forked from extern/wg-meshconf
245 lines
12 KiB
Markdown
245 lines
12 KiB
Markdown
# wg-meshconf
|
|
|
|
wg-meshconf is a tool that will help you to generate peer configuration files for WireGuard mesh networks. You can easily and quickly create WireGuard mesh networks using this tool.
|
|
|
|
## Installation (pip)
|
|
|
|
wg-meshconf is available on PyPI. You can install it with pip and run the program via the `wg-meshconf` command.
|
|
|
|
```shell
|
|
# installing the program with pip
|
|
pip3 install --user -U wg-meshconf
|
|
|
|
# running the program
|
|
wg-meshconf showpeers
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
## Installation (Manual)
|
|
|
|
Alternatively, if you do not want to install the program into the system with pip, you can clone this repository using `git` or download the [master branch's ZIP file](https://github.com/k4yt3x/wg-meshconf/archive/master.zip).
|
|
|
|
```shell
|
|
# cloning the repository with git
|
|
git clone https://github.com/k4yt3x/wg-meshconf.git
|
|
|
|
# download the master branch's ZIP file
|
|
wget https://github.com/k4yt3x/wg-meshconf/archive/master.zip
|
|
|
|
# decompress the ZIP file
|
|
unzip wg-meshconf-master.zip
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
Then, you will need to install Python's dependencies.
|
|
|
|
```shell
|
|
# if you cloned this repository
|
|
pip3 install --user -Ur wg-meshconf/wg_meshconf/requirements.txt
|
|
|
|
# if you downloaded and decompressed the zip file
|
|
pip3 install --user -Ur wg-meshconf-master/wg_meshconf/requirements.txt
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
## Learn by an Example
|
|
|
|
Usages are dull and boring. Let's see a real-life example of how this tool can be used. This section will demonstrate how to create a simple mesh network with four nodes using wg-meshconf.
|
|
|
|
For this example, suppose you have four servers as shown below. These servers can reach each other via the `Endpoint` address. For instance, server `tokyo1` can ping server `shanghai1` with the address `shanghai1.com`.
|
|
|
|
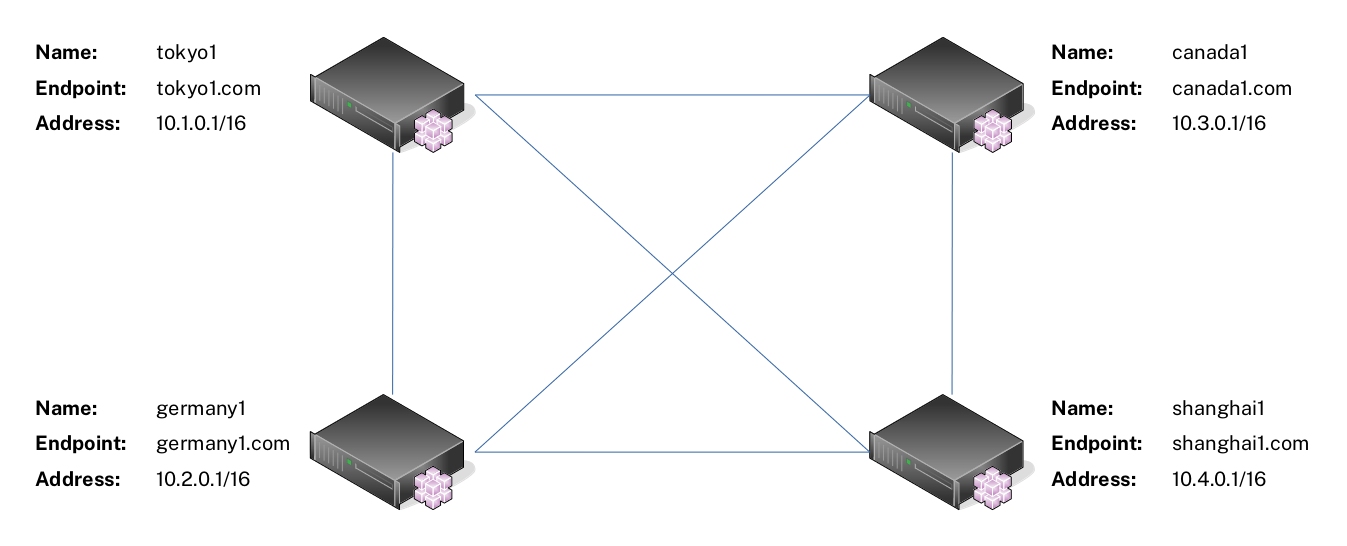
|
|
|
|
### Step 1: Add Basic Peer Information
|
|
|
|
You will first need to add the peers' information into the database. There are two ways to do it: via Excel and via the command line interface.
