# Description
Removes the `NU_DISABLE_IR` option and some code related to evaluating
blocks with the AST
evaluator.
Does not entirely remove the AST evaluator yet. We still have some
dependencies on expression
evaluation in a few minor places which will take a little bit of effort
to fix.
Also changes `debug profile` to always include instructions, because the
output is a little
confusing otherwise, and removes the different options for
instructions/exprs.
# User-Facing Changes
- `NU_DISABLE_IR` no longer has any effect, and is removed. There is no
way to use the AST
evaluator.
- `debug profile` no longer has `--exprs`, `--instructions` options.
- `debug profile` lists `pc` and `instruction` columns by default now.
# Tests + Formatting
Eval tests fixed to only use IR.
# After Submitting
- [ ] release notes
- [ ] finish removing AST evaluator, come up with solutions for the
expression evaluation.
<!--
if this PR closes one or more issues, you can automatically link the PR
with
them by using one of the [*linking
keywords*](https://docs.github.com/en/issues/tracking-your-work-with-issues/linking-a-pull-request-to-an-issue#linking-a-pull-request-to-an-issue-using-a-keyword),
e.g.
- this PR should close #xxxx
- fixes #xxxx
you can also mention related issues, PRs or discussions!
-->
# Description
<!--
Thank you for improving Nushell. Please, check our [contributing
guide](../CONTRIBUTING.md) and talk to the core team before making major
changes.
Description of your pull request goes here. **Provide examples and/or
screenshots** if your changes affect the user experience.
-->
Bump version to `0.100.0`
# User-Facing Changes
The new release `v0.100.0` is coming...
# Description
Fixes: #14110Fixes: #14087
I think it's ok to not generating instruction to `def` and `export def`
call. Because they just return `PipelineData::Empty` without doing
anything.
If nushell generates instructions for `def` and `export def`, nushell
will try to capture variables for these block. It's not the time to do
this.
# User-Facing Changes
```
nu -c "
def bar [] {
let x = 1
($x | foo)
}
def foo [] {
foo
}
"
```
Will no longer raise error.
# Tests + Formatting
Added 4 tests
# Description
This PR adds an indicator when listing subcommands. That indicator tells
whether the command is a plugin, alias, or custom_command.

I changed some of the API to make this work a little easier, namely
`get_signatures()` is now `get_signatures_and_declids()`. It was used in
only one other place (run-external), so I thought it was fine to change
it.
There is a long-standing issue with aliases where they reference the
command name instead of the alias name. This PR doesn't fix that bug.
Example.
```nushell
❯ alias "str fill" = str wrap
```
```nushell
❯ str
... other stuff
Subcommands:
str wrap (alias) - Alias for `str wrap`
str wrap (plugin) - Wrap text passed into pipeline.
```
# User-Facing Changes
Slightly different output of subcommands.
# Description
This PR adds a couple more options for dealing with try/catch errors. It
adds a `json` version of the error and a `rendered` version of the
error. It also respects the error_style configuration point.

# User-Facing Changes
<!-- List of all changes that impact the user experience here. This
helps us keep track of breaking changes. -->
# Tests + Formatting
<!--
Don't forget to add tests that cover your changes.
Make sure you've run and fixed any issues with these commands:
- `cargo fmt --all -- --check` to check standard code formatting (`cargo
fmt --all` applies these changes)
- `cargo clippy --workspace -- -D warnings -D clippy::unwrap_used` to
check that you're using the standard code style
- `cargo test --workspace` to check that all tests pass (on Windows make
sure to [enable developer
mode](https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/apps/get-started/developer-mode-features-and-debugging))
- `cargo run -- -c "use toolkit.nu; toolkit test stdlib"` to run the
tests for the standard library
> **Note**
> from `nushell` you can also use the `toolkit` as follows
> ```bash
> use toolkit.nu # or use an `env_change` hook to activate it
automatically
> toolkit check pr
> ```
-->
# After Submitting
<!-- If your PR had any user-facing changes, update [the
documentation](https://github.com/nushell/nushell.github.io) after the
PR is merged, if necessary. This will help us keep the docs up to date.
-->
# Description
This PR adds a couple more options for dealing with try/catch errors. It
adds a `json` version of the error and a `rendered` version of the
error. It also respects the error_style configuration point.

# User-Facing Changes
<!-- List of all changes that impact the user experience here. This
helps us keep track of breaking changes. -->
# Tests + Formatting
<!--
Don't forget to add tests that cover your changes.
