# Description
This PR adds two new `ParseError` and `ShellError` cases for type errors
relating to operators.
- `OperatorUnsupportedType` is used when a type is not supported by an
operator in any way, shape, or form. E.g., `+` does not support `bool`.
- `OperatorIncompatibleTypes` is used when a operator is used with types
it supports, but the combination of types provided cannot be used
together. E.g., `filesize + duration` is not a valid combination.
The other preexisting error cases related to operators have been removed
and replaced with the new ones above. Namely:
- `ShellError::OperatorMismatch`
- `ShellError::UnsupportedOperator`
- `ParseError::UnsupportedOperationLHS`
- `ParseError::UnsupportedOperationRHS`
- `ParseError::UnsupportedOperationTernary`
# User-Facing Changes
- `help operators` now lists the precedence of `not` as 55 instead of 0
(above the other boolean operators). Fixes#13675.
- `math median` and `math mode` now ignore NaN values so that `[NaN NaN]
| math median` and `[NaN NaN] | math mode` no longer trigger a type
error. Instead, it's now an empty input error. Fixing this in earnest
can be left for a future PR.
- Comparisons with `nan` now return false instead of causing an error.
E.g., `1 == nan` is now `false`.
- All the operator type errors have been standardized and reworked. In
particular, they can now have a help message, which is currently used
for types errors relating to `++`.
```nu
[1] ++ 2
```
```
Error: nu::parser::operator_unsupported_type
× The '++' operator does not work on values of type 'int'.
╭─[entry #1:1:5]
1 │ [1] ++ 2
· ─┬ ┬
· │ ╰── int
· ╰── does not support 'int'
╰────
help: if you meant to append a value to a list or a record to a table, use the `append` command or wrap the value in a list. For example: `$list ++ $value` should be
`$list ++ [$value]` or `$list | append $value`.
```
# Description
After this pr, nushell is able to raise errors with a backtrace, which
should make users easier to debug. To enable the feature, users need to
set env variable via `$env.NU_BACKTRACE = 1`. But yeah it might not work
perfectly, there are some corner cases which might not be handled.
I think it should close#13379 in another way.
### About the change
The implementation mostly contained with 2 parts:
1. introduce a new `ChainedError` struct as well as a new
`ShellError::ChainedError` variant. If `eval_instruction` returned an
error, it converts the error to `ShellError::ChainedError`.
`ChainedError` struct is responsable to display errors properly. It
needs to handle the following 2 cases:
- if we run a function which runs `error make` internally, it needs to
display the error itself along with caller span.
- if we run a `error make` directly, or some commands directly returns
an error, we just want nushell raise an error about `error make`.
2. Attach caller spans to `ListStream` and `ByteStream`, because they
are lazy streams, and *only* contains the span that runs it
directly(like `^false`, for example), so nushell needs to add all caller
spans to the stream.
For example: in `def a [] { ^false }; def b [] { a; 33 }; b`, when we
run `b`, which runs `a`, which runs `^false`, the `ByteStream` only
contains the span of `^false`, we need to make it contains the span of
`a`, so nushell is able to get all spans if something bad happened.
This behavior is happened after running `Instruction::Call`, if it
returns a `ByteStream` and `ListStream`, it will call `push_caller_span`
method to attach call spans.
# User-Facing Changes
It's better to demostrate how it works by examples, given the following
definition:
```nushell
> $env.NU_BACKTRACE = 1
> def a [x] { if $x == 3 { error make {msg: 'a custom error'}}}
> def a_2 [x] { if $x == 3 { ^false } else { $x } }
> def a_3 [x] { if $x == 3 { [1 2 3] | each {error make {msg: 'a custom error inside list stream'} } } }
> def b [--list-stream --external] {
if $external == true {
# error with non-zero exit code, which is generated from external command.
a_2 1; a_2 3; a_2 2
} else if $list_stream == true {
# error generated by list-stream
a_3 1; a_3 3; a_3 2
} else {
# error generated by command directly
a 1; a 2; a 3
}
}
```
Run `b` directly shows the following error:
<details>
```nushell
Error: chained_error
× oops
╭─[entry #27:1:1]
1 │ b
· ┬
· ╰── error happened when running this
╰────
Error: chained_error
× oops
╭─[entry #26:10:19]
9 │ # error generated by command directly
10 │ a 1; a 2; a 3
· ┬
· ╰── error happened when running this
11 │ }
╰────
Error:
× a custom error
╭─[entry #6:1:26]
1 │ def a [x] { if $x == 3 { error make {msg: 'a custom error'}}}
· ─────┬────
· ╰── originates from here
╰────
```
</details>
Run `b --list-stream` shows the following error
<details>
```nushell
Error: chained_error
× oops
╭─[entry #28:1:1]
1 │ b --list-stream
· ┬
· ╰── error happened when running this
╰────
Error: nu:🐚:eval_block_with_input
× Eval block failed with pipeline input
╭─[entry #26:7:16]
6 │ # error generated by list-stream
7 │ a_3 1; a_3 3; a_3 2
· ─┬─
· ╰── source value
8 │ } else {
╰────
Error: nu:🐚:eval_block_with_input
× Eval block failed with pipeline input
╭─[entry #23:1:29]
1 │ def a_3 [x] { if $x == 3 { [1 2 3] | each {error make {msg: 'a custom error inside list stream'} } } }
· ┬
· ╰── source value
╰────
Error:
× a custom error inside list stream
╭─[entry #23:1:44]
1 │ def a_3 [x] { if $x == 3 { [1 2 3] | each {error make {msg: 'a custom error inside list stream'} } } }
· ─────┬────
· ╰── originates from here
╰────
```
</details>
Run `b --external` shows the following error:
<details>
```nushell
Error: chained_error
× oops
╭─[entry #29:1:1]
1 │ b --external
· ┬
· ╰── error happened when running this
╰────
Error: nu:🐚:eval_block_with_input
× Eval block failed with pipeline input
╭─[entry #26:4:16]
3 │ # error with non-zero exit code, which is generated from external command.
4 │ a_2 1; a_2 3; a_2 2
· ─┬─
· ╰── source value
5 │ } else if $list_stream == true {
╰────
Error: nu:🐚:non_zero_exit_code
× External command had a non-zero exit code
╭─[entry #7:1:29]
1 │ def a_2 [x] { if $x == 3 { ^false } else { $x } }
· ──┬──
· ╰── exited with code 1
╰────
```
</details>
It also added a message to guide the usage of NU_BACKTRACE, see the last
line in the following example:
```shell
ls asdfasd
Error: nu:🐚:io::not_found
× I/O error
╰─▶ × Entity not found
╭─[entry #17:1:4]
1 │ ls asdfasd
· ───┬───
· ╰── Entity not found
╰────
help: The error occurred at '/home/windsoilder/projects/nushell/asdfasd'
set the `NU_BACKTRACE=1` environment variable to display a backtrace.
