mirror of
https://github.com/rclone/rclone.git
synced 2025-06-20 11:47:57 +02:00
vendor: remove github.com/VividCortex/ewma dependency
This commit is contained in:
parent
ca44fb1fba
commit
502d8b0cdd
9
Gopkg.lock
generated
9
Gopkg.lock
generated
@ -56,14 +56,6 @@
|
|||||||
pruneopts = ""
|
pruneopts = ""
|
||||||
revision = "ef1e4c783f8f0478bd8bff0edb3dd0bade552599"
|
revision = "ef1e4c783f8f0478bd8bff0edb3dd0bade552599"
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
[[projects]]
|
|
||||||
digest = "1:ac226c42eb54c121e0704c6f7f64c96c7817ad6d6286e5536e8cea72807e1079"
|
|
||||||
name = "github.com/VividCortex/ewma"
|
|
||||||
packages = ["."]
|
|
||||||
pruneopts = ""
|
|
||||||
revision = "b24eb346a94c3ba12c1da1e564dbac1b498a77ce"
|
|
||||||
version = "v1.1.1"
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
[[projects]]
|
[[projects]]
|
||||||
branch = "master"
|
branch = "master"
|
||||||
digest = "1:391632fa3a324c4f461f28baaf45cea8b21e13630b00f27059613f855bb544bb"
|
digest = "1:391632fa3a324c4f461f28baaf45cea8b21e13630b00f27059613f855bb544bb"
|
||||||
@ -580,7 +572,6 @@
|
|||||||
"github.com/Azure/go-ansiterm",
|
"github.com/Azure/go-ansiterm",
|
||||||
"github.com/Azure/go-ansiterm/winterm",
|
"github.com/Azure/go-ansiterm/winterm",
|
||||||
"github.com/Unknwon/goconfig",
|
"github.com/Unknwon/goconfig",
|
||||||
"github.com/VividCortex/ewma",
|
|
||||||
"github.com/a8m/tree",
|
"github.com/a8m/tree",
|
||||||
"github.com/abbot/go-http-auth",
|
"github.com/abbot/go-http-auth",
|
||||||
"github.com/aws/aws-sdk-go/aws",
|
"github.com/aws/aws-sdk-go/aws",
|
||||||
|
|||||||
10
vendor/github.com/VividCortex/ewma/.github/ISSUE_TEMPLATE.md
generated
vendored
10
vendor/github.com/VividCortex/ewma/.github/ISSUE_TEMPLATE.md
generated
vendored
@ -1,10 +0,0 @@
|
|||||||
Before you file an issue, please consider:
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
We only accept pull requests for minor fixes or improvements. This includes:
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
* Small bug fixes
|
|
||||||
* Typos
|
|
||||||
* Documentation or comments
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Please open issues to discuss new features. Pull requests for new features will be rejected,
|
|
||||||
so we recommend forking the repository and making changes in your fork for your use case.
|
|
||||||
10
vendor/github.com/VividCortex/ewma/.github/PULL_REQUEST_TEMPLATE.md
generated
vendored
10
vendor/github.com/VividCortex/ewma/.github/PULL_REQUEST_TEMPLATE.md
generated
vendored
@ -1,10 +0,0 @@
|
|||||||
Before you create a pull request, please consider:
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
We only accept pull requests for minor fixes or improvements. This includes:
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
* Small bug fixes
|
|
||||||
* Typos
|
|
||||||
* Documentation or comments
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Please open issues to discuss new features. Pull requests for new features will be rejected,
|
|
||||||
so we recommend forking the repository and making changes in your fork for your use case.
|
|
||||||
2
vendor/github.com/VividCortex/ewma/.gitignore
generated
vendored
2
vendor/github.com/VividCortex/ewma/.gitignore
generated
vendored
@ -1,2 +0,0 @@
|
|||||||
.DS_Store
|
|
||||||
.*.sw?
