pubkey) - Convenient for users to copy and paste
- generate by contents in
peer/del
Delete peer
There are two deletion modes, namely password deletion and private key deletion.
Designed to be used by administrators, or for people who join the network and want to leave the network.
Use Password to delete any node. Take the newly added node above as an example, use this API to delete the node
curl "http://127.0.0.1:3456/eg_net/eg_api/manage/peer/del?Password=passwd_delpeer&NodeID=100"
We can also use privkey to delete, the same as above, but use privkey parameter only.
curl "http://127.0.0.1:3456/eg_net/eg_api/manage/peer/del?PrivKey=iquaLyD%2BYLzW3zvI0JGSed9GfDqHYMh%2FvUaU0PYVAbQ%3D"
Parameter:
- URL query:
- Password: Password: Password. Configured in the config file.
- nodeid: Node ID that you want to delete
- privkey: The private key of the edge
Return value:
- http code != 200: Error reason
- http code == 200: Success message
peer/update
curl -X POST "http://127.0.0.1:3456/eg_net/eg_api/manage/peer/update?Password=passwd_updatepeer&NodeID=1" \
-H "Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded" \
-d "AdditionalCost=10&SkipLocalIP=false"
super/update
curl -X POST "http://127.0.0.1:3456/eg_net/eg_api/manage/super/update?Password=passwd_updatesuper" \
-H "Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded" \
-d "SendPingInterval=15&HttpPostInterval=60&PeerAliveTimeout=70&DampingFilterRadius=3"
SuperNode Config Parameter
| Key | Description |
|---|---|
| NodeName | node name |
| PostScript | Running script after initialized |
| PrivKeyV4 | Private key for IPv4 session |
| PrivKeyV6 | Private key for IPv6 session |
| ListenPort | UDP listen port |
| ListenPort_EdgeAPI | HTTP EdgeAPI listen port |
| ListenPort_ManageAPI | HTTP ManageAPI listen port |
| API_Prefix | HTTP API prefix |
| RePushConfigInterval | The interval of pushUpdateXXX |
| HttpPostInterval | The interval of report by HTTP Edge API |
| PeerAliveTimeout | The time of inactive which marks peer offline |
| SendPingInterval | The interval that send pings/pongs between EdgeNodes |
| LogLevel | Log related settings |
| Passwords | Password for HTTP ManageAPI, 5 API passwords are independent |
| GraphRecalculateSetting | Some parameters related to [Floyd-Warshall algorithm](https://zh.wikipedia.org/zh-tw/Floyd-Warshall algorithm) |
| NextHopTable | NextHopTable used by StaticMode |
| EdgeTemplate | for HTTP ManageAPI peer/add. Refer to this configuration file and show a sample configuration file of the edge to the user |
| UsePSKForInterEdge | Whether to enable pre-share key communication between edges. If enabled, SuperNode will generate PSK for edges automatically |
| Peers | EdgeNode information |
| GraphRecalculateSetting | Description |
|---|---|
| StaticMode | Disable Floyd-Warshall, use NextHopTablein the configuration instead.SuperNode for udp hole punching only. |
| ManualLatency | Set latency manually, ignore Edge reported latency. |
| JitterTolerance | Jitter tolerance, after receiving Pong, one 37ms and one 39ms will not trigger recalculation Compared to last calculation |
| JitterToleranceMultiplier | high ping allows more errors https://www.desmos.com/calculator/raoti16r5n |
| DampingFilterRadius | Windows radius for the low pass filter for latency damping prevention |
| TimeoutCheckInterval | The interval to check if there any Pong packet timed out, and recalculate the NhTable |
| RecalculateCoolDown | Floyd-Warshal is an O(n^3)time complexity algorithm This option set a cooldown, and prevent it cost too many CPU Connect/Disconnect event ignores this cooldown. |
| Peers | Description |
|---|---|
| NodeID | Peer's node ID |
| PubKey | Peer's public key |
| PSKey | Pre shared key |
| AdditionalCost | AdditionalCost(unit:ms)-1 means uses client's self configuration. |
| SkipLocalIP | Ignore Edge reported local IP, use public IP only while udp-hole-punching |
EdgeNode Config Parameter
EdgeConfig Root
| DynamicRoute | Description |
|---|---|
| SendPingInterval | The interval that send pings/pongs between EdgeNodes(sec) |
| PeerAliveTimeout | The time of inactive which marks peer offline(sec) |
| TimeoutCheckInterval | The interval of check PeerAliveTimeout(sec) |
| ConnNextTry | After marked offline, the interval of switching Endpoint(sec) |
| DupCheckTimeout | Duplication chack timeout.(sec) |
| AdditionalCost | AdditionalCost(unit:ms) |
| SaveNewPeers | Save peer info to local file. |
| SuperNode | SuperNode related configs |
| P2P | P2P related configs |
| NTPConfig | NTP related configs |
V4 V6 Two Keys
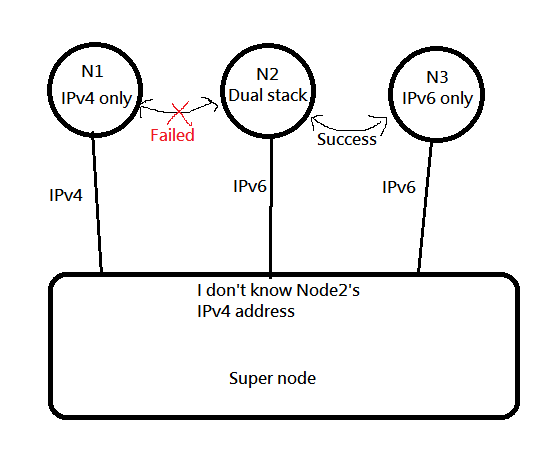
Why we split IPv4 and IPv6 into two session? Because of this situation
In this case, SuperNode does not know the external ipv4 address of Node02 and cannot help Node1 and Node2 to UDP hole punch.