Make sure you've run and fixed any issues with these commands:
- `cargo fmt --all -- --check` to check standard code formatting (`cargo
fmt --all` applies these changes)
- `cargo clippy --workspace -- -D warnings -D clippy::unwrap_used` to
check that you're using the standard code style
- `cargo test --workspace` to check that all tests pass (on Windows make
sure to [enable developer
mode](https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/apps/get-started/developer-mode-features-and-debugging))
- `cargo run -- -c "use toolkit.nu; toolkit test stdlib"` to run the
tests for the standard library
> **Note**
> from `nushell` you can also use the `toolkit` as follows
> ```bash
> use toolkit.nu # or use an `env_change` hook to activate it
automatically
> toolkit check pr
> ```
-->
# After Submitting
<!-- If your PR had any user-facing changes, update [the
documentation](https://github.com/nushell/nushell.github.io) after the
PR is merged, if necessary. This will help us keep the docs up to date.
-->
<!--
if this PR closes one or more issues, you can automatically link the PR
with
them by using one of the [*linking
keywords*](https://docs.github.com/en/issues/tracking-your-work-with-issues/linking-a-pull-request-to-an-issue#linking-a-pull-request-to-an-issue-using-a-keyword),
e.g.
- this PR should close #xxxx
- fixes #xxxx
you can also mention related issues, PRs or discussions!
-->
# Description
<!--
Thank you for improving Nushell. Please, check our [contributing
guide](../CONTRIBUTING.md) and talk to the core team before making major
changes.
Description of your pull request goes here. **Provide examples and/or
screenshots** if your changes affect the user experience.
-->
# User-Facing Changes
<!-- List of all changes that impact the user experience here. This
helps us keep track of breaking changes. -->
# Tests + Formatting
<!--
Don't forget to add tests that cover your changes.
Make sure you've run and fixed any issues with these commands:
- `cargo fmt --all -- --check` to check standard code formatting (`cargo
fmt --all` applies these changes)
- `cargo clippy --workspace -- -D warnings -D clippy::unwrap_used` to
check that you're using the standard code style
- `cargo test --workspace` to check that all tests pass (on Windows make
sure to [enable developer
mode](https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/apps/get-started/developer-mode-features-and-debugging))
- `cargo run -- -c "use toolkit.nu; toolkit test stdlib"` to run the
tests for the standard library
> **Note**
> from `nushell` you can also use the `toolkit` as follows
> ```bash
> use toolkit.nu # or use an `env_change` hook to activate it
automatically
> toolkit check pr
> ```
-->
# After Submitting
<!-- If your PR had any user-facing changes, update [the
documentation](https://github.com/nushell/nushell.github.io) after the
PR is merged, if necessary. This will help us keep the docs up to date.
-->
# Description
Fixes#13991. This was done by more clearly separating the case when a
pipeline is drained vs when it is being written (to a file).
I also added an `OutDest::Print` case which might not be strictly
necessary, but is a helpful addition.
# User-Facing Changes
Bug fix.
# Tests + Formatting
Added a test.
# After Submitting
There are still a few redirection bugs that I found, but they require
larger code changes, so I'll leave them until after the release.
# Description
Fixes a small side-issue in #10977 - If a command flag didn't have a
comment/description, it would still show an unnecessary separator at the
end of the line.
This fixes that, plus uses the `: ` (colon) to separate the flag from
the description. This aligns with the way that named parameters are
handled.
# User-Facing Changes
Help/doc only
# Tests + Formatting
- 🟢 `toolkit fmt`
- 🟢 `toolkit clippy`
- 🟢 `toolkit test`
- 🟢 `toolkit test stdlib`
# After Submitting
N/A
# Description
Title says it all, changes `EngineState::get_env_var` to return a
`Option<&'a Value>` instead of an owned `Option<Value>`. This avoids
some unnecessary clones.
I also made a similar change to the `PluginExecutionContext` trait.
# Description
In the PR #13832 I used some newtypes for the old IDs. `SpanId` and
`RegId` already used newtypes, to streamline the code, I made them into
the same style as the other marker-based IDs.
Since `RegId` should be a bit smaller (it uses a `u32` instead of
`usize`) according to @devyn, I made the `Id` type generic with `usize`
as the default inner value.
The question still stands how `Display` should be implemented if even.
# User-Facing Changes
Users of the internal values of `RegId` or `SpanId` have breaking
changes but who outside nushell itself even uses these?
# After Submitting
The IDs will be streamlined and all type-safe.
# Description
In this PR I replaced most of the raw usize IDs with
[newtypes](https://doc.rust-lang.org/rust-by-example/generics/new_types.html).
Some other IDs already started using new types and in this PR I did not
want to touch them. To make the implementation less repetitive, I made
use of a generic `Id<T>` with marker structs. If this lands I would try
to move make other IDs also in this pattern.
Also at some places I needed to use `cast`, I'm not sure if the type was
incorrect and therefore casting not needed or if actually different ID
types intermingle sometimes.