|
|
||||||
21
vendor/github.com/VividCortex/ewma/LICENSE
generated
vendored
21
vendor/github.com/VividCortex/ewma/LICENSE
generated
vendored
@ -1,21 +0,0 @@
|
|||||||
The MIT License
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Copyright (c) 2013 VividCortex
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy
|
|
||||||
of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal
|
|
||||||
in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights
|
|
||||||
to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell
|
|
||||||
copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is
|
|
||||||
furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in
|
|
||||||
all copies or substantial portions of the Software.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR
|
|
||||||
IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY,
|
|
||||||
FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE
|
|
||||||
AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER
|
|
||||||
LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM,
|
|
||||||
OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN
|
|
||||||
THE SOFTWARE.
|
|
||||||
140
vendor/github.com/VividCortex/ewma/README.md
generated
vendored
140
vendor/github.com/VividCortex/ewma/README.md
generated
vendored
@ -1,140 +0,0 @@
|
|||||||
# EWMA [](https://godoc.org/github.com/VividCortex/ewma) 
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
This repo provides Exponentially Weighted Moving Average algorithms, or EWMAs for short, [based on our
|
|
||||||
Quantifying Abnormal Behavior talk](https://vividcortex.com/blog/2013/07/23/a-fast-go-library-for-exponential-moving-averages/).
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### Exponentially Weighted Moving Average
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
An exponentially weighted moving average is a way to continuously compute a type of
|
|
||||||
average for a series of numbers, as the numbers arrive. After a value in the series is
|
|
||||||
added to the average, its weight in the average decreases exponentially over time. This
|