```
# Tests + Formatting
Added some tests for the behavior.
# After Submitting
# Description
This is a follow up for pr:
https://github.com/nushell/nushell/pull/13873
In that pr, I left 2 TODOs about tests, this pr is going to resolve
them.
# User-Facing Changes
NaN
# Tests + Formatting
Added 2 tests
# Description
This PR cleans up the code surrounding formatting and displaying file
sizes.
- The `byte_unit` crate we use for file size units displays kilobytes as
`KB`, which is not the SI or ISO/IEC standard. Rather it should be `kB`,
so this fixes#8872. On some systems, `KB` actually means `KiB`, so this
avoids any potential confusion.
- The `byte_unit` crate, when displaying file sizes, casts integers to
floats which will lose precision for large file sizes. This PR adds a
custom `Display` implementation for `Filesize` that can give an exact
string representation of a `Filesize` for metric/SI units.
- This PR also removes the dependency on the `byte_unit` crate which
brought in several other dependencies.
Additionally, this PR makes some changes to the config for filesize
formatting (`$env.config.filesize`).
- The previous filesize config had the `metric` and `format` options. If
a metric (SI) unit was set in `format`, but `metric` was set to false,
then the `metric` option would take precedence and convert `format` to
the corresponding binary unit (or vice versa). E.g., `{ format: kB,
metric: false }` => `KiB`. Instead, this PR adds the `unit` option to
replace the `format` and `metric` options. `unit` can be set to a fixed
file size unit like `kB` or `KiB`, or it can be set to one of the
special options: `binary` or `metric`. These options tells nushell to
format file sizes using an appropriately scaled metric or binary unit
(examples below).
```nushell
# precision = null
# unit = kB
1kB # 1 kB
1KiB # 1.024 kB
# unit = KiB
1kB # 0.9765625 KiB
1KiB # 1 KiB
# unit = metric
1000B # 1 kB
1024B # 1.024 kB
10_000MB # 10 GB
10_240MiB # 10.73741824 GB
# unit = binary
1000B # 1000 B
1024B # 1 KiB
10_000MB # 9.313225746154785 GiB
10_240MiB # 10 GiB
```
- In addition, this PR also adds the `precision` option to the filesize
config. It determines how many digits to show after the decimal point.
If set to null, then everything after the decimal point is shown.
- The default filesize config is `{ unit: metric, precision: 1 }`.
# User-Facing Changes
- Commands that use the config to format file sizes will follow the
changes described above (e.g., `table`, `into string`, `to text`, etc.).
- The file size unit/format passed to `format filesize` is now case
sensitive. An error with the valid units is shown if the case does not
match.
- `$env.config.filesize.format` and `$env.config.filesize.metric` are
deprecated and replaced by `$env.config.filesize.unit`.
- A new `$env.config.filesize.precision` option was added.
# Tests + Formatting
Mostly updated test expected outputs.
# After Submitting
This PR does not change the way NUON serializes file sizes, because that
would require changing the nu parser to be able to losslessly decode the
new, exact string representation introduced in this PR.
Similarly, this PR also does not change the file size parsing in any
way. Although the file size units provided to `format filesize` or the
filesize config are now case-sensitive, the same is not yet true for
file size literals in nushell code.
# Description
Fixes multiple issues related to `ENV_CONVERSION` and
path-conversion-to-list.
* #14681 removed some calls to `convert_env_values()`, but we found that
this caused `nu -n` to no longer convert the path properly.
* `ENV_CONVERSIONS` have apparently never preserved case, meaning a
conversion with a key of `foo` would not update `$env.FOO` but rather
create a new environment variable with a different case.
* There was a partial code-path that attempted to solve this for `PATH`,
but it only worked for `PATH` and `Path`.
* `convert_env_values()`, which handled `ENV_CONVERSIONS` was called in
multiple places in the startup depending on flags.
This PR:
* Refactors the startup to handle the conversion in `main()` rather than
in each potential startup path
* Updates `get_env_var_insensitive()` functions added in #14390 to
return the name of the environment variable with its original case. This
allows code that updates environment variables to preserve the case.
* Makes use of the updated function in `ENV_CONVERSIONS` to preserve the
case of any updated environment variables. The `ENV_CONVERSION` key
itself is still case **insensitive**.
* Makes use of the updated function to preserve the case of the `PATH`
environment variable (normally handled separately, regardless of whether
or not there was an `ENV_CONVERSION` for it).
## Before
`env_convert_values` was run:
* Before the user `env.nu` ran, which included `nu -c <commandstring>`
and `nu <script.nu>`
* Before the REPL loaded, which included `nu -n`
## After
`env_convert_values` always runs once in `main()` before any config file
is processed or the REPL is started
# User-Facing Changes
Bug fixes
# Tests + Formatting
- 🟢 `toolkit fmt`
- 🟢 `toolkit clippy`
- 🟢 `toolkit test`
- 🟢 `toolkit test stdlib`
Added additional tests to prevent future regression.
# After Submitting
There is additional cleanup that should probably be done in
`convert_env_values()`. This function previously handled
`ENV_CONVERSIONS`, but there is no longer any need for this since
`convert_env_vars()` runs whenever `$env.ENV_CONVERSIONS` changes now.
This means that the only relevant task in the old `convert_env_values()`
is to convert the `PATH` to a list, and ensure that it is a list of
strings. It's still calling the `from_string` conversion on every
variable (just once) even though there are no `ENV_CONVERSIONS` at this
point.
Leaving that to another PR though, while we get the core issue fixed
with this one.
Related:
- #14329
- #13872
- #8214
# Description & User-Facing Changes
This PR allows enables the following uses, which are all no-op.
```nushell
source null
source-env null
use null
overlay use null
```
The motivation for this change is conditional sourcing of files. For
example, with this change `login.nu` may be deprecated and replaced with
the following code in `config.nu`
```nushell
const login_module = if $nu.is-login { "login.nu" } else { null }
source $login_module
```
# Tests + Formatting
I'm hoping for CI to pass 😄
# After Submitting
Add a part about the conditional sourcing pattern to the website.
# Description
A follow-on to #14727:
* Instead of using `is-interactive` as the trigger for incrementing
`SHLVL`, this change puts the increment logic just before `run_repl()`
is called.
* Tests are changed to use `-e`
* Moves the `confirm_stdin_is_terminal()` call immediately **after** the
`prerun_cmd` (which executes `--execute (-e) <commandstring>`. The fact
that it was **before** that call seems to be a bug, since the error
message says *"or provide arguments to invoke a script"* even if
`--execute` was used. This change enables REPL testing using `--execute
(-e)`.
