| group_vars | ||
| innernet-src@8d058c8d87 | ||
| inventory@0908633b4c | ||
| roles | ||
| .dockerignore | ||
| .drone.yml | ||
| .gitignore | ||
| .gitmodules | ||
| ansible.cfg | ||
| build-debs.sh | ||
| deploy.yml | ||
| Dockerfile | ||
| fsfe-innernet.png | ||
| open_the_vault.sh | ||
| README.md | ||
| shell.nix | ||
| vault_passphrase.gpg | ||
| vault_passphrase.gpg.license | ||
Table of Contents
Motivation
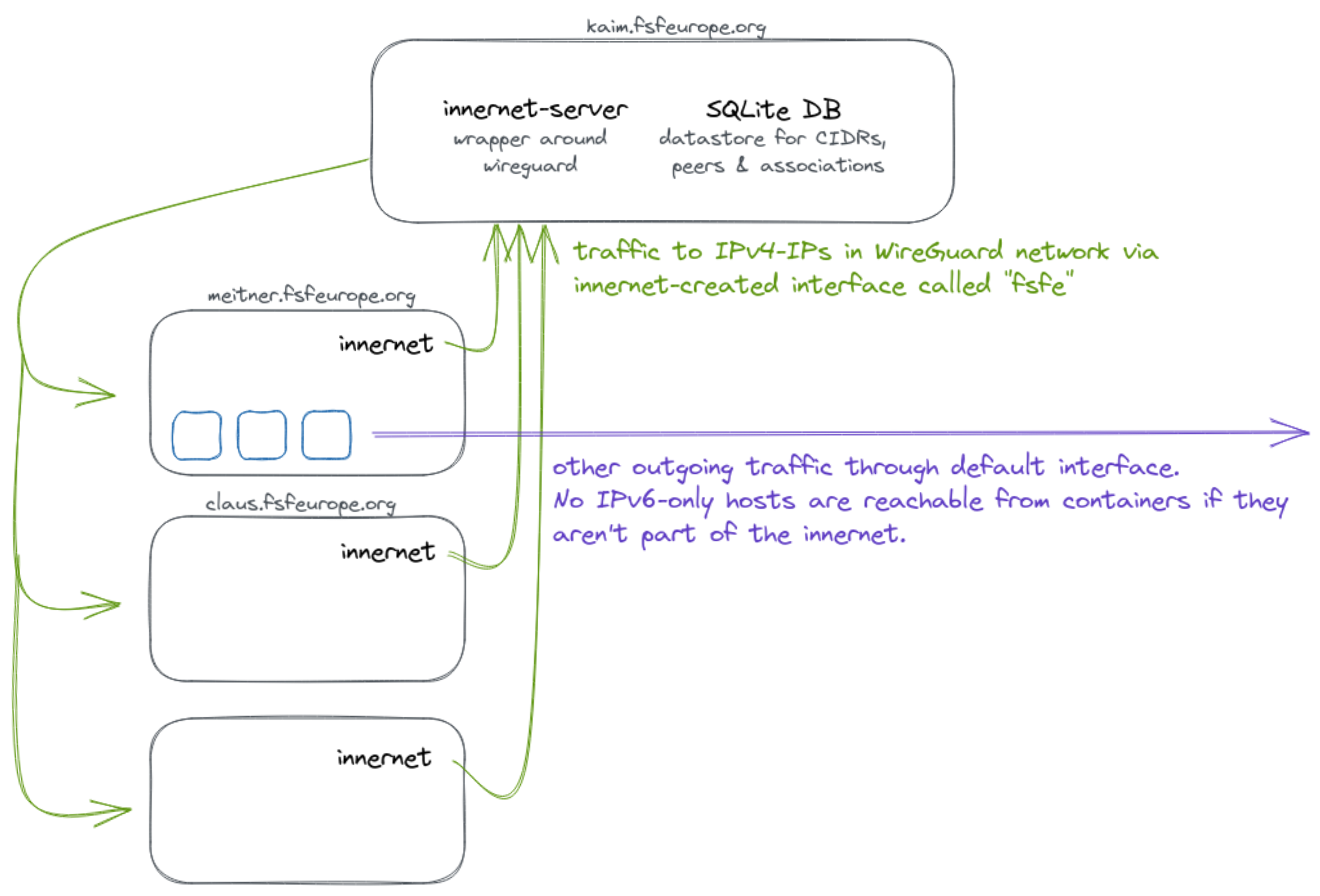
There is a need for some of our servers to connect to other IPv6-only hosts. Since this is not always possible without introducing major painpoints elsewhere, we simply create an internal WireGuard network so that the machines in question can communicate securely using IPv4.
You can learn more about innernet by looking at its source code or reading this informative blog post of its creator.
Preparation
Requirements
- A somewhat recent version of
ansible git
Clone the repo
git clone --recurse-submodules git@git.fsfe.org:fsfe-system-hackers/innernet-playbook.git
cd innernet-playbook
Deployment
In the scope of this playbook and its roles, we have three different categories of computers:
- The innernet server, being the central connector of all innernet peers
- Automatically managed machines that are innernet peers, mostly VMs
- Manually managed peers, for example admins and other humans
Configure server and all clients
Run the whole playbook to configure everything. For the innernet server and automatically managed machines, all will be handled. For the manually managed peers, you will be given an invitation file.
ansible-playbook deploy.yml
Add a new machine
In order to add e.g. a virtual machine to the networks, run these steps:
- In the inventory, add the
innernet_clientgroup to the host - Run the playbook with
ansible-playbook -l newserver.org deploy.yml
This will configure both the necessary parts on the server and the new machine.
Add a new manually managed peer
In order to add a new human or otherwise manually managed innernet peer, run these steps:
- In
all.yml, add a new entry formanual_peers - Run the playbook with
ansible-playbook -l innernet_server deploy.yml - Install innernet and import the invitation file on the new peer's computer
(see below). They are in
roles/client/files/then.
Distribute the invitation files
Some invitation files are for humans, so you need to send these files to them
securely. We suggest using something like wormohle.
sudo apt install magic-wormhole
cd roles/client/files
wormhole send <name_of_peer>.toml
Update
Since innernet is new software, it is
not yet included in the Debian repositories. Thus, before running the playbook
we need to build the innernet and innernet-server binaries.
In order to switch to a newer version of innernet, run the following steps:
- Check out the desired tag in the
innernet-srcsubmodule - Run the build script:
./build-debs.sh - Run the playbook with
ansible-playbook -t update deploy.yml
Associations
The different CIDRs can have associations, e.g. so that admins can access machines, although they are not in the same subnet.
These have to be configure by an admin!
Currently, the admins CIDR is associated with all other CIDRs (i.e. humans >
others and machines).
Ansible tags
Some tags allow you to specify just certain operations. Here are the currently available ones:
cidr: configure CIDRsupdate: update the innernet binarieslisten_port: edit/set the listen port between server and clientsuninstall: delete innernet configuration and packages from systems