|
||||||
biases the average towards more recent data. EWMAs are useful for several reasons, chiefly
|
|
||||||
their inexpensive computational and memory cost, as well as the fact that they represent
|
|
||||||
the recent central tendency of the series of values.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
The EWMA algorithm requires a decay factor, alpha. The larger the alpha, the more the average
|
|
||||||
is biased towards recent history. The alpha must be between 0 and 1, and is typically
|
|
||||||
a fairly small number, such as 0.04. We will discuss the choice of alpha later.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
The algorithm works thus, in pseudocode:
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
1. Multiply the next number in the series by alpha.
|
|
||||||
2. Multiply the current value of the average by 1 minus alpha.
|
|
||||||
3. Add the result of steps 1 and 2, and store it as the new current value of the average.
|
|
||||||
4. Repeat for each number in the series.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
There are special-case behaviors for how to initialize the current value, and these vary
|
|
||||||
between implementations. One approach is to start with the first value in the series;
|
|
||||||
another is to average the first 10 or so values in the series using an arithmetic average,
|
|
||||||
and then begin the incremental updating of the average. Each method has pros and cons.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
It may help to look at it pictorially. Suppose the series has five numbers, and we choose
|
|
||||||
alpha to be 0.50 for simplicity. Here's the series, with numbers in the neighborhood of 300.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
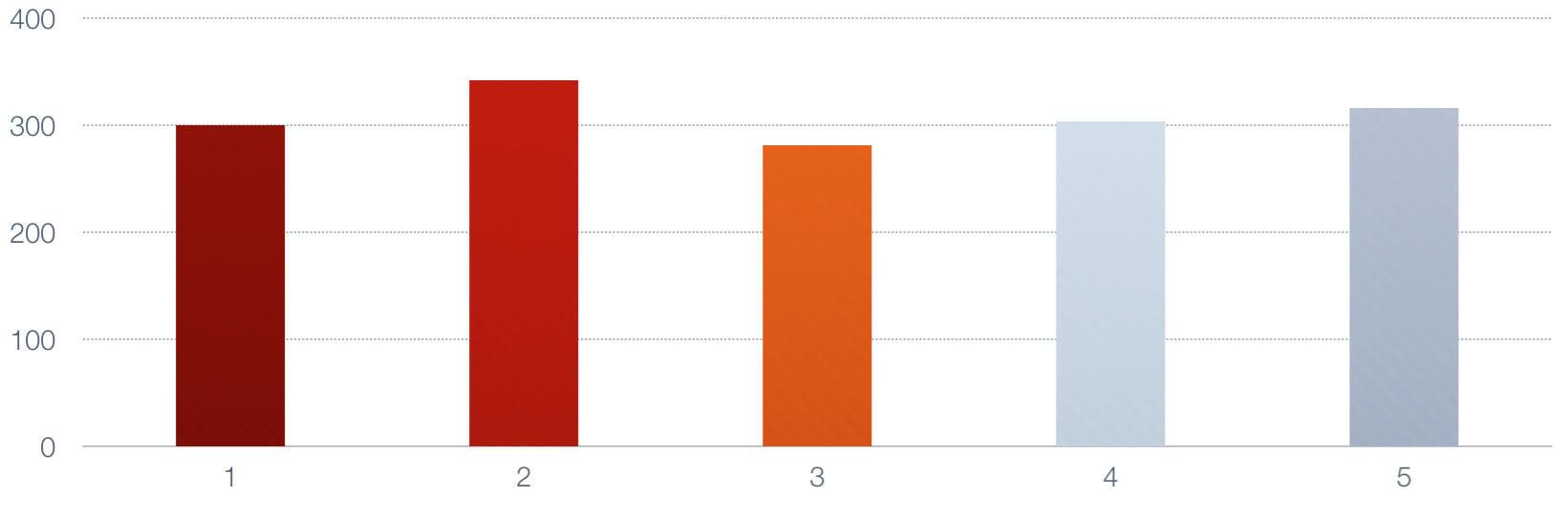
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Now let's take the moving average of those numbers. First we set the average to the value
|
|
||||||
of the first number.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
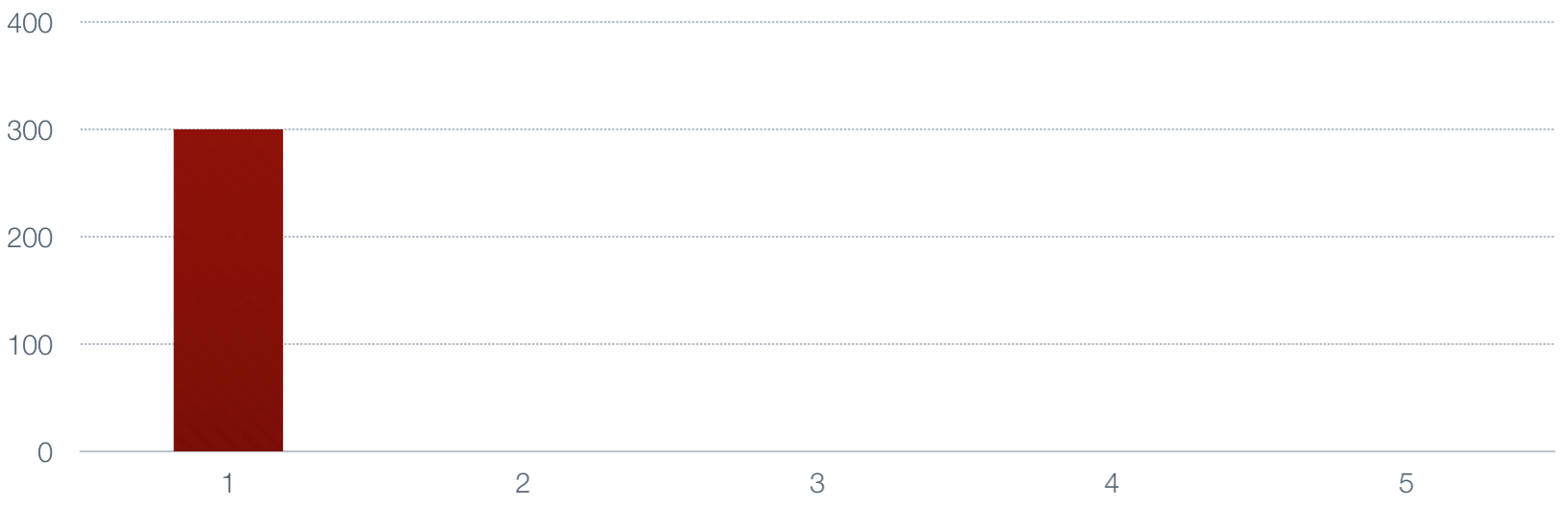