* Added a test to ensure `-c` does *not* increment SHLVL.
# User-Facing Changes
`$env.SHLVL` runs before the REPL is started, rather than when
`is-interactive`
# Tests + Formatting
- 🟢 `toolkit fmt`
- 🟢 `toolkit clippy`
- 🟢 `toolkit test`
- 🟢 `toolkit test stdlib`
# After Submitting
N/A
Tests for #14707 are causing hangs which are preventing `toolkit test`
from completing on some systems. This appears to be due to the use of
`-i` to force interactive mode, which is required in order to update the
`SHLVL`. Both tests are likely attempting to acquire the terminal at the
same time, and one is hanging as a result.
This is a temporary fix which runs both of these tests sequentially.
It's temporary because we need to find a solution which doesn't use
`-i`, since any other future `-it` test will cause the same situation
again.
# Description
Rework of #14570, fixing #14567.
`exec` will decrement `SHLVL` env value before passing it to target
executable (in interactive mode).
(Same as last pr, but this time there's no wrong change to current
working code)
Two `SHLVL` related tests were also added this time.
- this PR should close#14514
# Description
Makes updates to `$env.ENV_CONVERSIONS` take effect immediately.
# User-Facing Changes
No breaking change, `$env.ENV_CONVERSIONS` can be set and its effect
used in the same file.
# Tests + Formatting
- 🟢 toolkit fmt
- 🟢 toolkit clippy
- 🟢 toolkit test
- 🟢 toolkit test stdlib
# After Submitting
N/A
Just a quick change: the test I made for `--no-newline` was missing
`--no-config-file`, so it could false-negative if you have problems with
your config.
# Description
The `.nu-env` file feature was removed some time ago (probably in the
engine-q upgrade?). The tests, however, still remained as dead-code, so
this is just some basic clean-up.
If this feature was ever implemented again, the tests would need to be
rewritten anyway due to the changes in the way config is handled.
# User-Facing Changes
None
# Tests + Formatting
- 🟢 `toolkit fmt`
- 🟢 `toolkit clippy`
- 🟢 `toolkit test`
- 🟢 `toolkit test stdlib`
-
# After Submitting
N/A
# Release Notes Excerpt
* Hooks now default to an empty value of the proper type (e.g., `[]` or
`{}`) when not otherwise specified
# Description
```nushell
# Start with no config
nu -n
# Populate with defaults
$env.config = {}
$env.config.hooks
```
* Before: All hooks other than `display_output` were set to `null`.
Attempting to append a hook using `++=` would fail unless it had already
been assigned.
* After:
* `pre_prompt`, `pre_execution`, and `command_not_found` are set to
empty lists. This allows the user to simply append new hooks using
`++=`.
* `env_change` is set to an empty record. This allows the user to add
new hooks using `merge`, although a "helper" command would still be
useful (TODO: stdlib).
Also fixed a typo in an error message.
# User-Facing Changes
There shouldn't be any breaking changes since (before) there were no
guarantees of the hook's value/type. Previously, users would have to
check for `null` and `default` to an empty list before appending. Any
user-strategies for dealing with the problem should continue to work
after this change.
# Tests + Formatting
- 🟢 `toolkit fmt`
- 🟢 `toolkit clippy`
- 🟢 `toolkit test`
- 🟢 `toolkit test stdlib`
Note that, for reasons I cannot ascertain, this PR appears to have
*fixed* the `command_not_found_error_recognizes_non_executable_file`
test that was previously broken by #12953. That PR essentially rewrote
the test to match the new behavior, but it no longer tested what it was
intended to test.
Now, the test is working again as designed (and as it works in the
REPL).
# After Submitting
This will be covered in the Configuration update for #14249. This PR
will simplify several examples in the doc.
# Description
Fixes: #14202
After looking into the issue, I think #13910 it's not good to cut the
span if it's in external argument.
This pr is somehow revert the change, and fix
https://github.com/nushell/nushell/issues/13431 in another way.
It introduce a new state named `State::BackTickQuote`, so if an external
arg include backtick quote, it enters the state, so backtick quote won't
be the body of a string.
# User-Facing Changes
### Before
```nushell
> ^echo `(echo aa)`
aa
> ^echo `"aa"` # maybe it's not right to remove the inner quote.
aa
```
### After
```nushell
> ^echo `(echo aa)`
(echo aa)
> ^echo `"aa"` # inner quote is keeped if there are backtick quote outside.
"aa"
```
# Tests + Formatting
Added 3 tests.
The idea comes from @amtoine, I think it would be good to keey
`display_error.exit_code` same value, if user is using default config or
using no config file at all.
Updated summary for commit
[612e0e2](612e0e2160)
- While folks are welcome to read through the entire comments, the core
information is summarized here.
# Description
This PR drastically improves startup times of Nushell by only parsing a
single submodule of the Standard Library that provides the `banner` and
`pwd` commands. All other Standard Library commands and submodules are
parsed when imported by the user. This cuts startup times by more than
60%.
At the moment, we have stopped adding to `std-lib` because every
addition adds a small amount to the Nushell startup time.
With this change, we should once again be able to allow new
functionality to be added to the Standard Library without it impacting
`nu` startup times.
# User-Facing Changes
* Nushell now starts about 60% faster
* Breaking change: The `dirs` (Shells) aliases will return a warning
message that it will not be auto-loaded in the following release, along
with instructions on how to restore it (and disable the message)
* The `use std <submodule> *` syntax is available for convenience, but
should be avoided in scripts as it parses the entire `std` module and
all other submodules and places it in scope. The correct syntax to
*just* load a submodule is `use std/<submodule> *` (asterisk optional).
The slash is important. This will be documented.
* `use std *` can be used for convenience to load all of the library but
still incurs the full loading-time.
* `std/dirs`: Semi-breaking change. The `dirs` command replaces the
`show` command. This is more in line with the directory-stack
functionality found in other shells. Existing users will not be impacted
by this as the alias (`shells`) remains the same.
* Breaking-change: Technically a breaking change, but probably only
impacts maintainers of `std`. The virtual path for the standard library
has changed. It could previously be imported using its virtual path (and
technically, this would have been the correct way to do it):
```nu
use NU_STDLIB_VIRTUAL_DIR/std
```
The path is now simply `std/`:
```nu
use std
```
All submodules have moved accordingly.
# Timings
Comparisons below were made:
* In a temporary, clean config directory using `$env.XDG_CONFIG_HOME =
(mktemp -d)`.