# User-Facing Changes
Probably few, if you got a `DeclId` via a function and placed it later
again it will still work.
# Description
Partialy addresses #13868. `try` does not catch non-zero exit code
errors from the last command in a pipeline if the result is assigned to
a variable using `let` (or `mut`).
This was fixed by adding a new `OutDest::Value` case. This is used when
the pipeline is in a "value" position. I.e., it will be collected into a
value. This ended up replacing most of the usages of `OutDest::Capture`.
So, this PR also renames `OutDest::Capture` to `OutDest::PipeSeparate`
to better fit the few remaining use cases for it.
# User-Facing Changes
Bug fix.
# Tests + Formatting
Added two tests.
# Description
Fixes a bug with `set_last_error()` introduced by @IanManske not being
called during the jump to an error handler in IR eval. Without this,
`$env.LAST_EXIT_CODE` wasn't getting set in the `catch` block for an
external.
# Tests + Formatting
Added a `tests/eval` test to cover this in both IR and non-IR eval
# Description
This fixes a couple of remaining differences between the IR evaluator's
handling of env vars and the AST evaluator's handling of env vars.
Blocker for #13718 (this is why those tests failed)
# User-Facing Changes
1. Handles checking overlays for hidden env vars properly, when getting
an env var from IR instruction
2. Updates config properly when doing `redirect_env()` (these probably
shouldn't be separate functions anyway, though, they're basically the
same. I did this because I intended to remove one, but now it's just
like that)
# Tests + Formatting
The `nu_repl` testbin now handles `NU_USE_IR` properly, so these tests
now work as expected.
# After Submitting
- [ ] check in on #13718 again
# Description
Fixes a bug in the IR for `try` to match that of the regular evaluator
(continuing from #13515):
```nushell
# without IR:
try { ^false } catch { 'caught' } # == 'caught'
# with IR:
try { ^false } catch { 'caught' } # error, non-zero exit code
```
In this PR, both now evaluate to `caught`. For the implementation, I had
to add another instruction, and feel free to suggest better
alternatives. In the future, it might be possible to get rid of this
extra instruction.
# User-Facing Changes
Bug fix, `try { ^false } catch { 'caught' }` now works in IR.
# Description
This PR makes it so that non-zero exit codes and termination by signal
are treated as a normal `ShellError`. Currently, these are silent
errors. That is, if an external command fails, then it's code block is
aborted, but the parent block can sometimes continue execution. E.g.,
see #8569 and this example:
```nushell
[1 2] | each { ^false }
```
Before this would give:
```
╭───┬──╮
│ 0 │ │
│ 1 │ │
╰───┴──╯
```
Now, this shows an error:
```
Error: nu:🐚:eval_block_with_input
× Eval block failed with pipeline input
╭─[entry #1:1:2]
1 │ [1 2] | each { ^false }
· ┬
· ╰── source value
╰────
Error: nu:🐚:non_zero_exit_code
× External command had a non-zero exit code
╭─[entry #1:1:17]
1 │ [1 2] | each { ^false }
· ──┬──
· ╰── exited with code 1
╰────
```
This PR fixes#12874, fixes#5960, fixes#10856, and fixes#5347. This
PR also partially addresses #10633 and #10624 (only the last command of
a pipeline is currently checked). It looks like #8569 is already fixed,
but this PR will make sure it is definitely fixed (fixes#8569).
# User-Facing Changes
- Non-zero exit codes and termination by signal now cause an error to be
thrown.
- The error record value passed to a `catch` block may now have an
`exit_code` column containing the integer exit code if the error was due
to an external command.
- Adds new config values, `display_errors.exit_code` and
`display_errors.termination_signal`, which determine whether an error
message should be printed in the respective error cases. For
non-interactive sessions, these are set to `true`, and for interactive
sessions `display_errors.exit_code` is false (via the default config).
# Tests
Added a few tests.
# After Submitting
- Update docs and book.
- Future work:
- Error if other external commands besides the last in a pipeline exit
with a non-zero exit code. Then, deprecate `do -c` since this will be
the default behavior everywhere.
- Add a better mechanism for exit codes and deprecate
`$env.LAST_EXIT_CODE` (it's buggy).
# Description
`cargo` somewhat recently gained the capability to store `lints`
settings for the crate and workspace, that can override the defaults
from `rustc` and `clippy` lints. This means we can enforce some lints
without having to actively pass them to clippy via `cargo clippy -- -W
...`. So users just forking the repo have an easier time to follow
similar requirements like our CI.
## Limitation
An exception that remains is that those lints apply to both the primary
code base and the tests. Thus we can't include e.g. `unwrap_used`
without generating noise in the tests. Here the setup in the CI remains
the most helpful.