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Next we multiply the next number by alpha, multiply the current value by 1-alpha, and add
|
|
||||||
them to generate a new value.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
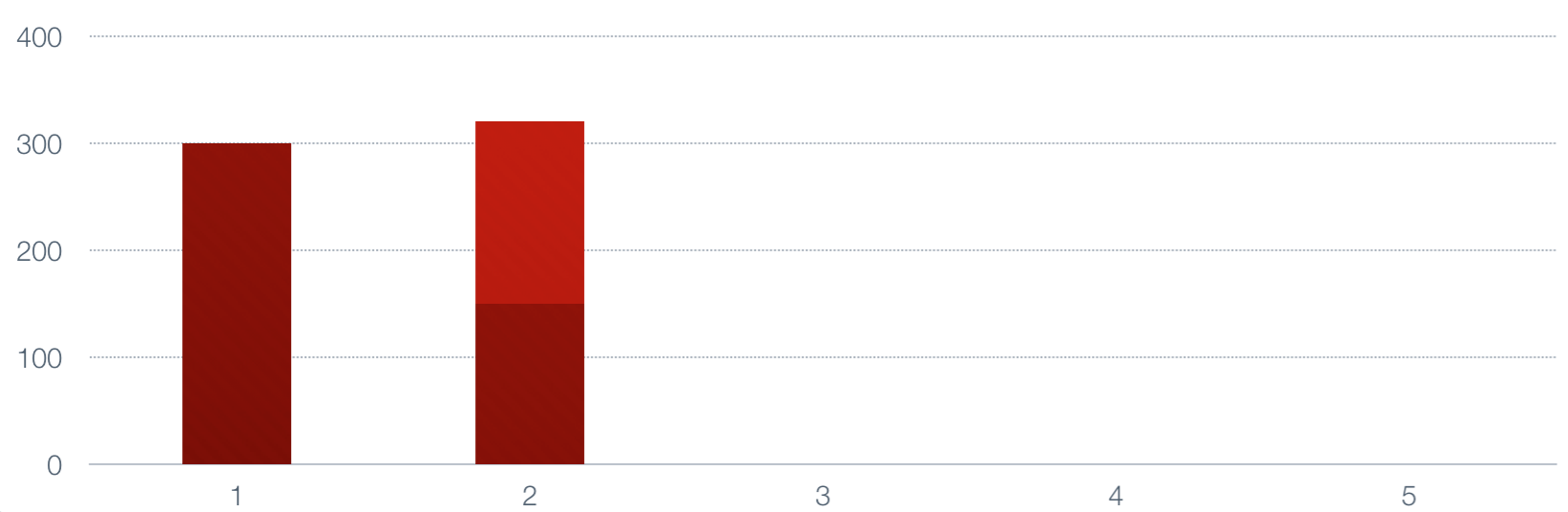
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
This continues until we are done.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
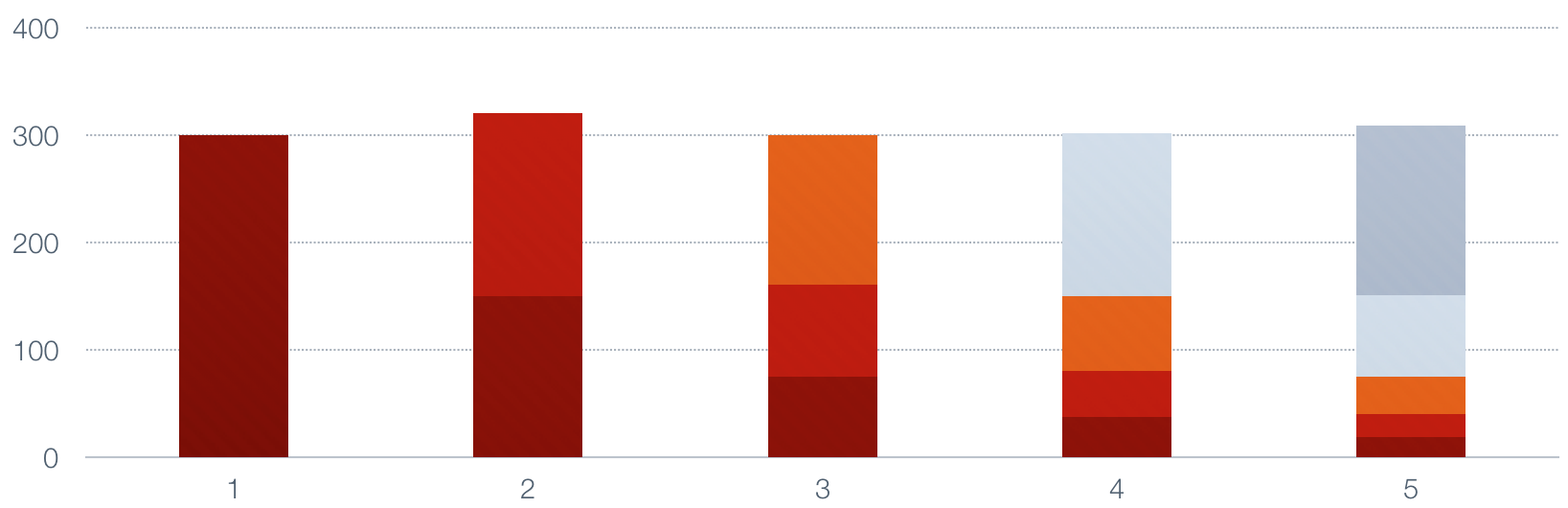
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Notice how each of the values in the series decays by half each time a new value
|
|
||||||
is added, and the top of the bars in the lower portion of the image represents the
|
|
||||||
size of the moving average. It is a smoothed, or low-pass, average of the original
|
|
||||||
series.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
For further reading, see [Exponentially weighted moving average](http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Moving_average#Exponential_moving_average) on wikipedia.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### Choosing Alpha
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Consider a fixed-size sliding-window moving average (not an exponentially weighted moving average)
|
|
||||||
that averages over the previous N samples. What is the average age of each sample? It is N/2.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Now suppose that you wish to construct a EWMA whose samples have the same average age. The formula
|
|
||||||
to compute the alpha required for this is: alpha = 2/(N+1). Proof is in the book
|
|
||||||
"Production and Operations Analysis" by Steven Nahmias.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
So, for example, if you have a time-series with samples once per second, and you want to get the
|
|
||||||
moving average over the previous minute, you should use an alpha of .032786885. This, by the way,
|
|
||||||
is the constant alpha used for this repository's SimpleEWMA.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### Implementations
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
