mirror of
https://github.com/nushell/nushell.git
synced 2024-11-22 16:33:37 +01:00
This PR is an attempt to fix #8257 and fix #10985 (which is duplicate-ish) # Description The parser currently doesn't know how to deal with colons appearing while lexing whitespace-terminated tokens specifying a record value. Most notably, this means you can't use datetime literals in record value position (and as a consequence, `| to nuon | from nuon` roundtrips can fail), but it also means that bare words containing colons cause a non-useful error message. 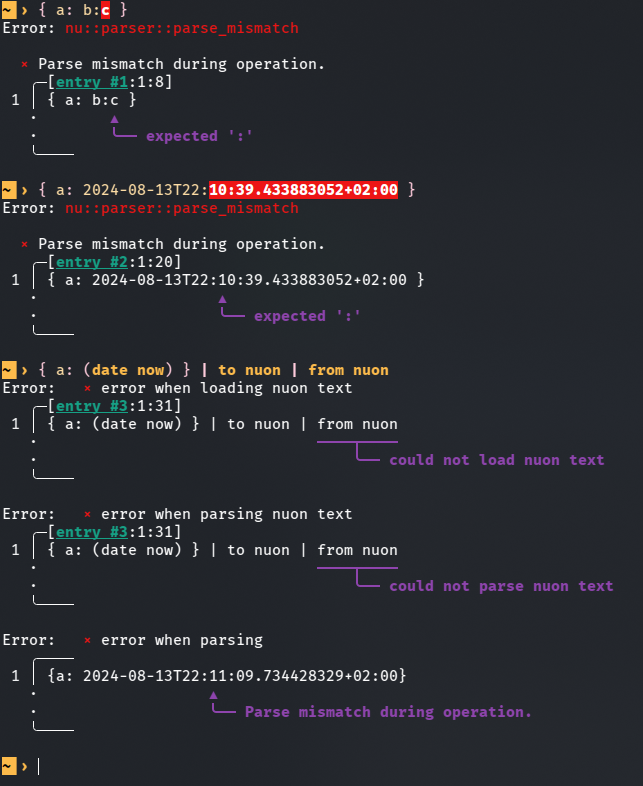 `parser::parse_record` calls `lex::lex` with the `:` colon character in the `special_tokens` argument. This allows colons to terminate record keys, but as a side effect, it also causes colons to terminate record *values*. I added a new function `lex::lex_n_tokens`, which allows the caller to drive the lexing process more explicitly, and used it in `parser::parse_record` to let colons terminate record keys while not giving them special treatment when appearing in record values. This PR description previously said: *Another approach suggested in one of the issues was to support an additional datetime literal format that doesn't require colons. I like that that wouldn't require new `lex::lex_internal` behaviour, but an advantage of my approach is that it also newly allows for string record values given as bare words containing colons. I think this eliminates another possible source of confusion.* It was determined that this is undesirable, and in the current state of this PR, bare word record values with colons are rejected explicitly. The better error message is still a win. # User-Facing Changes In addition to the above, this PR also disables the use of "special" (non-item) tokens in record key and value position, and the use of a single bare `:` as a record key. Examples of behaviour *before* this PR: ```nu { a: b } # Valid, same as { 'a': 'b' } { a: b:c } # Error: expected ':' { a: 2024-08-13T22:11:09 } # Error: expected ':' { :: 1 } # Valid, same as { ':': 1 } { ;: 1 } # Valid, same as { ';': 1 } { a: || } # Valid, same as { 'a': '||' } ``` Examples of behaviour *after* this PR: ```nu { a: b } # (Unchanged) Valid, same as { 'a': 'b' } { a: b:c } # Error: colon in bare word specifying record value { a: 2024-08-13T22:11:09 } # Valid, same as { a: (2024-08-13T22:11:09) } { :: 1 } # Error: colon in bare word specifying record key { ;: 1 } # Error: expected item in record key position { a: || } # Error: expected item in record value position ``` # Tests + Formatting I added tests, but I'm not sure if they're sufficient and in the right place. # After Submitting I don't think documentation changes are needed for this, but please let me know if you disagree.