## Included lints
- Add `clippy::unchecked_duration_subtraction` (added by #12549)
# User-Facing Changes
Running `cargo clippy --workspace` should be closer to the CI. This has
benefits for editor configured runs of clippy and saves you from having
to use `toolkit` to be close to CI in more cases.
# Description
<!--
Thank you for improving Nushell. Please, check our [contributing
guide](../CONTRIBUTING.md) and talk to the core team before making major
changes.
Description of your pull request goes here. **Provide examples and/or
screenshots** if your changes affect the user experience.
-->
Currently the parser and the documentation generation use the signature
of the command, which means that it doesn't pick up on the changed name
of the `main` block, and therefore shows the name of the command as
"main" and doesn't find the subcommands. This PR changes the
aforementioned places to use the block signature to fix these issues.
This closes#13397. Incidentally it also causes input/output types to be
shown in the help, which is kinda pointless for scripts since they don't
operate on structured data but maybe not worth the effort to remove.
# User-Facing Changes
<!-- List of all changes that impact the user experience here. This
helps us keep track of breaking changes. -->
```
# example.nu
export def main [] { help main }
export def 'main sub' [] { print 'sub' }
```
Before:
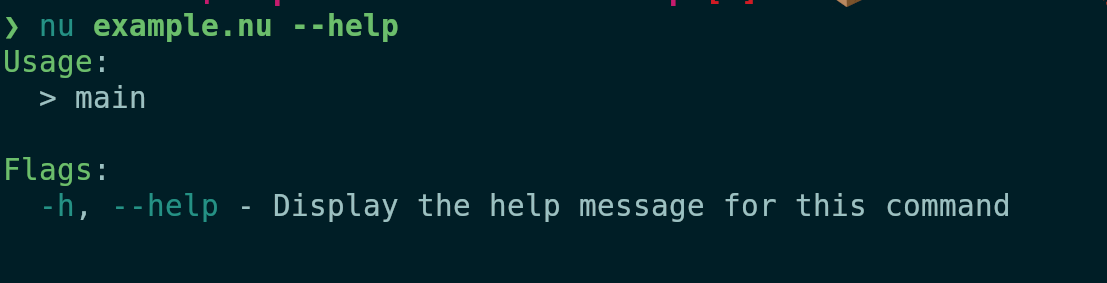

After:
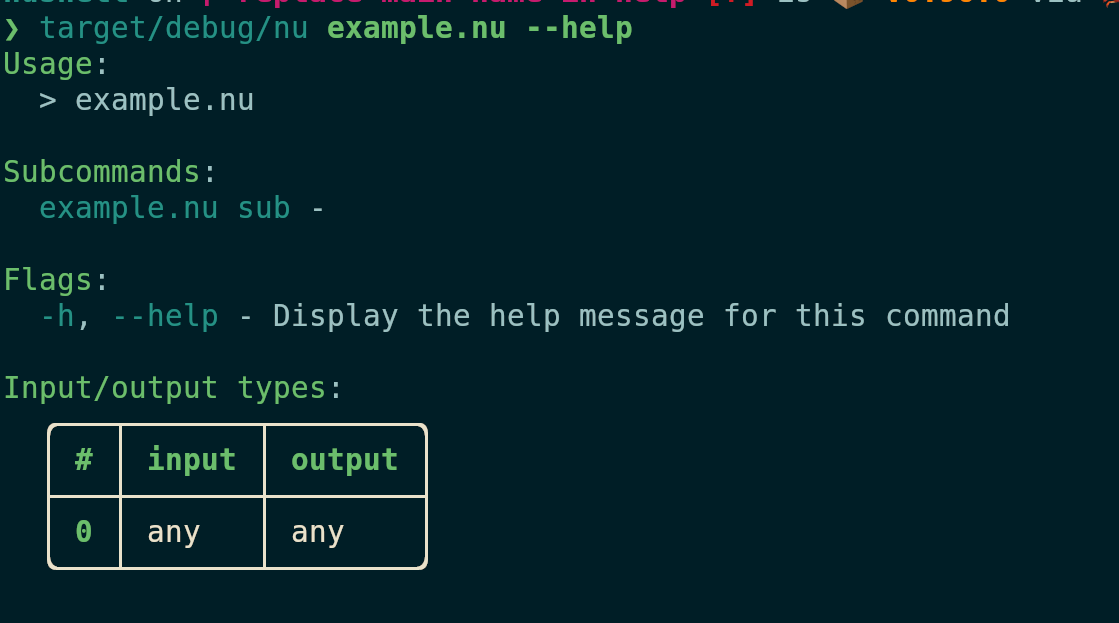
# Tests
<!--
Don't forget to add tests that cover your changes.