This repository contains two implementations of the EWMA algorithm, with different properties.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
The implementations all conform to the MovingAverage interface, and the constructor returns
|
|
||||||
that type.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Current implementations assume an implicit time interval of 1.0 between every sample added.
|
|
||||||
That is, the passage of time is treated as though it's the same as the arrival of samples.
|
|
||||||
If you need time-based decay when samples are not arriving precisely at set intervals, then
|
|
||||||
this package will not support your needs at present.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
#### SimpleEWMA
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
A SimpleEWMA is designed for low CPU and memory consumption. It **will** have different behavior than the VariableEWMA
|
|
||||||
for multiple reasons. It has no warm-up period and it uses a constant
|
|
||||||
decay. These properties let it use less memory. It will also behave
|
|
||||||
differently when it's equal to zero, which is assumed to mean
|
|
||||||
uninitialized, so if a value is likely to actually become zero over time,
|
|
||||||
then any non-zero value will cause a sharp jump instead of a small change.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
#### VariableEWMA
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Unlike SimpleEWMA, this supports a custom age which must be stored, and thus uses more memory.
|
|
||||||
It also has a "warmup" time when you start adding values to it. It will report a value of 0.0
|
|
||||||
until you have added the required number of samples to it. It uses some memory to store the
|
|
||||||
number of samples added to it. As a result it uses a little over twice the memory of SimpleEWMA.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## Usage
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### API Documentation
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
View the GoDoc generated documentation [here](http://godoc.org/github.com/VividCortex/ewma).