307 lines
7.5 KiB
Rust
307 lines
7.5 KiB
Rust
use nu_parser::{lex, lex_n_tokens, lex_signature, LexState, Token, TokenContents};
|
|
use nu_protocol::{ParseError, Span};
|
|
|
|
#[test]
|
|
fn lex_basic() {
|
|
let file = b"let x = 4";
|
|
|
|
let output = lex(file, 0, &[], &[], true);
|
|
|
|
assert!(output.1.is_none());
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
#[test]
|
|
fn lex_newline() {
|
|
let file = b"let x = 300\nlet y = 500;";
|
|
|
|
let output = lex(file, 0, &[], &[], true);
|
|
|
|
assert!(output.0.contains(&Token {
|
|
contents: TokenContents::Eol,
|
|
span: Span::new(11, 12)
|
|
}));
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
#[test]
|
|
fn lex_annotations_list() {
|
|
let file = b"items: list<string>";
|
|
|
|
let (output, err) = lex_signature(file, 0, &[b'\n', b'\r'], &[b':', b'=', b','], false);
|
|
|
|
assert!(err.is_none());
|
|
assert_eq!(output.len(), 3);
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
#[test]
|
|
fn lex_annotations_record() {
|
|
let file = b"config: record<name: string>";
|
|
|
|
let (output, err) = lex_signature(file, 0, &[b'\n', b'\r'], &[b':', b'=', b','], false);
|
|
|
|
assert!(err.is_none());
|
|
assert_eq!(output.len(), 3);
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
#[test]
|
|
fn lex_annotations_empty() {
|
|
let file = b"items: list<>";
|
|
|
|
let (output, err) = lex_signature(file, 0, &[b'\n', b'\r'], &[b':', b'=', b','], false);
|
|
|
|
assert!(err.is_none());
|
|
assert_eq!(output.len(), 3);
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
#[test]
|
|
fn lex_annotations_space_before_annotations() {
|
|
let file = b"items: list <string>";
|
|
|
|
let (output, err) = lex_signature(file, 0, &[b'\n', b'\r'], &[b':', b'=', b','], false);
|
|
|
|
assert!(err.is_none());
|
|
assert_eq!(output.len(), 4);
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
#[test]
|
|
fn lex_annotations_space_within_annotations() {
|
|
let file = b"items: list< string>";
|
|
|
|
let (output, err) = lex_signature(file, 0, &[b'\n', b'\r'], &[b':', b'=', b','], false);
|
|
|
|
assert!(err.is_none());
|
|
assert_eq!(output.len(), 3);
|
|
|
|
let file = b"items: list<string >";
|
|
|
|
let (output, err) = lex_signature(file, 0, &[b'\n', b'\r'], &[b':', b'=', b','], false);
|
|
|
|
assert!(err.is_none());
|
|
assert_eq!(output.len(), 3);
|
|
|
|
let file = b"items: list< string >";
|
|
|
|
let (output, err) = lex_signature(file, 0, &[b'\n', b'\r'], &[b':', b'=', b','], false);
|
|
|
|
assert!(err.is_none());
|
|
assert_eq!(output.len(), 3);
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
#[test]
|
|
fn lex_annotations_nested() {
|
|
let file = b"items: list<record<name: string>>";
|
|
|
|
let (output, err) = lex_signature(file, 0, &[b'\n', b'\r'], &[b':', b'=', b','], false);
|
|
|
|
assert!(err.is_none());
|
|
assert_eq!(output.len(), 3);
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
#[test]
|
|
fn lex_annotations_nested_unterminated() {
|
|
let file = b"items: list<record<name: string>";
|
|
|
|
let (output, err) = lex_signature(file, 0, &[b'\n', b'\r'], &[b':', b'=', b','], false);
|
|
|
|
assert!(matches!(err.unwrap(), ParseError::UnexpectedEof(_, _)));
|
|
assert_eq!(output.len(), 3);
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
#[test]
|
|
fn lex_annotations_unterminated() {
|
|
let file = b"items: list<string";
|
|
|
|
let (output, err) = lex_signature(file, 0, &[b'\n', b'\r'], &[b':', b'=', b','], false);
|
|
|
|
assert!(matches!(err.unwrap(), ParseError::UnexpectedEof(_, _)));
|
|
assert_eq!(output.len(), 3);
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
#[test]
|
|
fn lex_empty() {
|
|
let file = b"";
|
|
|
|
let output = lex(file, 0, &[], &[], true);
|
|
|
|
assert!(output.0.is_empty());
|
|
assert!(output.1.is_none());
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
#[test]
|
|
fn lex_parenthesis() {
|
|
// The whole parenthesis is an item for the lexer
|
|
let file = b"let x = (300 + (322 * 444));";
|
|
|
|
let output = lex(file, 0, &[], &[], true);
|
|
|
|
assert_eq!(
|
|
output.0.get(3).unwrap(),
|
|
&Token {
|
|
contents: TokenContents::Item,
|
|
span: Span::new(8, 27)
|
|
}
|
|
);
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
#[test]
|
|
fn lex_comment() {