Make sure you've run and fixed any issues with these commands:
- `cargo fmt --all -- --check` to check standard code formatting (`cargo
fmt --all` applies these changes)
- `cargo clippy --workspace -- -D warnings -D clippy::unwrap_used` to
check that you're using the standard code style
- `cargo test --workspace` to check that all tests pass (on Windows make
sure to [enable developer
mode](https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/apps/get-started/developer-mode-features-and-debugging))
- `cargo run -- -c "use toolkit.nu; toolkit test stdlib"` to run the
tests for the standard library
> **Note**
> from `nushell` you can also use the `toolkit` as follows
> ```bash
> use toolkit.nu # or use an `env_change` hook to activate it
automatically
> toolkit check pr
> ```
-->
Tests are still missing for the subcommands and the input/output types
---------
Co-authored-by: Stefan Holderbach <sholderbach@users.noreply.github.com>
# Description
The meaning of the word usage is specific to describing how a command
function is *used* and not a synonym for general description. Usage can
be used to describe the SYNOPSIS or EXAMPLES sections of a man page
where the permitted argument combinations are shown or example *uses*
are given.
Let's not confuse people and call it what it is a description.
Our `help` command already creates its own *Usage* section based on the
available arguments and doesn't refer to the description with usage.
# User-Facing Changes
`help commands` and `scope commands` will now use `description` or
`extra_description`
`usage`-> `description`
`extra_usage` -> `extra_description`
Breaking change in the plugin protocol:
In the signature record communicated with the engine.
`usage`-> `description`
`extra_usage` -> `extra_description`
The same rename also takes place for the methods on
`SimplePluginCommand` and `PluginCommand`
# Tests + Formatting
- Updated plugin protocol specific changes
# After Submitting
- [ ] update plugin protocol doc
# Description
This seems to be a minor copy paste mistake. cc @Embers-of-the-Fire
Followup to #13526
# User-Facing Changes
(-)
# Tests + Formatting
(-)
- **Suggested default impl for the new `*Stack`s**
- **Change a hashmap to make clippy happy**
- **Clone from fix**
- **Fix conditional unused in test**
- then **Bump rust toolchain**
# Description
Seems like I developed a bit of a bad habit of trying to link
```rust
/// [`.foo()`]
```
in docstrings, and this just doesn't work automatically; you have to do
```rust
/// [`.foo()`](Self::foo)
```
if you want it to actually link. I think I found and replaced all of
these.
# User-Facing Changes
Just docs.
# Description
[Discovered](https://discord.com/channels/601130461678272522/614593951969574961/1266503282554179604)
by `@warp` on Discord.
The IR compiler was not properly setting redirect modes for
subexpressions because `FullCellPath` was always being compiled with
capture-out redirection. This is the correct behavior if there is a tail
to the `FullCellPath`, as we need the value in order to try to extract
anything from it (although this is unlikely to work) - however, the
parser also generates `FullCellPath`s with an empty tail quite often,
including for bare subexpressions.
Because of this, the following did not behave as expected:
```nushell
(docker run -it --rm alpine)
```
Capturing the output meant that `docker` didn't have direct access to
the terminal as a TTY.
As this is a minor bug fix, it should be okay to include in the 0.96.1
patch release.
# User-Facing Changes
- Fixes the bug as described when running with IR evaluation enabled.
# Tests + Formatting
I added a test for this, though we're not currently running all tests
with IR on the CI, but it should ensure this behaviour is consistent.
The equivalent minimum repro I could find was:
```nushell
(nu --testbin cococo); null
```
as this should cause the `cococo` message to appear on stdout, and if
Nushell is capturing the output, it would be discarded instead.
# Description
This grew quite a bit beyond its original scope, but I've tried to make
`$in` a bit more consistent and easier to work with.
Instead of the parser generating calls to `collect` and creating
closures, this adds `Expr::Collect` which just evaluates in the same
scope and doesn't require any closure.
When `$in` is detected in an expression, it is replaced with a new
variable (also called `$in`) and wrapped in `Expr::Collect`. During
eval, this expression is evaluated directly, with the input and with
that new variable set to the collected value.
Other than being faster and less prone to gotchas, it also makes it
possible to typecheck the output of an expression containing `$in`,
which is nice. This is a breaking change though, because of the lack of
the closure and because now typechecking will actually happen. Also, I
haven't attempted to typecheck the input yet.
The IR generated now just looks like this:
```gas
collect %in
clone %tmp, %in
store-variable $in, %tmp
# %out <- ...expression... <- %in
drop-variable $in
```
(where `$in` is the local variable created for this collection, and not
`IN_VARIABLE_ID`)
which is a lot better than having to create a closure and call `collect
--keep-env`, dealing with all of the capture gathering and allocation
that entails. Ideally we can also detect whether that input is actually
needed, so maybe we don't have to clone, but I haven't tried to do that
yet. Theoretically now that the variable is a unique one every time, it
should be possible to give it a type - I just don't know how to
determine that yet.