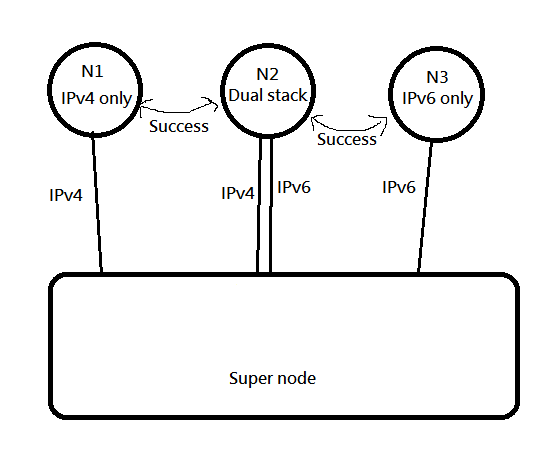
So like this, both V4 and V6 establish a session, so that both V4 and V6 can be taken care of at the same time.
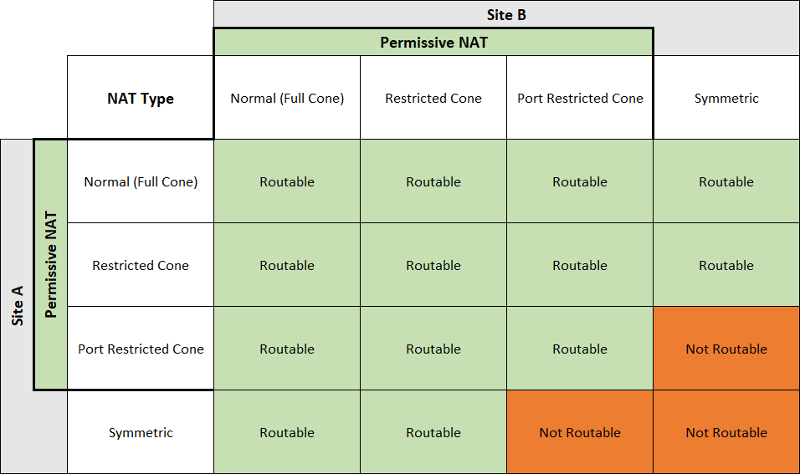
UDP hole punch reachability
For different NAT type, the UDP hole punch reachability can refer this table.(Origin)
And if both sides are using ConeNAT, it's not gerenteed to punch success. It depends on the topology and the devices attributes.
Like the section 3.5 in this article, we can't punch success.
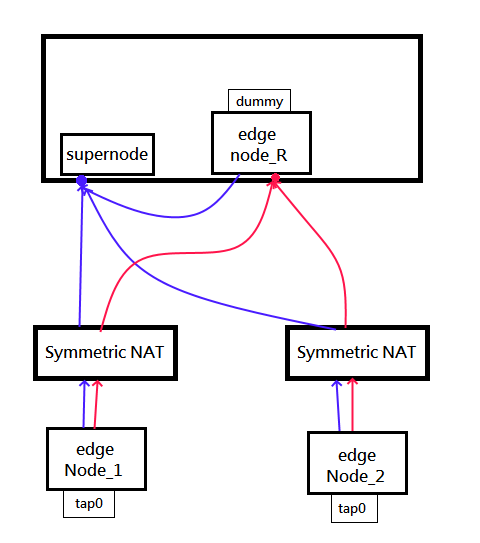
Notice for Relay node
Unlike n2n, our supernode do not relay any packet for edges.
If the edge punch failed and no any route available, it's just unreachable. In this case we need to setup a relay node.
Relay node is a regular edge in public network, but interface=dummy.
And we have to note that do not use 127.0.0.1 to connect to supernode.
Because supernode well distribute the source IP of the nodes to all other edges. But 127.0.0.1 is not accessible from other edge.
To avoid this issue, please use the external IP of the supernode in the edge config.
Quick start
Run this example_config (please open three terminals):
./etherguard-go -config example_config/super_mode/EgNet_super.yaml -mode super
./etherguard-go -config example_config/super_mode/EgNet_edge001.yaml -mode edge
./etherguard-go -config example_config/super_mode/EgNet_edge002.yaml -mode edge
Because it is in stdio mode, stdin will be read into the VPN network
Please type in one of the edge windows
b1aaaaaaaaaa
b1 will be converted into a 12byte layer 2 header, b is the broadcast address FF:FF:FF:FF:FF:FF, 1 is the ordinary MAC address AA:BB:CC:DD:EE:01, aaaaaaaaaa is the payload, and then feed it into the VPN
You should be able to see the string b1aaaaaaaaaa on another window. The first 12 bytes are converted back