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```go
|
|
||||||
package main
|
|
||||||
import "github.com/VividCortex/ewma"
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
func main() {
|
|
||||||
samples := [100]float64{
|
|
||||||
4599, 5711, 4746, 4621, 5037, 4218, 4925, 4281, 5207, 5203, 5594, 5149,
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
e := ewma.NewMovingAverage() //=> Returns a SimpleEWMA if called without params
|
|
||||||
a := ewma.NewMovingAverage(5) //=> returns a VariableEWMA with a decay of 2 / (5 + 1)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
for _, f := range samples {
|
|
||||||
e.Add(f)
|
|
||||||
a.Add(f)
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
e.Value() //=> 13.577404704631077
|
|
||||||
a.Value() //=> 1.5806140565521463e-12
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
```
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## Contributing
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
We only accept pull requests for minor fixes or improvements. This includes:
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
* Small bug fixes
|
|
||||||
* Typos
|
|
||||||
* Documentation or comments
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Please open issues to discuss new features. Pull requests for new features will be rejected,
|
|
||||||
so we recommend forking the repository and making changes in your fork for your use case.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## License
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
This repository is Copyright (c) 2013 VividCortex, Inc. All rights reserved.
|
|
||||||
It is licensed under the MIT license. Please see the LICENSE file for applicable license terms.
|
|
||||||
126
vendor/github.com/VividCortex/ewma/ewma.go
generated
vendored
126
vendor/github.com/VividCortex/ewma/ewma.go
generated
vendored
@ -1,126 +0,0 @@
|
|||||||
// Package ewma implements exponentially weighted moving averages.
|
|
||||||
package ewma
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
// Copyright (c) 2013 VividCortex, Inc. All rights reserved.
|
|
||||||
// Please see the LICENSE file for applicable license terms.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
const (
|
|
||||||
// By default, we average over a one-minute period, which means the average
|
|
||||||
// age of the metrics in the period is 30 seconds.
|
|
||||||
AVG_METRIC_AGE float64 = 30.0
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
// The formula for computing the decay factor from the average age comes
|
|
||||||
// from "Production and Operations Analysis" by Steven Nahmias.
|
|
||||||
DECAY float64 = 2 / (float64(AVG_METRIC_AGE) + 1)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
// For best results, the moving average should not be initialized to the
|
|
||||||
// samples it sees immediately. The book "Production and Operations
|
|
||||||
// Analysis" by Steven Nahmias suggests initializing the moving average to
|
|
||||||
// the mean of the first 10 samples. Until the VariableEwma has seen this
|
|
||||||
// many samples, it is not "ready" to be queried for the value of the
|
|
||||||
// moving average. This adds some memory cost.
|
|
||||||
WARMUP_SAMPLES uint8 = 10
|
|
||||||
)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
// MovingAverage is the interface that computes a moving average over a time-
|
|
||||||
// series stream of numbers. The average may be over a window or exponentially
|
|
||||||
// decaying.
|
|
||||||
type MovingAverage interface {
|
|
||||||
Add(float64)
|
|
||||||
Value() float64
|
|
||||||
Set(float64)
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
// NewMovingAverage constructs a MovingAverage that computes an average with the
|
|
||||||
// desired characteristics in the moving window or exponential decay. If no
|
|
||||||
// age is given, it constructs a default exponentially weighted implementation
|
|
||||||
// that consumes minimal memory. The age is related to the decay factor alpha
|
|
||||||
// by the formula given for the DECAY constant. It signifies the average age
|
|
||||||
// of the samples as time goes to infinity.
|
|
||||||
func NewMovingAverage(age ...float64) MovingAverage {
|
|
||||||
if len(age) == 0 || age[0] == AVG_METRIC_AGE {
|
|
||||||
return new(SimpleEWMA)
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
return &VariableEWMA{
|
|
||||||
decay: 2 / (age[0] + 1),
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
// A SimpleEWMA represents the exponentially weighted moving average of a
|
|
||||||
// series of numbers. It WILL have different behavior than the VariableEWMA
|
|
||||||
// for multiple reasons. It has no warm-up period and it uses a constant
|
|
||||||
// decay. These properties let it use less memory. It will also behave
|
|
||||||
// differently when it's equal to zero, which is assumed to mean
|
|
||||||
// uninitialized, so if a value is likely to actually become zero over time,
|
|
||||||
// then any non-zero value will cause a sharp jump instead of a small change.
