| .. | ||
| EgNet_edge1.yaml | ||
| EgNet_edge2.yaml | ||
| EgNet_edge3.yaml | ||
| EgNet_edge4.yaml | ||
| EgNet_edge5.yaml | ||
| EgNet_edge6.yaml | ||
| Example_static.png | ||
| genstatic.yaml | ||
| path.txt | ||
| README_zh.md | ||
| README.md | ||
Etherguard
Static mode
No dynamic routing, no handshake server.
Similar to original wireguard , all configs are static.
Include the route table, you have to configure it in NextHopTable section in the config file.
In this mode, there are no any Control Message, no connectivity check.
Please maintains the predefined topology, otherwise if the relay node offline, part of this network will broken,
Quick Start
First, edit the genstatic.yaml
Config output dir: /tmp/eg_gen_static # Profile output location
ConfigTemplate for edge node: "" # Profile Template
Network name: "EgNet"
Edge Node:
MacAddress prefix: "" # Leave blank to generate randomly
IPv4 range: 192.168.76.0/24 # By the way, the IP part can be omitted.
IPv6 range: fd95:71cb:a3df:e586::/64 # The only purpose of this field is to call the ip command after startup to add an ip to the tap interface
IPv6 LL range: fe80::a3df:0/112 #
Edge Nodes: # Node related settings
1:
Endpoint(optional): 127.0.0.1:3001
2:
Endpoint(optional): 127.0.0.1:3002
3:
Endpoint(optional): 127.0.0.1:3003
4:
Endpoint(optional): 127.0.0.1:3004
5:
Endpoint(optional): 127.0.0.1:3005
6:
Endpoint(optional): 127.0.0.1:3006
Distance matrix for all nodes: |- # The left is the starting point, and the upper is the ending point. Inf represents that the two nodes are not connected, and the value represents connected. The size of the value represents the cost of the route (usually latency)
X 1 2 3 4 5 6
1 0 1.0 Inf Inf Inf Inf
2 1.0 0 1.0 1.0 Inf Inf
3 Inf 1.0 0 1 1.0 Inf
4 Inf 1.0 1.0 0 Inf 1.0
5 Inf Inf 1.0 Inf 1.0 Inf
6 Inf Inf Inf 1.0 Inf 1.0
Run this, it will generate the required configuration file
./etherguard-go -mode gencfg -cfgmode static -config example_config/static_mode/genstatic.yaml
Deploy these configuration files to the corresponding nodes, and then execute
./etherguard-go -config [config path] -mode edge
you can turn off unnecessary logs to increase performance after it works.
Documentation
The topology of this example_config:
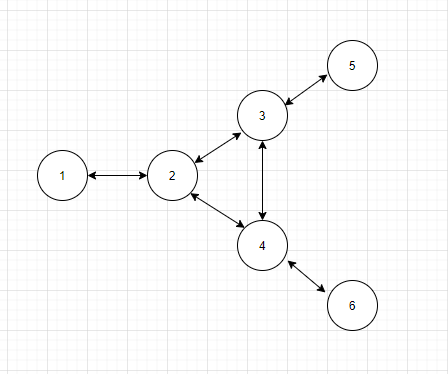
Before sending packet, We will set the SrcID to my NodeID. And the DstID will be found from l2fib table. If lookup failed or it's a Broadcast address, It will be set to Broadcast(65535)
While receiving packet, if the DstID==NodeID, or DstID==65535, it will receive the packet, and send to correspond tap device. And meanwhile, add the NodeID->SrcMacAddress to l2fib.
If not, it will lookup from the Next hop table, to determine who will be sent of this packet.
Here is an example of the Next hop table in this example topology. A yaml formatted nested dictionary. NhTable[SrcID][DstID]= Next hop ID
NextHopTable:
1:
2: 2
3: 2
2:
1: 1
3: 3
3:
1: 2
2: 2
Broadcast
Broadcast is a special case.
Today I am Node 4, and I received a Src=1, dst=Broadcast.
I should send to Node 6 ONLY without sending it to Node 3.
Cuz Node 3 should receive it from Node 2 Instead of me.
So if dst=Broadcast, I will check src to all my neighbors whether I am a required route of this packet.
1 -> 6 : [1 2 4 6] , I am a required route
1 -> 3 : [1 2 3] , I am not a required route
1 -> 3 : Skip check, packet is coming from it
So I knows I should send this packet to Node 6 only.
Next Hop Table calculator
This tool can also calculate Next Hop Table for you.
Prepare a path.txt first, mark all single way latency in it like this:
X 1 2 3 4 5 6
1 0 0.5 Inf Inf Inf Inf
2 0.5 0 0.5 0.5 Inf Inf
3 Inf 0.5 0 0.5 0.5 Inf
4 Inf 0.5 0.5 0 Inf 0.5
5 Inf Inf 0.5 Inf 0 Inf
6 Inf Inf Inf 0.5 Inf 0
Inf means unreachable.
Then use this command to calculate it.
EdgeNode Config Parameter
| EdgeConfig | Description |
|---|---|
| Interface | Interface related config |
| NodeID | NodeID. Must be unique in the whole Etherguard network. |
| NodeName | Node Name. |
| PostScript | Script that will run after initialized |
| DefaultTTL | TTL(etherguard layer. not affect ethernet layer) |
| L2FIBTimeout | The timeout of the L2FIB table(Similar to ARP table) |
| PrivKey | Private key. Same spec as wireguard. |
| ListenPort | UDP lesten port |
| LogLevel | Log related settings |
| DynamicRoute | Dynamic Route related settings. Not work at static mode. |
| NextHopTable | NextHopTable, Next hop = NhTable[start][destnation] |
| ResetConnInterval | Reset the endpoint for peers. You may need this if that peer use DDNS. |
| Peers | Peer info. |
| Interface | Description |
|---|---|
| IType | Interface type. |
| Name | Device name |
| VPPIFaceID | VPP Interface ID. Muse be unique in same VPP runtime |
| VPPBridgeID | VPP Bridge ID. Fill 0 if you don't use it. |
| MacAddrPrefix | Mac address Prefix. Real Mac address=[Prefix]:[NodeID]. |
| IPv4CIDR | After starting, call the ip command to add an ip to the tap interface. |
| IPv4CIDR | After starting, call the ip command to add an ip to the tap interface. |
| IPv6LLPrefix | After starting, call the ip command to add an ip to the tap interface. |
| MTU | Interface MTU,only valid on tap, vpp mode |
| RecvAddr | Listen address for *sock mode(server mode) |
| SendAddr | Packet send address for *sock mode(client mode) |
| L2HeaderMode | For stdio mode only for debugging |
Run example config
Execute following command in Different Terminal
./etherguard-go -config example_config/super_mode/EgNet_edge1.yaml -mode edge
./etherguard-go -config example_config/super_mode/EgNet_edge2.yaml -mode edge
./etherguard-go -config example_config/super_mode/EgNet_edge3.yaml -mode edge
./etherguard-go -config example_config/super_mode/EgNet_edge4.yaml -mode edge
./etherguard-go -config example_config/super_mode/EgNet_edge5.yaml -mode edge
./etherguard-go -config example_config/super_mode/EgNet_edge6.yaml -mode edge
The IType of this example config is stdio (keyboard debug), so it will read data from stdin.
Then input following text in the terminal
b1message
The L2HeaderMode is kbdbg, means Keyboard debug. So that the first two byte will be convert to FF:FF:FF:FF:FF:FF, and AA:BB:CC:DD:EE:01. And the message is the real payload.
With other debug message, you should be able to see the message in other terminal.