On top of that, I've also reworked how `$in` works in pipeline-initial
position. Previously, it was a little bit inconsistent. For example,
this worked:
```nushell
> 3 | do { let x = $in; let y = $in; print $x $y }
3
3
```
However, this causes a runtime variable not found error on the second
`$in`:
```nushell
> def foo [] { let x = $in; let y = $in; print $x $y }; 3 | foo
Error: nu:🐚:variable_not_found
× Variable not found
╭─[entry #115:1:35]
1 │ def foo [] { let x = $in; let y = $in; print $x $y }; 3 | foo
· ─┬─
· ╰── variable not found
╰────
```
I've fixed this by making the first element `$in` detection *always*
happen at the block level, so if you use `$in` in pipeline-initial
position anywhere in a block, it will collect with an implicit
subexpression around the whole thing, and you can then use that `$in`
more than once. In doing this I also rewrote `parse_pipeline()` and
hopefully it's a bit more straightforward and possibly more efficient
too now.
Finally, I've tried to make `let` and `mut` a lot more straightforward
with how they handle the rest of the pipeline, and using a redirection
with `let`/`mut` now does what you'd expect if you assume that they
consume the whole pipeline - the redirection is just processed as
normal. These both work now:
```nushell
let x = ^foo err> err.txt
let y = ^foo out+err>| str length
```
It was previously possible to accomplish this with a subexpression, but
it just seemed like a weird gotcha that you couldn't do it. Intuitively,
`let` and `mut` just seem to take the whole line.
- closes#13137
# User-Facing Changes
- `$in` will behave more consistently with blocks and closures, since
the entire block is now just wrapped to handle it if it appears in the
first pipeline element
- `$in` no longer creates a closure, so what can be done within an
expression containing `$in` is less restrictive
- `$in` containing expressions are now type checked, rather than just
resulting in `any`. However, `$in` itself is still `any`, so this isn't
quite perfect yet
- Redirections are now allowed in `let` and `mut` and behave pretty much
how you'd expect
# Tests + Formatting
Added tests to cover the new behaviour.
# After Submitting
- [ ] release notes (definitely breaking change)
# Description
Add `README.md` files to each crate in our workspace (-plugins) and also
include it in the `lib.rs` documentation for <docs.rs> (if there is no
existing `lib.rs` crate documentation)
In all new README I added the defensive comment that the crates are not
considered stable for public consumption. If necessary we can adjust
this if we deem a crate useful for plugin authors.
# Description
This adds tracing for each individual instruction to the `Debugger`
trait. Register contents can be inspected both when entering and leaving
an instruction, and if an instruction produced an error, a reference to
the error is also available. It's not the full `EvalContext` but it's
most of the important parts for getting an idea of what's going on.
Added support for all of this to the `Profiler` / `debug profile` as
well, and the output is quite incredible - super verbose, but you can
see every instruction that's executed and also what the result was if
it's an instruction that has a clearly defined output (many do).
# User-Facing Changes
- Added `--instructions` to `debug profile`, which adds the `pc` and
`instruction` columns to the output.
- `--expr` only works in AST mode, and `--instructions` only works in IR
mode. In the wrong mode, the output for those columns is just blank.
# Tests + Formatting
All passing.
# After Submitting
- [ ] release notes
# Description
Follow up fix to #13332, so that changes to config when running under IR
actually happen as well. Since I merged them around the same time, I
forgot about this.
# Description
Allows `Stack` to have a modified local `Config`, which is updated
immediately when `$env.config` is assigned to. This means that even
within a script, commands that come after `$env.config` changes will
always see those changes in `Stack::get_config()`.
Also fixed a lot of cases where `engine_state.get_config()` was used
even when `Stack` was available.
Closes#13324.
# User-Facing Changes
- Config changes apply immediately after the assignment is executed,
rather than whenever config is read by a command that needs it.
- Potentially slower performance when executing a lot of lines that
change `$env.config` one after another. Recommended to get `$env.config`
into a `mut` variable first and do modifications, then assign it back.
- Much faster performance when executing a script that made
modifications to `$env.config`, as the changes are only parsed once.
# Tests + Formatting
All passing.
# After Submitting
- [ ] release notes
# Description
Was having an issue compiling main after the IR pr. Talked to devyn and
he led me to change a couple things real quick and we're compiling once
again.
# Description
This is another easy performance lift that just changes `env_vars` and
`env_hidden` on `Stack` to use `Arc`. I noticed that these were being
cloned on essentially every closure invocation during captures
gathering, so we're paying the cost for all of that even when we don't
change anything. On top of that, for `env_vars`, there's actually an
entirely fresh `HashMap` created for each child scope, so it's highly
unlikely that we'll modify the parent ones.