* `nu` was run with a release build
* `nu` was run one time to generate the default `config.nu` (etc.) files
- Otherwise timings would include the user-prompt
* The shell was exited and then restarted several times to get timing
samples
(Note: Old timings based on 0.97 rather than 0.98, but in the range of
being accurate)
| Scenario | `$nu.startup-time` |
| --- | --- |
| 0.97.2
([aaaab8e](aaaab8e070))
Without this PR | 23ms - 24ms |
| This PR with deprecated commands | 9ms - <11ms |
| This PR after deprecated commands are removed in following release |
8ms - <10ms |
| Final PR (remove deprecated), using `--no-std-lib` | 6.1ms to 6.4ms |
| Final PR (remove deprecated), using `--no-config-file` | 3.1ms - 3.6ms
|
| Final PR (remove deprecated), using `--no-config-file --no-std-lib` |
1ms - 1.5ms |
*These last two timings point to the opportunity for further
optimization (see comment in thread below (will link once I write it).*
# Implementation details for future maintenance
* `use std banner` is a ridiculously deceptive call. That call parses
and imports *all* of `std` into scope. Simply replacing it with `use
std/core *` is essentially what saves ~14-15ms. This *only* imports the
submodule with the `banner` and `pwd` commands.
* From the code-comments, the reason that `NU_STDLIB_VIRTUAL_DIR` was
used as a prefix was so that there wouldn't be an issue if a user had a
`./std/mod.nu` in the current directory. This does **not** appear to be
an issue. After removing the prefix, I tested with both a relative
module as well as one in the `$env.NU_LIB_DIRS` path, and in all cases
the *internal* `std` still took precedence.
* By removing the prefix, users can now `use std` (and variants) without
requiring that it already be parsed and in scope.
* In the next release, we'll stop autoloading the `dirs` (shells)
functionality. While this only costs an additional 1-1.5ms, I think it's
better moved to the `config.nu` where the user can optionally remove it.
The main reason is its use of aliases (which have also caused issues) -
The `n`, `p`, and `g` short-commands are valuable real-estate, and users
may want to map these to something else.
For this release, there's an `deprecated_dirs` module that is still
autoloaded. As with the top-level commands, use of these will give a
deprecation warning with instructions on how to handle going forward.
To help with this, moved the aliases to their own submodule inside the
`dirs` module.
* Also sneaks in a small change where the top-level `dirs` command is
now the replacement for `dirs show`
* Fixed a double-import of `assert` in `dirs.nu`
* The `show_banner` step is replaced with simply `banner` rather than
re-importing it.
* A `virtual_path` may now be referenced with either a forward-slash or
a backward-slash on Windows. This allows `use std/<submodule>` to work
on all platforms.
# Performance side-notes:
* Future parsing and/or IR improvements should improve performance even
further.
* While the existing load time penalty of `std-lib` was not noticeable
on many systems, Nushell runs on a wide-variety of hardware and OS
platforms. Slower platforms will naturally see a bigger jump in
performance here. For users starting multiple Nushell sessions
frequently (e.g., `tmux`, Zellij, `screen`, et. al.) it is recommended
to keep total startup time (including user configuration) under ~250ms.
# Tests + Formatting
* All tests are green
* Updated tests:
- Removed the test that confirmed that `std` was loaded (since we
don't).
- Removed the `shells` test since it is not autoloaded. Main `dirs.nu`
functionality is tested through `stdlib-test`.
- Many tests assumed that the library was fully loaded, because it was
(even though we didn't intend for it to be). Fixed those tests.
- Tests now import only the necessary submodules (e.g., `use
std/assert`, rather than `use std assert`)
- Some tests *thought* they were loading `std/log`, but were doing so
improperly. This was masked by the now-fixed "load-everything-into-scope
bug". Local CI would pass due the `$env.NU_LOG_<...>` variables being
inherited from the calling process, but would fail in the "clean" GitHub
CI environment. These tests have also been fixed.
* Added additional tests for the changes
# After Submitting
Will update the Standard Library doc page
This PR sets the current working directory to the location of the
Nushell executable at startup, using `std::env::set_current_dir()`. This
is desirable because after PR
https://github.com/nushell/nushell/pull/12922, we no longer change our
current working directory even after `cd` is executed, and some OS might
lock the directory where Nushell started.
The location of the Nushell executable is chosen because it cannot be
removed while Nushell is running anyways, so we don't have to worry
about OS locking it.
This PR has the side effect that it breaks buggy command even harder.
I'll keep this PR as a draft until these commands are fixed, but it
might be helpful to pull this PR if you're working on fixing one of
those bugs.
---------
Co-authored-by: Devyn Cairns <devyn.cairns@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: Darren Schroeder <343840+fdncred@users.noreply.github.com>
# Description
This PR makes it so that non-zero exit codes and termination by signal
are treated as a normal `ShellError`. Currently, these are silent
errors. That is, if an external command fails, then it's code block is
aborted, but the parent block can sometimes continue execution. E.g.,
see #8569 and this example:
```nushell
[1 2] | each { ^false }
```
Before this would give:
```
╭───┬──╮
│ 0 │ │
│ 1 │ │
╰───┴──╯
```
Now, this shows an error:
```
Error: nu:🐚:eval_block_with_input
× Eval block failed with pipeline input
╭─[entry #1:1:2]
1 │ [1 2] | each { ^false }
· ┬
· ╰── source value
╰────
Error: nu:🐚:non_zero_exit_code
× External command had a non-zero exit code
╭─[entry #1:1:17]
1 │ [1 2] | each { ^false }
· ──┬──
· ╰── exited with code 1
╰────
```
This PR fixes#12874, fixes#5960, fixes#10856, and fixes#5347. This
PR also partially addresses #10633 and #10624 (only the last command of
a pipeline is currently checked). It looks like #8569 is already fixed,
but this PR will make sure it is definitely fixed (fixes#8569).
# User-Facing Changes
- Non-zero exit codes and termination by signal now cause an error to be
thrown.
- The error record value passed to a `catch` block may now have an
`exit_code` column containing the integer exit code if the error was due
to an external command.
- Adds new config values, `display_errors.exit_code` and
`display_errors.termination_signal`, which determine whether an error
message should be printed in the respective error cases. For
non-interactive sessions, these are set to `true`, and for interactive
sessions `display_errors.exit_code` is false (via the default config).
# Tests
Added a few tests.
# After Submitting
- Update docs and book.
- Future work:
- Error if other external commands besides the last in a pipeline exit
with a non-zero exit code. Then, deprecate `do -c` since this will be
the default behavior everywhere.
- Add a better mechanism for exit codes and deprecate
`$env.LAST_EXIT_CODE` (it's buggy).