|
|
|
|
#### Method A: With Excel
|
|
|
|
wg-meshconf has changed its database format from JSON to CSV and added the `init` command since version 2.4.0. This means that it is now possible for users to directly edit the database file with Excel or other CSV-compatible editors to create/read/update/delete peer information.
|
|
|
|
> (P.S. I thought about making a fancy GUI for wg-meshconf like the other tools, but then I thought, why do it the complex way when you can simply "borrow" Excel's GUI?)
|
|
|
|
Run the following command to initialize a new database file. By default, the database file is named `database.csv`. You can also specify the file's name via `-d`.
|
|
|
|
```shell
|
|
wg-meshconf init
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
Open the database CSV file with an editor like Excel or LibreOffice Calc. You should see the following column headers.
|
|
|
|
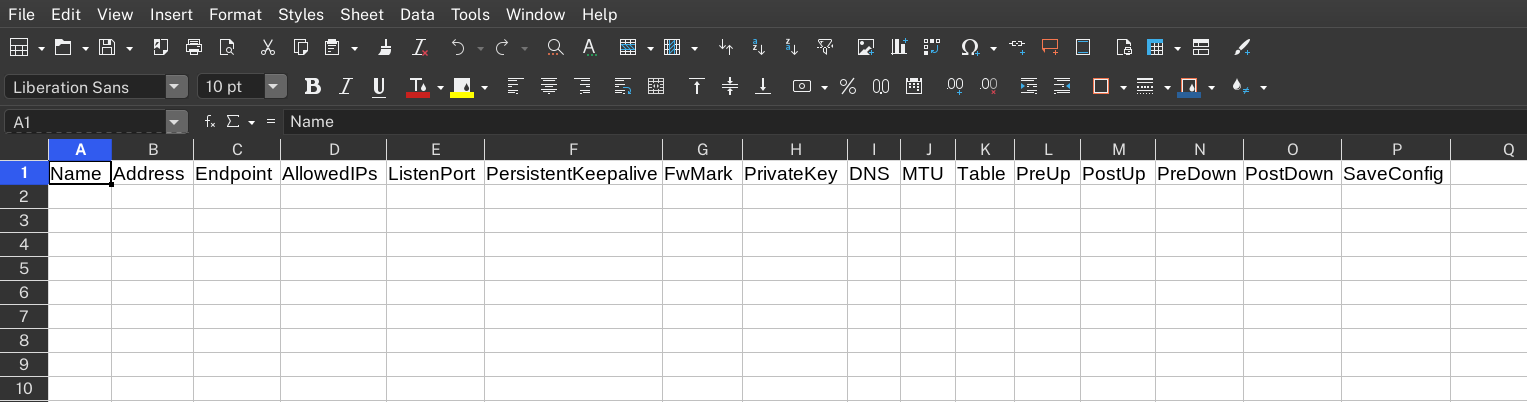
|
|
|
|
You can then fill in the peers' information. **You will need to fill in at least the peers' `Name`, `Address`, and `Endpoint` values.** These values cannot be automatically generated.
|
|
|
|
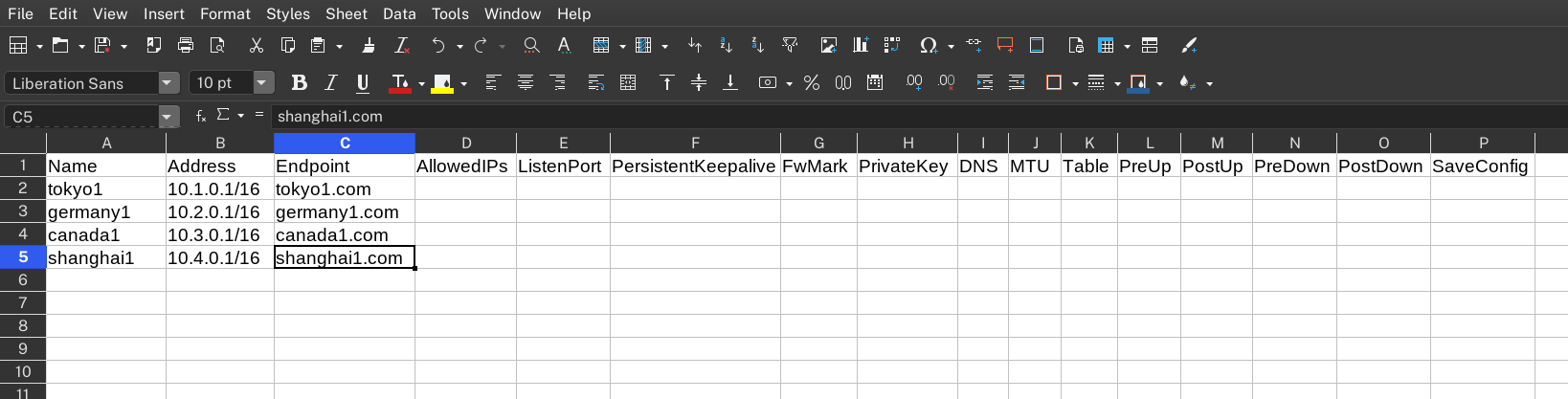
|
|
|
|
Once you're done, save the file and execute the `init` command again to automatically generate the rest of the needed information such as peer private keys.