Uses `Arc::make_mut` instead to take care of things when we need to
mutate something, and most of the time nothing has to be cloned at all.
# Benchmarks
The benefits are greater the more calls there are to env-cloning
functions like `captures_to_stack()`. Calling custom commands in a loop
is basically best case for a performance improvement. Plain `each` with
a literal block isn't so badly affected because the stack is set up
once.
## random_bytes.nu
```nushell
use std bench
do {
const SCRIPT = ../nu_scripts/benchmarks/random-bytes.nu
let before_change = bench { nu $SCRIPT }
let after_change = bench { target/release/nu $SCRIPT }
{
before: ($before_change | reject times),
after: ($after_change | reject times)
}
}
```
```
╭────────┬──────────────────────────────╮
│ │ ╭──────┬───────────────────╮ │
│ before │ │ mean │ 603ms 759µs 727ns │ │
│ │ │ min │ 593ms 298µs 167ns │ │
│ │ │ max │ 648ms 612µs 291ns │ │
│ │ │ std │ 9ms 335µs 251ns │ │
│ │ ╰──────┴───────────────────╯ │
│ │ ╭──────┬───────────────────╮ │
│ after │ │ mean │ 518ms 400µs 557ns │ │
│ │ │ min │ 507ms 762µs 583ns │ │
│ │ │ max │ 566ms 695µs 166ns │ │
│ │ │ std │ 9ms 554µs 767ns │ │
│ │ ╰──────┴───────────────────╯ │
╰────────┴──────────────────────────────╯
```
## gradient_benchmark_no_check.nu
```nushell
use std bench
do {
const SCRIPT = ../nu_scripts/benchmarks/gradient_benchmark_no_check.nu
let before_change = bench { nu $SCRIPT }
let after_change = bench { target/release/nu $SCRIPT }
{
before: ($before_change | reject times),
after: ($after_change | reject times)
}
}
```
```
╭────────┬──────────────────────────────╮
│ │ ╭──────┬───────────────────╮ │
│ before │ │ mean │ 146ms 543µs 380ns │ │
│ │ │ min │ 142ms 416µs 166ns │ │
│ │ │ max │ 189ms 595µs │ │
│ │ │ std │ 7ms 140µs 342ns │ │
│ │ ╰──────┴───────────────────╯ │
│ │ ╭──────┬───────────────────╮ │
│ after │ │ mean │ 134ms 211µs 678ns │ │
│ │ │ min │ 132ms 433µs 125ns │ │
│ │ │ max │ 135ms 722µs 583ns │ │
│ │ │ std │ 793µs 134ns │ │
│ │ ╰──────┴───────────────────╯ │
╰────────┴──────────────────────────────╯
```
# User-Facing Changes
Better performance, particularly for custom commands, especially if
there are a lot of environment variables. Nothing else.
# Tests + Formatting
All passing.
# Description
This PR adds an internal representation language to Nushell, offering an
alternative evaluator based on simple instructions, stream-containing
registers, and indexed control flow. The number of registers required is
determined statically at compile-time, and the fixed size required is
allocated upon entering the block.
Each instruction is associated with a span, which makes going backwards
from IR instructions to source code very easy.
Motivations for IR:
1. **Performance.** By simplifying the evaluation path and making it
more cache-friendly and branch predictor-friendly, code that does a lot
of computation in Nushell itself can be sped up a decent bit. Because
the IR is fairly easy to reason about, we can also implement
optimization passes in the future to eliminate and simplify code.
2. **Correctness.** The instructions mostly have very simple and
easily-specified behavior, so hopefully engine changes are a little bit
easier to reason about, and they can be specified in a more formal way
at some point. I have made an effort to document each of the
instructions in the docs for the enum itself in a reasonably specific
way. Some of the errors that would have happened during evaluation
before are now moved to the compilation step instead, because they don't
make sense to check during evaluation.
3. **As an intermediate target.** This is a good step for us to bring
the [`new-nu-parser`](https://github.com/nushell/new-nu-parser) in at
some point, as code generated from new AST can be directly compared to
code generated from old AST. If the IR code is functionally equivalent,
it will behave the exact same way.
4. **Debugging.** With a little bit more work, we can probably give
control over advancing the virtual machine that `IrBlock`s run on to
some sort of external driver, making things like breakpoints and single
stepping possible. Tools like `view ir` and [`explore
ir`](https://github.com/devyn/nu_plugin_explore_ir) make it easier than
before to see what exactly is going on with your Nushell code.
The goal is to eventually replace the AST evaluator entirely, once we're
sure it's working just as well. You can help dogfood this by running
Nushell with `$env.NU_USE_IR` set to some value. The environment
variable is checked when Nushell starts, so config runs with IR, or it
can also be set on a line at the REPL to change it dynamically. It is
also checked when running `do` in case within a script you want to just
run a specific piece of code with or without IR.