Fixesnushell/nushell#13689
# Description
Respect user-defined `$env.NU_LOG_FORMAT` and `$env.NU_LOG_DATE_FORMAT`
Additionally I fixed `nu_with_std!()` macro (it was not working
correctly)
# User-Facing Changes
Users now may set `$env.NU_LOG_FORMAT` and `$env.NU_LOG_DATE_FORMAT` in
`env.nu` and it will work even if `use std` is used after that.
# Tests + Formatting
Added a couple of tests for the new functionality.
# After Submitting
# Description
<!--
Thank you for improving Nushell. Please, check our [contributing
guide](../CONTRIBUTING.md) and talk to the core team before making major
changes.
Description of your pull request goes here. **Provide examples and/or
screenshots** if your changes affect the user experience.
-->
Currently the parser and the documentation generation use the signature
of the command, which means that it doesn't pick up on the changed name
of the `main` block, and therefore shows the name of the command as
"main" and doesn't find the subcommands. This PR changes the
aforementioned places to use the block signature to fix these issues.
This closes#13397. Incidentally it also causes input/output types to be
shown in the help, which is kinda pointless for scripts since they don't
operate on structured data but maybe not worth the effort to remove.
# User-Facing Changes
<!-- List of all changes that impact the user experience here. This
helps us keep track of breaking changes. -->
```
# example.nu
export def main [] { help main }
export def 'main sub' [] { print 'sub' }
```
Before:
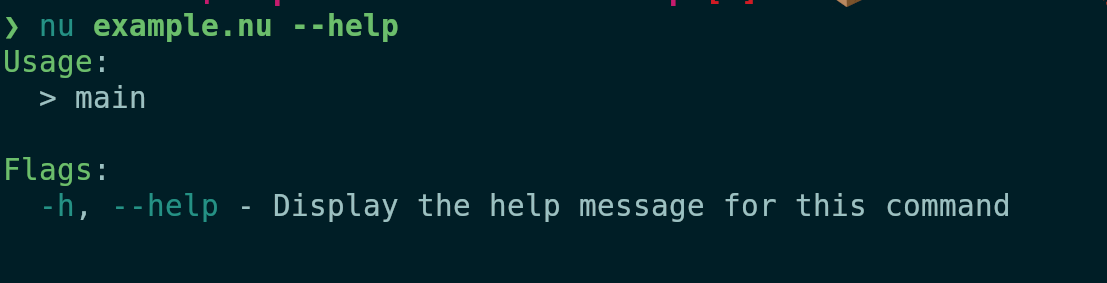

After:
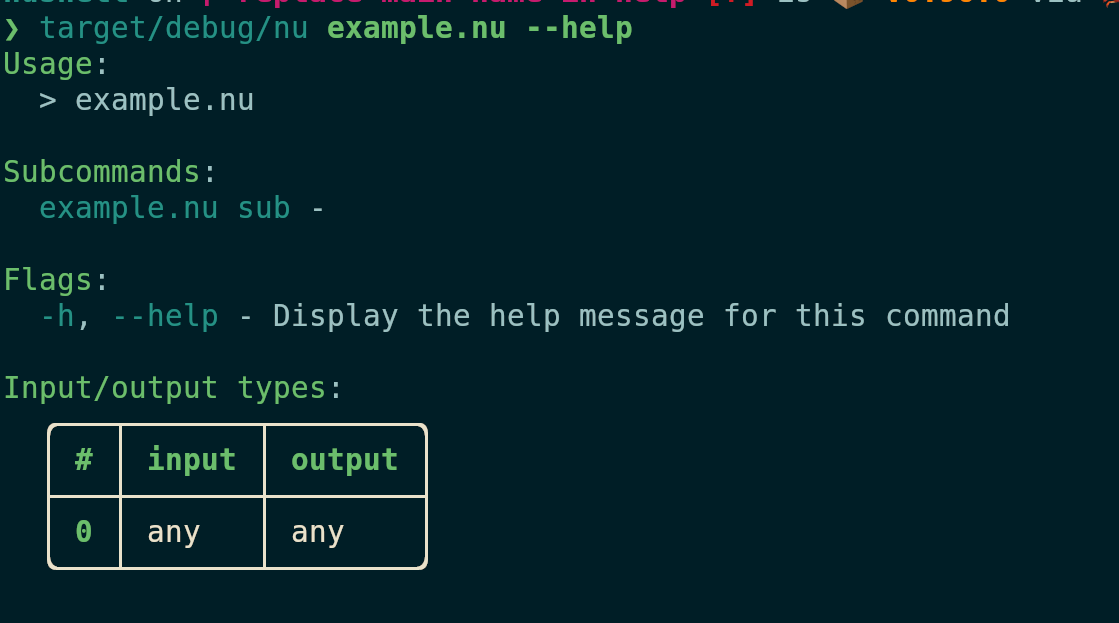
# Tests
<!--
Don't forget to add tests that cover your changes.
Make sure you've run and fixed any issues with these commands:
- `cargo fmt --all -- --check` to check standard code formatting (`cargo
fmt --all` applies these changes)
- `cargo clippy --workspace -- -D warnings -D clippy::unwrap_used` to
check that you're using the standard code style
- `cargo test --workspace` to check that all tests pass (on Windows make
sure to [enable developer
mode](https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/apps/get-started/developer-mode-features-and-debugging))
- `cargo run -- -c "use toolkit.nu; toolkit test stdlib"` to run the
tests for the standard library
> **Note**
> from `nushell` you can also use the `toolkit` as follows
> ```bash
> use toolkit.nu # or use an `env_change` hook to activate it
automatically
> toolkit check pr
> ```
-->
Tests are still missing for the subcommands and the input/output types
---------
Co-authored-by: Stefan Holderbach <sholderbach@users.noreply.github.com>
# Description
Fixes Issue #13477
This adds a check to see if a user is trying to invoke a
(non-executable) file as a command and returns a helpful error if so.
EDIT: this will not work on Windows, and is arguably not relevant there,
because of the different semantics of executables. I think the
equivalent on Windows would be if a user tries to invoke `./foo`, we
should look for `foo.exe` or `foo.bat` in the directory and recommend
that if it exists.
# User-Facing Changes
When a user invokes an unrecognized command that is the path to an
existing file, the error used to say:
`{name} is neither a Nushell built-in or a known external command`
This PR proposes to change the message to:
`{name} refers to a file that is not executable. Did you forget to to
set execute permissions?`
# Tests + Formatting
Ran cargo fmt, clippy and test on the workspace.
EDIT: added test asserting the new behavior
# Description
[Discovered](https://discord.com/channels/601130461678272522/614593951969574961/1266503282554179604)
by `@warp` on Discord.
The IR compiler was not properly setting redirect modes for
subexpressions because `FullCellPath` was always being compiled with
capture-out redirection. This is the correct behavior if there is a tail
to the `FullCellPath`, as we need the value in order to try to extract
anything from it (although this is unlikely to work) - however, the
parser also generates `FullCellPath`s with an empty tail quite often,
including for bare subexpressions.
