mirror of
https://github.com/nushell/nushell.git
synced 2025-08-01 00:43:24 +02:00
# Description
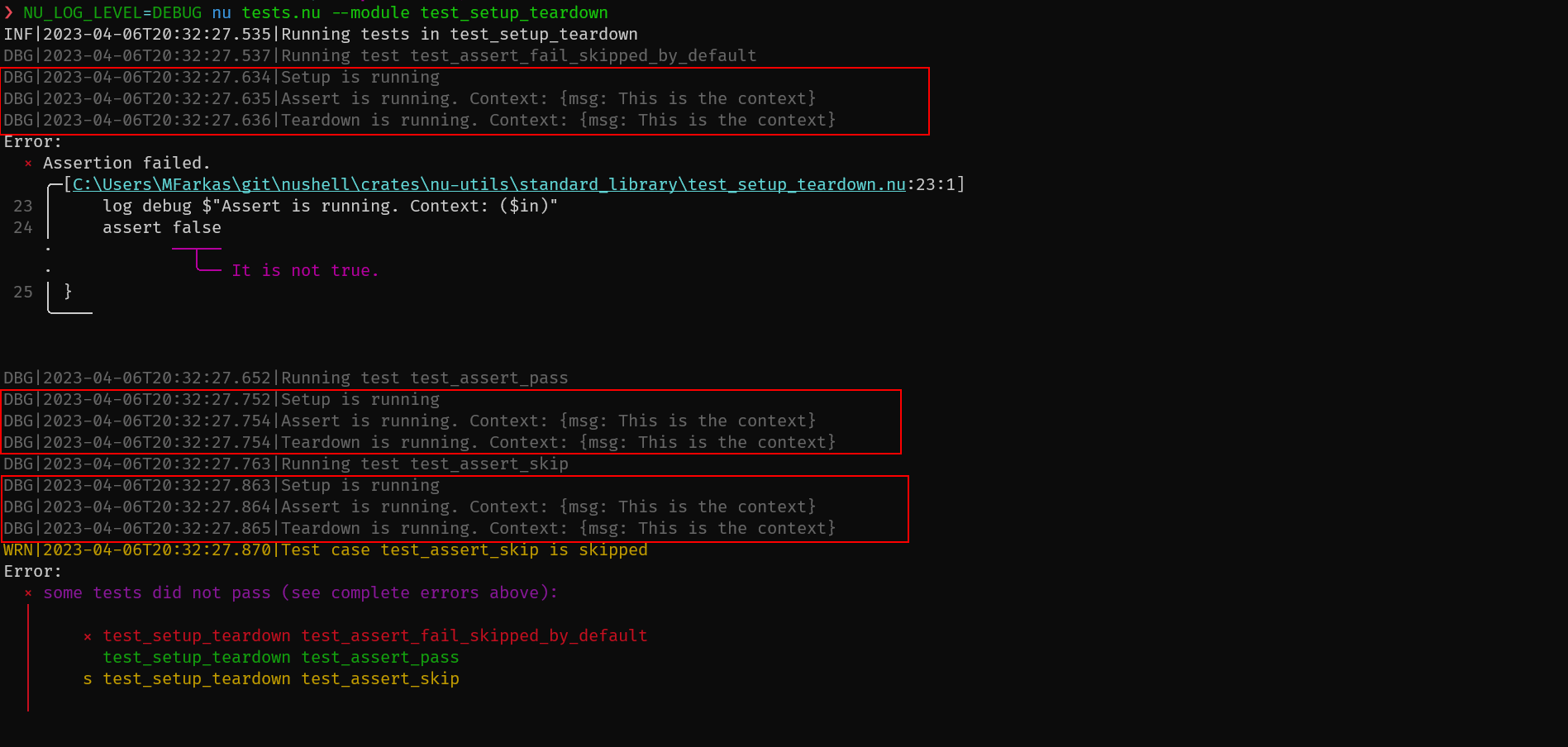
As in other testing frameworks, the `setup` runs before every test case,
and the `teardown` after that. A context can be created in `setup`,
which will be in the `$in` variable in the test cases, and in the
`teardown`. The `teardown` is called regardless of the test is passed,
skipped, or failed.
For example:
```nushell
use std.nu *
export def setup [] {
log debug "Setup is running"
{msg: "This is the context"}
}
export def teardown [] {
log debug $"Teardown is running. Context: ($in)"
}
export def test_assert_pass [] {
log debug $"Assert is running. Context: ($in)"
}
export def test_assert_skip [] {
log debug $"Assert is running. Context: ($in)"
assert skip
}
export def test_assert_fail_skipped_by_default [] {
log debug $"Assert is running. Context: ($in)"
assert false
}
```
# After Submitting
I'll update the documentation.
---------
Co-authored-by: Mate Farkas <Mate.Farkas@oneidentity.com>
Nushell core libraries and plugins
These sub-crates form both the foundation for Nu and a set of plugins which extend Nu with additional functionality.
Foundational libraries are split into two kinds of crates:
- Core crates - those crates that work together to build the Nushell language engine
- Support crates - a set of crates that support the engine with additional features like JSON support, ANSI support, and more.
Plugins are likewise also split into two types:
- Core plugins - plugins that provide part of the default experience of Nu, including access to the system properties, processes, and web-connectivity features.
- Extra plugins - these plugins run a wide range of different capabilities like working with different file types, charting, viewing binary data, and more.