# Example
```nushell
view ir { |data|
mut sum = 0
for n in $data {
$sum += $n
}
$sum
}
```
```gas
# 3 registers, 19 instructions, 0 bytes of data
0: load-literal %0, int(0)
1: store-variable var 904, %0 # let
2: drain %0
3: drop %0
4: load-variable %1, var 903
5: iterate %0, %1, end 15 # for, label(1), from(14:)
6: store-variable var 905, %0
7: load-variable %0, var 904
8: load-variable %2, var 905
9: binary-op %0, Math(Plus), %2
10: span %0
11: store-variable var 904, %0
12: load-literal %0, nothing
13: drain %0
14: jump 5
15: drop %0 # label(0), from(5:)
16: drain %0
17: load-variable %0, var 904
18: return %0
```
# Benchmarks
All benchmarks run on a base model Mac Mini M1.
## Iterative Fibonacci sequence
This is about as best case as possible, making use of the much faster
control flow. Most code will not experience a speed improvement nearly
this large.
```nushell
def fib [n: int] {
mut a = 0
mut b = 1
for _ in 2..=$n {
let c = $a + $b
$a = $b
$b = $c
}
$b
}
use std bench
bench { 0..50 | each { |n| fib $n } }
```
IR disabled:
```
╭───────┬─────────────────╮
│ mean │ 1ms 924µs 665ns │
│ min │ 1ms 700µs 83ns │
│ max │ 3ms 450µs 125ns │
│ std │ 395µs 759ns │
│ times │ [list 50 items] │
╰───────┴─────────────────╯
```
IR enabled:
```
╭───────┬─────────────────╮
│ mean │ 452µs 820ns │
│ min │ 427µs 417ns │
│ max │ 540µs 167ns │
│ std │ 17µs 158ns │
│ times │ [list 50 items] │
╰───────┴─────────────────╯
```

##
[gradient_benchmark_no_check.nu](https://github.com/nushell/nu_scripts/blob/main/benchmarks/gradient_benchmark_no_check.nu)
IR disabled:
```
╭───┬──────────────────╮
│ 0 │ 27ms 929µs 958ns │
│ 1 │ 21ms 153µs 459ns │
│ 2 │ 18ms 639µs 666ns │
│ 3 │ 19ms 554µs 583ns │
│ 4 │ 13ms 383µs 375ns │
│ 5 │ 11ms 328µs 208ns │
│ 6 │ 5ms 659µs 542ns │
╰───┴──────────────────╯
```
IR enabled:
```
╭───┬──────────────────╮
│ 0 │ 22ms 662µs │
│ 1 │ 17ms 221µs 792ns │
│ 2 │ 14ms 786µs 708ns │
│ 3 │ 13ms 876µs 834ns │
│ 4 │ 13ms 52µs 875ns │
│ 5 │ 11ms 269µs 666ns │
│ 6 │ 6ms 942µs 500ns │
╰───┴──────────────────╯
```
##
[random-bytes.nu](https://github.com/nushell/nu_scripts/blob/main/benchmarks/random-bytes.nu)
I got pretty random results out of this benchmark so I decided not to
include it. Not clear why.
# User-Facing Changes
- IR compilation errors may appear even if the user isn't evaluating
with IR.
- IR evaluation can be enabled by setting the `NU_USE_IR` environment
variable to any value.
- New command `view ir` pretty-prints the IR for a block, and `view ir
--json` can be piped into an external tool like [`explore
ir`](https://github.com/devyn/nu_plugin_explore_ir).
# Tests + Formatting
All tests are passing with `NU_USE_IR=1`, and I've added some more eval
tests to compare the results for some very core operations. I will
probably want to add some more so we don't have to always check
`NU_USE_IR=1 toolkit test --workspace` on a regular basis.
# After Submitting
- [ ] release notes
- [ ] further documentation of instructions?
- [ ] post-release: publish `nu_plugin_explore_ir`
# Description
This PR introduces a new `Signals` struct to replace our adhoc passing
around of `ctrlc: Option<Arc<AtomicBool>>`. Doing so has a few benefits:
- We can better enforce when/where resetting or triggering an interrupt
is allowed.
- Consolidates `nu_utils::ctrl_c::was_pressed` and other ad-hoc
re-implementations into a single place: `Signals::check`.
- This allows us to add other types of signals later if we want. E.g.,
exiting or suspension.
- Similarly, we can more easily change the underlying implementation if
we need to in the future.
- Places that used to have a `ctrlc` of `None` now use
`Signals::empty()`, so we can double check these usages for correctness
in the future.