Because of this, the following did not behave as expected:
```nushell
(docker run -it --rm alpine)
```
Capturing the output meant that `docker` didn't have direct access to
the terminal as a TTY.
As this is a minor bug fix, it should be okay to include in the 0.96.1
patch release.
# User-Facing Changes
- Fixes the bug as described when running with IR evaluation enabled.
# Tests + Formatting
I added a test for this, though we're not currently running all tests
with IR on the CI, but it should ensure this behaviour is consistent.
The equivalent minimum repro I could find was:
```nushell
(nu --testbin cococo); null
```
as this should cause the `cococo` message to appear on stdout, and if
Nushell is capturing the output, it would be discarded instead.
# Description
Fixes the lexer to recognize `out>|`, `err>|`, `out+err>|`, etc.
Previously only the short-style forms were recognized, which was
inconsistent with normal file redirections.
I also integrated it all more into the normal lex path by checking `|`
in a special way, which should be more performant and consistent, and
cleans up the code a bunch.
Closes#13331.
# User-Facing Changes
- Adds `out>|` (error), `err>|`, `out+err>|`, `err+out>|` as recognized
forms of the pipe redirection.
# Tests + Formatting
All passing. Added tests for the new forms.
# After Submitting
- [ ] release notes
# Description
From the feedbacks from @amtoine , it's good to make nushell shows error
for `o>|` syntax.
# User-Facing Changes
## Before
```nushell
'foo' o>| print 07/09/2024 06:44:23 AM
Error: nu::parser::parse_mismatch
× Parse mismatch during operation.
╭─[entry #6:1:9]
1 │ 'foo' o>| print
· ┬
· ╰── expected redirection target
```
## After
```nushell
'foo' o>| print 07/09/2024 06:47:26 AM
Error: nu::parser::parse_mismatch
× Parse mismatch during operation.
╭─[entry #1:1:7]
1 │ 'foo' o>| print
· ─┬─
· ╰── expected `|`. Redirection stdout to pipe is the same as piping directly.
╰────
```
# Tests + Formatting
Added one test
---------
Co-authored-by: Darren Schroeder <343840+fdncred@users.noreply.github.com>
# Description
Removes the `which-support` cargo feature and makes all of its
feature-gated code enabled by default in all builds. I'm not sure why
this one command is gated behind a feature. It seems to be a relic of
older code where we had features for what seems like every command.
<!--
if this PR closes one or more issues, you can automatically link the PR
with
them by using one of the [*linking
keywords*](https://docs.github.com/en/issues/tracking-your-work-with-issues/linking-a-pull-request-to-an-issue#linking-a-pull-request-to-an-issue-using-a-keyword),
e.g.
- this PR should close #xxxx
- fixes #xxxx
you can also mention related issues, PRs or discussions!
-->
# Description
<!--
Thank you for improving Nushell. Please, check our [contributing
guide](../CONTRIBUTING.md) and talk to the core team before making major
changes.
Description of your pull request goes here. **Provide examples and/or
screenshots** if your changes affect the user experience.
-->
Test was failing with “did you mean” due to the `NEXTEST` env var being
present when running tests via `cargo nextest run`.
# User-Facing Changes
<!-- List of all changes that impact the user experience here. This
helps us keep track of breaking changes. -->
# Tests + Formatting
<!--
Don't forget to add tests that cover your changes.
Make sure you've run and fixed any issues with these commands:
- `cargo fmt --all -- --check` to check standard code formatting (`cargo
fmt --all` applies these changes)
- `cargo clippy --workspace -- -D warnings -D clippy::unwrap_used` to
check that you're using the standard code style
- `cargo test --workspace` to check that all tests pass (on Windows make
sure to [enable developer
mode](https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/apps/get-started/developer-mode-features-and-debugging))
- `cargo run -- -c "use toolkit.nu; toolkit test stdlib"` to run the
tests for the standard library
> **Note**
> from `nushell` you can also use the `toolkit` as follows
> ```bash
> use toolkit.nu # or use an `env_change` hook to activate it
automatically
> toolkit check pr
> ```
-->
# After Submitting
<!-- If your PR had any user-facing changes, update [the
documentation](https://github.com/nushell/nushell.github.io) after the
PR is merged, if necessary. This will help us keep the docs up to date.
-->
# Description
Fixes: #13066
nushell should remove argument values' inner quote once it gets `=`.
Whatever it's a flag or not, and it also replace from `\"` to `"` before
passing it to external commands.
# User-Facing Changes
Given the shell script:
```shell
# test.sh
echo $@
```
## Before
```
> sh test.sh -ldflags="-s -w" github.com
-ldflags="-s -w" github.com
> sh test.sh exp='-s -w' github.com
exp='-s -w' github.com
```
## After
```
> sh test.sh -ldflags="-s -w" github.com
-ldflags=-s -w github.com
> sh test.sh exp='-s -w' github.com
exp=-s -w github.com
```
# Tests + Formatting
Added some tests
This PR fixes a bug where `.` is expanded into an empty string when used
as an argument to external commands. Fixes
https://github.com/nushell/nushell/issues/12948.
---------
Co-authored-by: Ian Manske <ian.manske@pm.me>
# Description
There is a bug when `hide-env` is used on environment variables that
were present at shell startup. Namely, child processes still inherit the
hidden environment variable. This PR fixes#12900, fixes#11495, and
fixes#7937.
# Tests + Formatting
Added a test.
# Description
This PR introduces a `ByteStream` type which is a `Read`-able stream of
bytes. Internally, it has an enum over three different byte stream
sources:
```rust
pub enum ByteStreamSource {
Read(Box<dyn Read + Send + 'static>),
File(File),
Child(ChildProcess),
}
```
This is in comparison to the current `RawStream` type, which is an
`Iterator<Item = Vec<u8>>` and has to allocate for each read chunk.
Currently, `PipelineData::ExternalStream` serves a weird dual role where
it is either external command output or a wrapper around `RawStream`.
`ByteStream` makes this distinction more clear (via `ByteStreamSource`)
and replaces `PipelineData::ExternalStream` in this PR:
```rust
pub enum PipelineData {
Empty,
Value(Value, Option<PipelineMetadata>),
ListStream(ListStream, Option<PipelineMetadata>),
ByteStream(ByteStream, Option<PipelineMetadata>),
}
```
The PR is relatively large, but a decent amount of it is just repetitive
changes.
This PR fixes#7017, fixes#10763, and fixes#12369.