|
|
||||||
// However, note that this takes a long time, and the value may just
|
|
||||||
// decays to a stable value that's close to zero, but which won't be mistaken
|
|
||||||
// for uninitialized. See http://play.golang.org/p/litxBDr_RC for example.
|
|
||||||
type SimpleEWMA struct {
|
|
||||||
// The current value of the average. After adding with Add(), this is
|
|
||||||
// updated to reflect the average of all values seen thus far.
|
|
||||||
value float64
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
// Add adds a value to the series and updates the moving average.
|
|
||||||
func (e *SimpleEWMA) Add(value float64) {
|
|
||||||
if e.value == 0 { // this is a proxy for "uninitialized"
|
|
||||||
e.value = value
|
|
||||||
} else {
|
|
||||||
e.value = (value * DECAY) + (e.value * (1 - DECAY))
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
// Value returns the current value of the moving average.
|
|
||||||
func (e *SimpleEWMA) Value() float64 {
|
|
||||||
return e.value
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
// Set sets the EWMA's value.
|
|
||||||
func (e *SimpleEWMA) Set(value float64) {
|
|
||||||
e.value = value
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
// VariableEWMA represents the exponentially weighted moving average of a series of
|
|
||||||
// numbers. Unlike SimpleEWMA, it supports a custom age, and thus uses more memory.
|
|
||||||
type VariableEWMA struct {
|
|
||||||
// The multiplier factor by which the previous samples decay.
|
|
||||||
decay float64
|
|
||||||
// The current value of the average.
|
|
||||||
value float64
|
|
||||||
// The number of samples added to this instance.
|
|
||||||
count uint8
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
// Add adds a value to the series and updates the moving average.
|
|
||||||
func (e *VariableEWMA) Add(value float64) {
|
|
||||||
switch {
|
|
||||||
case e.count < WARMUP_SAMPLES:
|
|
||||||
e.count++
|
|
||||||
e.value += value
|
|
||||||
case e.count == WARMUP_SAMPLES:
|
|
||||||
e.count++
|
|
||||||
e.value = e.value / float64(WARMUP_SAMPLES)
|
|
||||||
e.value = (value * e.decay) + (e.value * (1 - e.decay))
|
|
||||||
default:
|
|
||||||
e.value = (value * e.decay) + (e.value * (1 - e.decay))
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
// Value returns the current value of the average, or 0.0 if the series hasn't
|
|
||||||
// warmed up yet.
|
|
||||||
func (e *VariableEWMA) Value() float64 {
|
|
||||||
if e.count <= WARMUP_SAMPLES {
|
|
||||||
return 0.0
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
return e.value
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
// Set sets the EWMA's value.
|
|
||||||
func (e *VariableEWMA) Set(value float64) {
|
|
||||||
e.value = value
|
|
||||||
if e.count <= WARMUP_SAMPLES {
|
|
||||||
e.count = WARMUP_SAMPLES + 1
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
103
vendor/github.com/VividCortex/ewma/ewma_test.go
generated
vendored
103
vendor/github.com/VividCortex/ewma/ewma_test.go
generated
vendored
@ -1,103 +0,0 @@
|
|||||||
package ewma
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
// Copyright (c) 2013 VividCortex, Inc. All rights reserved.