|
|
|
|
```shell
|
|
wg-meshconf init
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
If you check the file again, you'll see the necessary fields getting automatically filed in.
|
|
|
|
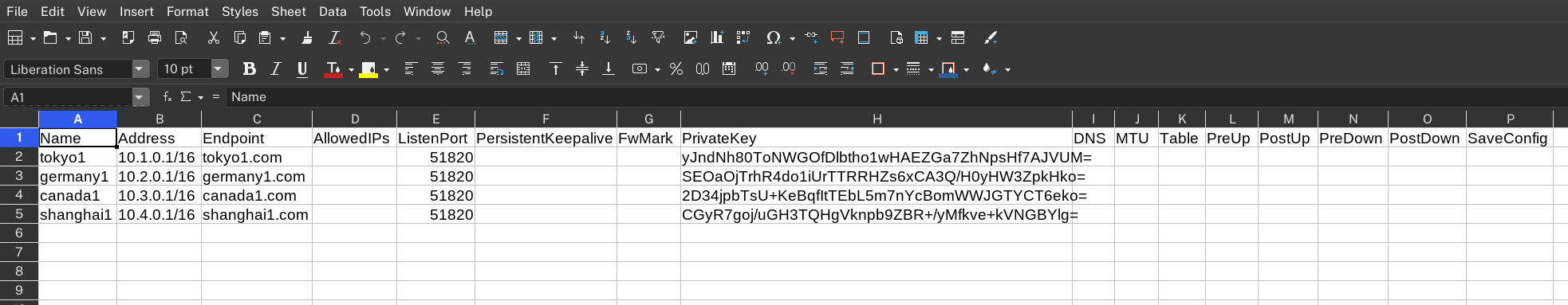
|
|
|
|
#### Method B: With Terminal
|
|
|
|
If, for some reason, you don't want to edit the database file directly, you can also use this tool purely through its command line interface.
|
|
|
|
First we need to add all peers in the mesh network into the database. The basic syntax for adding new peers is:
|
|
|
|
```shell
|
|
wg-meshconf addpeer NAME --address IP_ADDRESS --address IP_ADDRESS_2 --endpoint ENDPOINT
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
- New private key will be generated automatically if unspecified
|
|
- ListenPort defaults to 51820 per WireGuard standard
|
|
- All other values are left empty by default
|
|
|
|
There are more options which you can specify. Use the command `wg-meshconf addpeer -h` for more details.