This PR also improves performance when piping external commands. Nushell
should, in most cases, have competitive pipeline throughput compared to,
e.g., bash.
| Command | Before (MB/s) | After (MB/s) | Bash (MB/s) |
| -------------------------------------------------- | -------------:|
------------:| -----------:|
| `throughput \| rg 'x'` | 3059 | 3744 | 3739 |
| `throughput \| nu --testbin relay o> /dev/null` | 3508 | 8087 | 8136 |
# User-Facing Changes
- This is a breaking change for the plugin communication protocol,
because the `ExternalStreamInfo` was replaced with `ByteStreamInfo`.
Plugins now only have to deal with a single input stream, as opposed to
the previous three streams: stdout, stderr, and exit code.
- The output of `describe` has been changed for external/byte streams.
- Temporary breaking change: `bytes starts-with` no longer works with
byte streams. This is to keep the PR smaller, and `bytes ends-with`
already does not work on byte streams.
- If a process core dumped, then instead of having a `Value::Error` in
the `exit_code` column of the output returned from `complete`, it now is
a `Value::Int` with the negation of the signal number.
# After Submitting
- Update docs and book as necessary
- Release notes (e.g., plugin protocol changes)
- Adapt/convert commands to work with byte streams (high priority is
`str length`, `bytes starts-with`, and maybe `bytes ends-with`).
- Refactor the `tee` code, Devyn has already done some work on this.
---------
Co-authored-by: Devyn Cairns <devyn.cairns@gmail.com>
# Description
Make typos config more strict: ignore false positives where they occur.
1. Ignore only files with typos
2. Add regexp-s with context
3. Ignore variable names only in Rust code
4. Ignore only 1 "identifier"
5. Check dot files
🎁 Extra bonus: fix typos!!
# Description
Judiciously try to avoid allocations/clone by changing the signature of
functions
- **Don't pass str by value unnecessarily if only read**
- **Don't require a vec in `Sandbox::with_files`**
- **Remove unnecessary string clone**
- **Fixup unnecessary borrow**
- **Use `&str` in shape color instead**
- **Vec -> Slice**
- **Elide string clone**
- **Elide `Path` clone**
- **Take &str to elide clone in tests**
# User-Facing Changes
None
# Tests + Formatting
This touches many tests purely in changing from owned to borrowed/static
data
This PR changes `$env` to be **case-preserving** instead of
case-sensitive. That is, it preserves the case of the environment
variable when it is first assigned, but subsequent retrieval and update
ignores the case.
Notably, both `$env.PATH` and `$env.Path` can now be used to read or set
the environment variable, but child processes will always see the
correct case based on the platform.
Fixes#11268.
---
This feature was surprising simple to implement, because most of the
infrastructure to support case-insensitive cell path access already
exists. The `get` command extracts data using a cell path in a
case-insensitive way (!), but accepts a `--sensitive` flag. (I think
this should be flipped around?)
# Description
Work for #7149
- **Error `with-env` given uneven count in list form**
- **Fix `with-env` `CantConvert` to record**
- **Error `with-env` when given protected env vars**
- **Deprecate list/table input of vars to `with-env`**
- **Remove examples for deprecated input**
# User-Facing Changes
## Deprecation of the following forms
```
> with-env [MYENV "my env value"] { $env.MYENV }
my env value
> with-env [X Y W Z] { $env.X }
Y
> with-env [[X W]; [Y Z]] { $env.W }
Z
```
## recommended standardized form
```
# Set by key-value record
> with-env {X: "Y", W: "Z"} { [$env.X $env.W] }
╭───┬───╮
│ 0 │ Y │
│ 1 │ Z │
╰───┴───╯
```
## (Side effect) Repeated definitions in an env shorthand are now
disallowed
```
> FOO=bar FOO=baz $env
Error: nu:🐚:column_defined_twice
× Record field or table column used twice: FOO
╭─[entry #1:1:1]
1 │ FOO=bar FOO=baz $env
· ─┬─ ─┬─
· │ ╰── field redefined here
· ╰── field first defined here
╰────
```
# Description
This is an attempt to isolate the unit tests from whatever might be in
the user's config. If the
user's config is broken in some way or incompatible with this version
(for example, especially if
there are plugins that aren't built for this version), tests can
spuriously fail.
This makes tests more reliably pass the same way they would on CI even
if the user has config, and
should also make them run faster.
I think this is _good enough_, but I still think we should have a
specific config dir env variable for nushell specifically (rather than
having to use `XDG_CONFIG_HOME`, which would mess with other things) and
then we can just have `nu-test-support` set that to a temporary dir
containing the shipped default config files.
# Tests + Formatting
- 🟢 `toolkit fmt`
- 🟢 `toolkit clippy`
- 🟢 `toolkit test`
- 🟢 `toolkit test stdlib`
# Description
I have `nu` set as my shell in my editor, which allows me to easily pipe
selections of text to things like `str pascal-case` or even more complex
string operation pipelines, which I find super handy. However, the only
annoying thing is that I pretty much always have to add `| print -n` at
the end, because `nu` adds a newline when it prints the resulting value.
This adds a `--no-newline` option to stop that from happening, and then
you don't need to pipe to `print -n` anymore, you can just have your
shell command for your editor contain that flag.
# User-Facing Changes
- Add `--no-newline` command line option
# Tests + Formatting
- 🟢 `toolkit fmt`
- 🟢 `toolkit clippy`
- 🟢 `toolkit test`
- 🟢 `toolkit test stdlib`
# Description
Some of the tests in `tests::shell` were using `sh` unnecessarily, and
had `#[cfg(not(windows))]` when they should be testable on Windows if
`sh` is not used.
I also found that they were using `.expect()` incorrectly, under the
assumption that that would check their output, when really an
`assert_eq!` on the output is needed to do that. So these tests weren't
even really working properly before.
# User-Facing Changes
None
# Tests + Formatting
- 🟢 `toolkit fmt`
- 🟢 `toolkit clippy`
- 🟢 `toolkit test`
- 🟢 `toolkit test stdlib`
fixes#11900
# Description
Use `serde_json` instead.
# User-Facing Changes
The problem described in the issue now no longer persists.
No whitespace in the output of `to json --raw`
Output of unicode escape changed to consistent `\uffff`
# Tests + Formatting
I corrected all Tests that were affected by this change.
# Description
The PR overhauls how IO redirection is handled, allowing more explicit
and fine-grain control over `stdout` and `stderr` output as well as more
efficient IO and piping.
To summarize the changes in this PR:
- Added a new `IoStream` type to indicate the intended destination for a
pipeline element's `stdout` and `stderr`.
- The `stdout` and `stderr` `IoStream`s are stored in the `Stack` and to
avoid adding 6 additional arguments to every eval function and
`Command::run`. The `stdout` and `stderr` streams can be temporarily
overwritten through functions on `Stack` and these functions will return
a guard that restores the original `stdout` and `stderr` when dropped.