|
|
||||||
// Please see the LICENSE file for applicable license terms.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
import (
|
|
||||||
"math"
|
|
||||||
"testing"
|
|
||||||
)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
const testMargin = 0.00000001
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
var samples = [100]float64{
|
|
||||||
4599, 5711, 4746, 4621, 5037, 4218, 4925, 4281, 5207, 5203, 5594, 5149,
|
|
||||||
4948, 4994, 6056, 4417, 4973, 4714, 4964, 5280, 5074, 4913, 4119, 4522,
|
|
||||||
4631, 4341, 4909, 4750, 4663, 5167, 3683, 4964, 5151, 4892, 4171, 5097,
|
|
||||||
3546, 4144, 4551, 6557, 4234, 5026, 5220, 4144, 5547, 4747, 4732, 5327,
|
|
||||||
5442, 4176, 4907, 3570, 4684, 4161, 5206, 4952, 4317, 4819, 4668, 4603,
|
|
||||||
4885, 4645, 4401, 4362, 5035, 3954, 4738, 4545, 5433, 6326, 5927, 4983,
|
|
||||||
5364, 4598, 5071, 5231, 5250, 4621, 4269, 3953, 3308, 3623, 5264, 5322,
|
|
||||||
5395, 4753, 4936, 5315, 5243, 5060, 4989, 4921, 4480, 3426, 3687, 4220,
|
|
||||||
3197, 5139, 6101, 5279,
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
func withinMargin(a, b float64) bool {
|
|
||||||
return math.Abs(a-b) <= testMargin
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
func TestSimpleEWMA(t *testing.T) {
|
|
||||||
var e SimpleEWMA
|
|
||||||
for _, f := range samples {
|
|
||||||
e.Add(f)
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
if !withinMargin(e.Value(), 4734.500946466118) {
|
|
||||||
t.Errorf("e.Value() is %v, wanted %v", e.Value(), 4734.500946466118)
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
e.Set(1.0)
|
|
||||||
if e.Value() != 1.0 {
|
|
||||||
t.Errorf("e.Value() is %d", e.Value())
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
func TestVariableEWMA(t *testing.T) {
|
|
||||||
e := NewMovingAverage(30)
|
|
||||||
for _, f := range samples {
|
|
||||||
e.Add(f)
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
if !withinMargin(e.Value(), 4734.500946466118) {
|
|
||||||
t.Errorf("e.Value() is %v, wanted %v", e.Value(), 4734.500946466118)
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
e.Set(1.0)
|
|
||||||
if e.Value() != 1.0 {
|
|
||||||
t.Errorf("e.Value() is %d", e.Value())
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
func TestVariableEWMA2(t *testing.T) {
|
|
||||||
e := NewMovingAverage(5)
|
|
||||||
for _, f := range samples {
|
|
||||||
e.Add(f)
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
if !withinMargin(e.Value(), 5015.397367486725) {
|
|
||||||
t.Errorf("e.Value() is %v, wanted %v", e.Value(), 5015.397367486725)
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
func TestVariableEWMAWarmup(t *testing.T) {
|
|
||||||
e := NewMovingAverage(5)
|
|
||||||
for i, f := range samples {
|
|
||||||
e.Add(f)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
// all values returned during warmup should be 0.0
|
|
||||||
if uint8(i) < WARMUP_SAMPLES {
|
|
||||||
if e.Value() != 0.0 {
|
|
||||||
t.Errorf("e.Value() is %v, expected %v", e.Value(), 0.0)
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
e = NewMovingAverage(5)
|
|
||||||
e.Set(5)
|
|
||||||
e.Add(1)
|
|
||||||
if e.Value() >= 5 {
|
|
||||||
t.Errorf("e.Value() is %d, expected it to decay towards 0", e.Value())
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
func TestVariableEWMAWarmup2(t *testing.T) {
|
|
||||||
e := NewMovingAverage(5)
|
|
||||||
testSamples := [12]float64{1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 10000, 1}
|
|
||||||
for i, f := range testSamples {
|
|
||||||
e.Add(f)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
// all values returned during warmup should be 0.0
|
|
||||||
if uint8(i) < WARMUP_SAMPLES {
|
|
||||||
if e.Value() != 0.0 {
|
|
||||||
t.Errorf("e.Value() is %v, expected %v", e.Value(), 0.0)
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
if val := e.Value(); val == 1.0 {
|
|
||||||
t.Errorf("e.Value() is expected to be greater than %v", 1.0)
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
Loading…
x
Reference in New Issue
Block a user