|
|
|
|
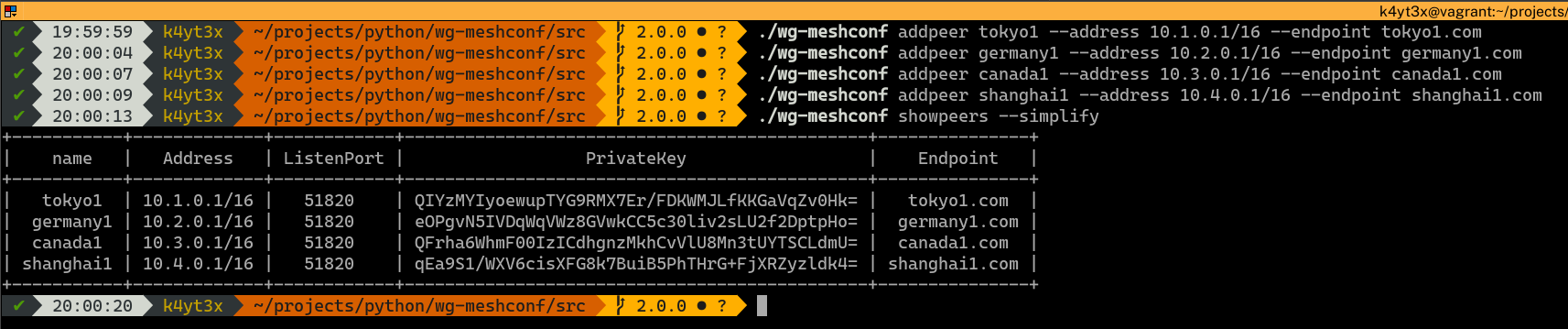
After adding all the peers into the database, you can verify that they have all been added correctly via the `wg-meshconf showpeers` command. The `simplify` switch here omits all columns with only `None`s.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
### Step 2: Export Configuration Files
|
|
|
|
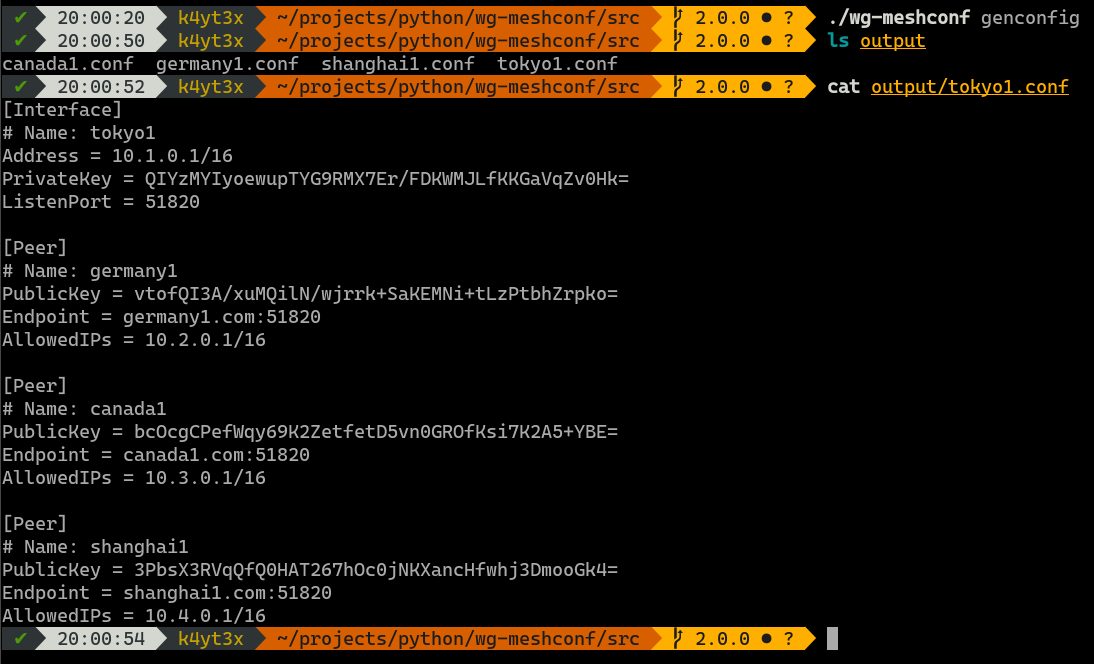
Use the `genconfig` command to generate configuration files for all peers. You may also export configurations for only one peer by specifying the peer's name.
|
|
|
|
The configuration files will be named after the peers' names. By default, all configuration files are exported into a subdirectory named `output`. You can change this by specifying output directory using the `-o` or the `--output` option.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