|
|
let file = b"let x = 300 # a comment \n $x + 444";
|
|
|
|
let output = lex(file, 0, &[], &[], false);
|
|
|
|
assert_eq!(
|
|
output.0.get(4).unwrap(),
|
|
&Token {
|
|
contents: TokenContents::Comment,
|
|
span: Span::new(12, 24)
|
|
}
|
|
);
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
#[test]
|
|
fn lex_is_incomplete() {
|
|
let file = b"let x = 300 | ;";
|
|
|
|
let output = lex(file, 0, &[], &[], true);
|
|
|
|
let err = output.1.unwrap();
|
|
assert!(matches!(err, ParseError::ExtraTokens(_)));
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
#[test]
|
|
fn lex_incomplete_paren() {
|
|
let file = b"let x = (300 + ( 4 + 1)";
|
|
|
|
let output = lex(file, 0, &[], &[], true);
|
|
|
|
let err = output.1.unwrap();
|
|
assert!(matches!(err, ParseError::UnexpectedEof(v, _) if v == ")"));
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
#[test]
|
|
fn lex_incomplete_quote() {
|
|
let file = b"let x = '300 + 4 + 1";
|
|
|
|
let output = lex(file, 0, &[], &[], true);
|
|
|
|
let err = output.1.unwrap();
|
|
assert!(matches!(err, ParseError::UnexpectedEof(v, _) if v == "'"));
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
#[test]
|
|
fn lex_comments_no_space() {
|
|
// test for parses that contain tokens that normally introduce comments
|
|
// Code:
|
|
// let z = 42 #the comment
|
|
// let x#y = 69 #hello
|
|
// let flk = nixpkgs#hello #hello
|
|
let file = b"let z = 42 #the comment \n let x#y = 69 #hello \n let flk = nixpkgs#hello #hello";
|
|
let output = lex(file, 0, &[], &[], false);
|
|
|
|
assert_eq!(
|
|
output.0.get(4).unwrap(),
|
|
&Token {
|
|
contents: TokenContents::Comment,
|
|
span: Span::new(11, 24)
|
|
}
|
|
);
|
|
|
|
assert_eq!(
|
|
output.0.get(7).unwrap(),
|
|
&Token {
|
|
contents: TokenContents::Item,
|
|
span: Span::new(30, 33)
|
|
}
|
|
);
|
|
|
|
assert_eq!(
|
|
output.0.get(10).unwrap(),
|
|
&Token {
|
|
contents: TokenContents::Comment,
|
|
span: Span::new(39, 46)
|
|
}
|
|
);
|
|
|
|
assert_eq!(
|
|
output.0.get(15).unwrap(),
|
|
&Token {
|
|
contents: TokenContents::Item,
|
|
span: Span::new(58, 71)
|
|
}
|
|
);
|
|
|
|
assert_eq!(
|
|
output.0.get(16).unwrap(),
|
|
&Token {
|
|
contents: TokenContents::Comment,
|
|
span: Span::new(72, 78)
|
|
}
|
|
);
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
#[test]
|
|
fn lex_comments() {
|
|
// Comments should keep the end of line token
|
|
// Code:
|
|
// let z = 4
|
|
// let x = 4 #comment
|
|
// let y = 1 # comment
|
|
let file = b"let z = 4 #comment \n let x = 4 # comment\n let y = 1 # comment";
|
|
|
|
let output = lex(file, 0, &[], &[], false);
|
|
|
|
assert_eq!(
|
|
output.0.get(4).unwrap(),
|
|
&Token {
|
|
contents: TokenContents::Comment,
|
|
span: Span::new(10, 19)
|
|
}
|
|
);
|
|
assert_eq!(
|
|
output.0.get(5).unwrap(),
|
|
&Token {
|
|
contents: TokenContents::Eol,
|
|
span: Span::new(19, 20)
|
|
}
|
|
);
|
|
|
|
// When there is no space between the comment and the new line the span
|
|
// for the command and the EOL overlaps
|
|
assert_eq!(
|
|
output.0.get(10).unwrap(),
|
|
&Token {
|
|
contents: TokenContents::Comment,
|
|
span: Span::new(31, 40)
|
|
}
|
|
);
|
|
assert_eq!(
|
|
output.0.get(11).unwrap(),
|
|
&Token {
|
|
contents: TokenContents::Eol,
|
|
span: Span::new(40, 41)
|
|
}
|
|
);
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
#[test]
|
|
fn lex_manually() {
|
|
let file = b"'a'\n#comment\n#comment again\n| continue";
|
|
let mut lex_state = LexState {
|
|
input: file,
|
|
output: Vec::new(),
|
|
error: None,
|
|
span_offset: 10,
|
|
};
|
|
assert_eq!(lex_n_tokens(&mut lex_state, &[], &[], false, 1), 1);
|
|
assert_eq!(lex_state.output.len(), 1);
|
|
assert_eq!(lex_n_tokens(&mut lex_state, &[], &[], false, 5), 5);
|
|
assert_eq!(lex_state.output.len(), 6);
|
|
// Next token is the pipe.
|
|
// This shortens the output because it exhausts the input before it can
|
|
// compensate for the EOL tokens lost to the line continuation
|
|
assert_eq!(lex_n_tokens(&mut lex_state, &[], &[], false, 1), -1);
|
|
assert_eq!(lex_state.output.len(), 5);
|
|
assert_eq!(file.len(), lex_state.span_offset - 10);
|
|
let last_span = lex_state.output.last().unwrap().span;
|
|
assert_eq!(&file[last_span.start - 10..last_span.end - 10], b"continue");
|
|
}
|