- In the AST, redirections are now directly part of a `PipelineElement`
as a `Option<Redirection>` field instead of having multiple different
`PipelineElement` enum variants for each kind of redirection. This
required changes to the parser, mainly in `lite_parser.rs`.
- `Command`s can also set a `IoStream` override/redirection which will
apply to the previous command in the pipeline. This is used, for
example, in `ignore` to allow the previous external command to have its
stdout redirected to `Stdio::null()` at spawn time. In contrast, the
current implementation has to create an os pipe and manually consume the
output on nushell's side. File and pipe redirections (`o>`, `e>`, `e>|`,
etc.) have precedence over overrides from commands.
This PR improves piping and IO speed, partially addressing #10763. Using
the `throughput` command from that issue, this PR gives the following
speedup on my setup for the commands below:
| Command | Before (MB/s) | After (MB/s) | Bash (MB/s) |
| --------------------------- | -------------:| ------------:|
-----------:|
| `throughput o> /dev/null` | 1169 | 52938 | 54305 |
| `throughput \| ignore` | 840 | 55438 | N/A |
| `throughput \| null` | Error | 53617 | N/A |
| `throughput \| rg 'x'` | 1165 | 3049 | 3736 |
| `(throughput) \| rg 'x'` | 810 | 3085 | 3815 |
(Numbers above are the median samples for throughput)
This PR also paves the way to refactor our `ExternalStream` handling in
the various commands. For example, this PR already fixes the following
code:
```nushell
^sh -c 'echo -n "hello "; sleep 0; echo "world"' | find "hello world"
```
This returns an empty list on 0.90.1 and returns a highlighted "hello
world" on this PR.
Since the `stdout` and `stderr` `IoStream`s are available to commands
when they are run, then this unlocks the potential for more convenient
behavior. E.g., the `find` command can disable its ansi highlighting if
it detects that the output `IoStream` is not the terminal. Knowing the
output streams will also allow background job output to be redirected
more easily and efficiently.
# User-Facing Changes
- External commands returned from closures will be collected (in most
cases):
```nushell
1..2 | each {|_| nu -c "print a" }
```
This gives `["a", "a"]` on this PR, whereas this used to print "a\na\n"
and then return an empty list.
```nushell
1..2 | each {|_| nu -c "print -e a" }
```
This gives `["", ""]` and prints "a\na\n" to stderr, whereas this used
to return an empty list and print "a\na\n" to stderr.
- Trailing new lines are always trimmed for external commands when
piping into internal commands or collecting it as a value. (Failure to
decode the output as utf-8 will keep the trailing newline for the last
binary value.) In the current nushell version, the following three code
snippets differ only in parenthesis placement, but they all also have
different outputs:
1. `1..2 | each { ^echo a }`
```
a
a
╭────────────╮
│ empty list │
╰────────────╯
```
2. `1..2 | each { (^echo a) }`
```
╭───┬───╮
│ 0 │ a │
│ 1 │ a │
╰───┴───╯
```
3. `1..2 | (each { ^echo a })`
```
╭───┬───╮
│ 0 │ a │
│ │ │
│ 1 │ a │
│ │ │
╰───┴───╯
```
But in this PR, the above snippets will all have the same output:
```
╭───┬───╮
│ 0 │ a │
│ 1 │ a │
╰───┴───╯
```
- All existing flags on `run-external` are now deprecated.
- File redirections now apply to all commands inside a code block:
```nushell
(nu -c "print -e a"; nu -c "print -e b") e> test.out
```
This gives "a\nb\n" in `test.out` and prints nothing. The same result
would happen when printing to stdout and using a `o>` file redirection.
- External command output will (almost) never be ignored, and ignoring
output must be explicit now:
```nushell
(^echo a; ^echo b)
```
This prints "a\nb\n", whereas this used to print only "b\n". This only
applies to external commands; values and internal commands not in return
position will not print anything (e.g., `(echo a; echo b)` still only
prints "b").
- `complete` now always captures stderr (`do` is not necessary).
# After Submitting
The language guide and other documentation will need to be updated.
# Description
Fixes: #11287Fixes: #11318
It's implemented by porting the similar logic in `eval_call`, I've tried
to reduce duplicate code, but it seems that it's hard without using
macros.
3ee2fc60f9/crates/nu-engine/src/eval.rs (L60-L130)
It only works for `do` command.
# User-Facing Changes
## Closure supports optional parameter
```nushell
let code = {|x?| print ($x | default "i'm the default")}
do $code
```
Previously it raises an error, after this change, it prints `i'm the
default`.
## Closure supports type checking
```nushell
let code = {|x: int| echo $x}
do $code "aa"
```
After this change, it will raise an error with a message: `can't convert
string to int`
# Tests + Formatting
Done
# After Submitting
NaN
# Description
Fixes: #11912
# User-Facing Changes
After this change:
```
let x = '*.nu'; ^echo $x
```
will no longer expand glob.
If users still want to expand glob, there are also 3 ways to do this:
```
# 1. use spread operation with `glob` command
let x = '*.nu'; ^echo ...(glob $x)
```
# Tests + Formatting
Done
# After Submitting
NaN
# Description
Fixes: #11913
When running external command, nushell shouldn't consumes stderr
messages, if user want to redirect stderr.
# User-Facing Changes
NaN
# Tests + Formatting
Done
# After Submitting
NaN
# Description
Close: #9673Close: #8277Close: #10944
This pr introduces the following syntax:
1. `e>|`, pipe stderr to next command. Example: `$env.FOO=bar nu
--testbin echo_env_stderr FOO e>| str length`
2. `o+e>|` and `e+o>|`, pipe both stdout and stderr to next command,
example: `$env.FOO=bar nu --testbin echo_env_mixed out-err FOO FOO e+o>|
str length`
Note: it only works for external commands. ~There is no different for
internal commands, that is, the following three commands do the same
things:~ Edit: it raises errors if we want to pipes for internal
commands
```
❯ ls e>| str length
Error: × `e>|` only works with external streams
╭─[entry #1:1:1]
1 │ ls e>| str length
· ─┬─
· ╰── `e>|` only works on external streams
╰────
❯ ls e+o>| str length
Error: × `o+e>|` only works with external streams
╭─[entry #2:1:1]
1 │ ls e+o>| str length
· ──┬──
· ╰── `o+e>|` only works on external streams
╰────
```
This can help us to avoid some strange issues like the following:
`$env.FOO=bar (nu --testbin echo_env_stderr FOO) e>| str length`
Which is hard to understand and hard to explain to users.
# User-Facing Changes
Nan
# Tests + Formatting
To be done
# After Submitting
Maybe update documentation about these syntax.