### Step 3: Copy Configuration Files to Peers
|
|
|
|
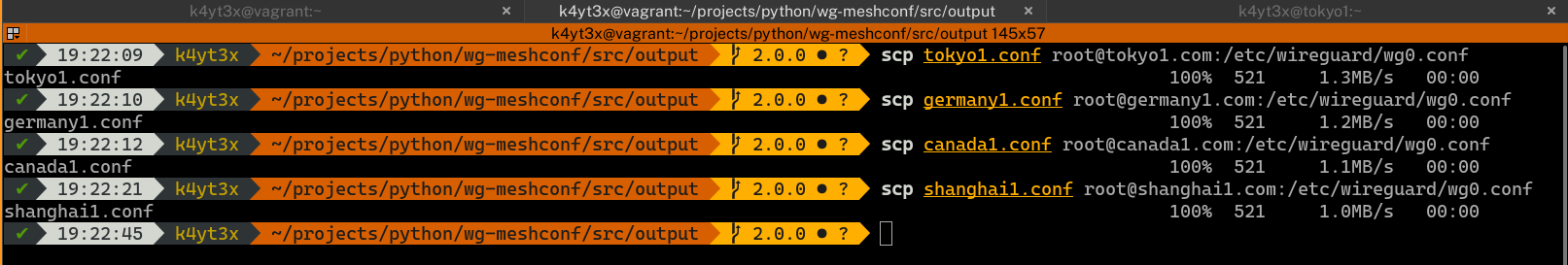
Copy each of the configuration files to the corresponding peers.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
### Step 4: Start WireGuard Services
|
|
|
|
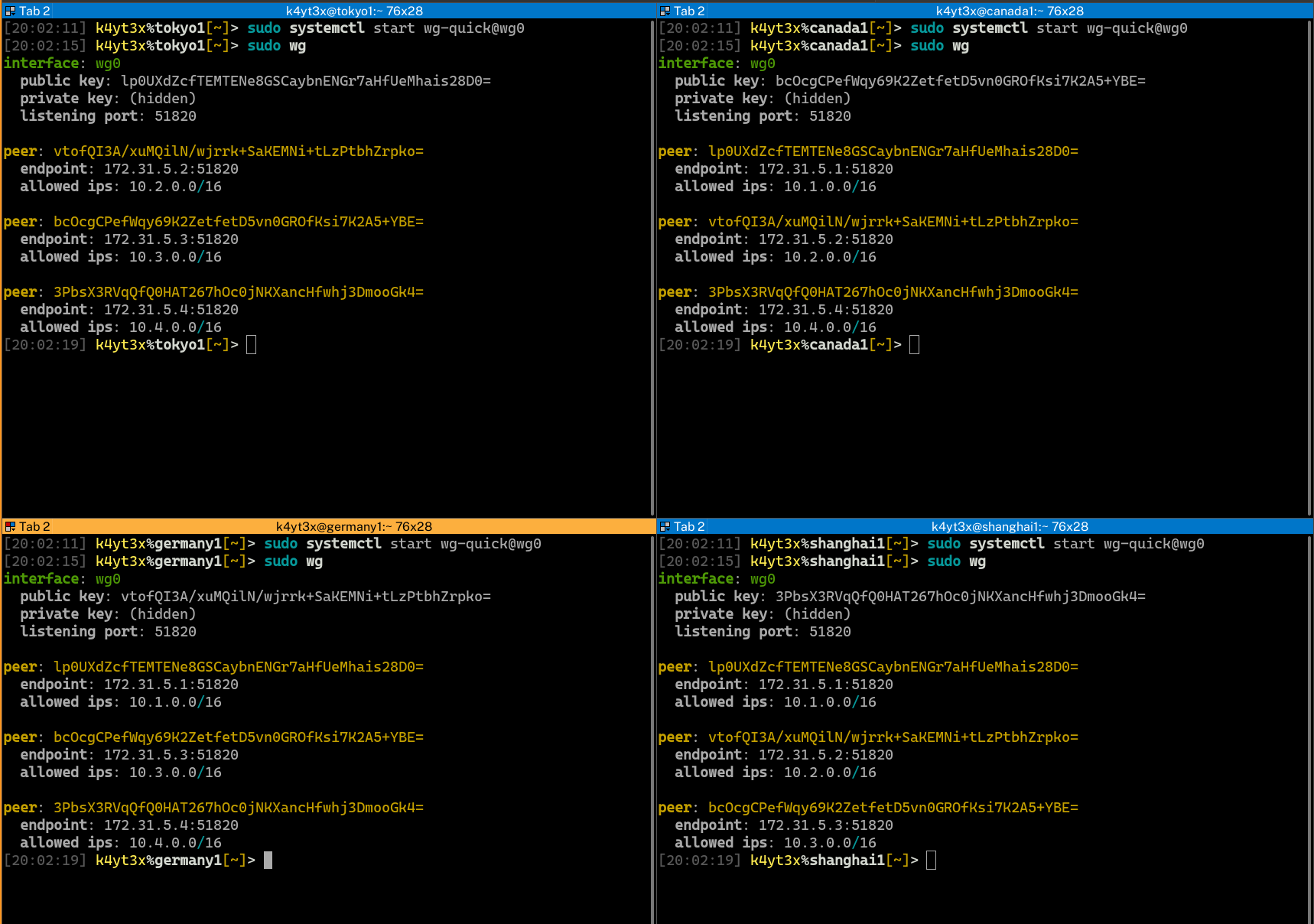
Start up the WireGuard interfaces using the `wg-quick` command. It is also possible to control WireGuard interfaces via WireGuard's `wg-quick@` systemd service. WireGuard status can be verified via the `wg` command after WireGuard interfaces are set up.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
### Step 5: Verify Connectivity
|
|
|
|
Verify that all endpoints have been configured properly and can connect to each other.
|
|
|
|
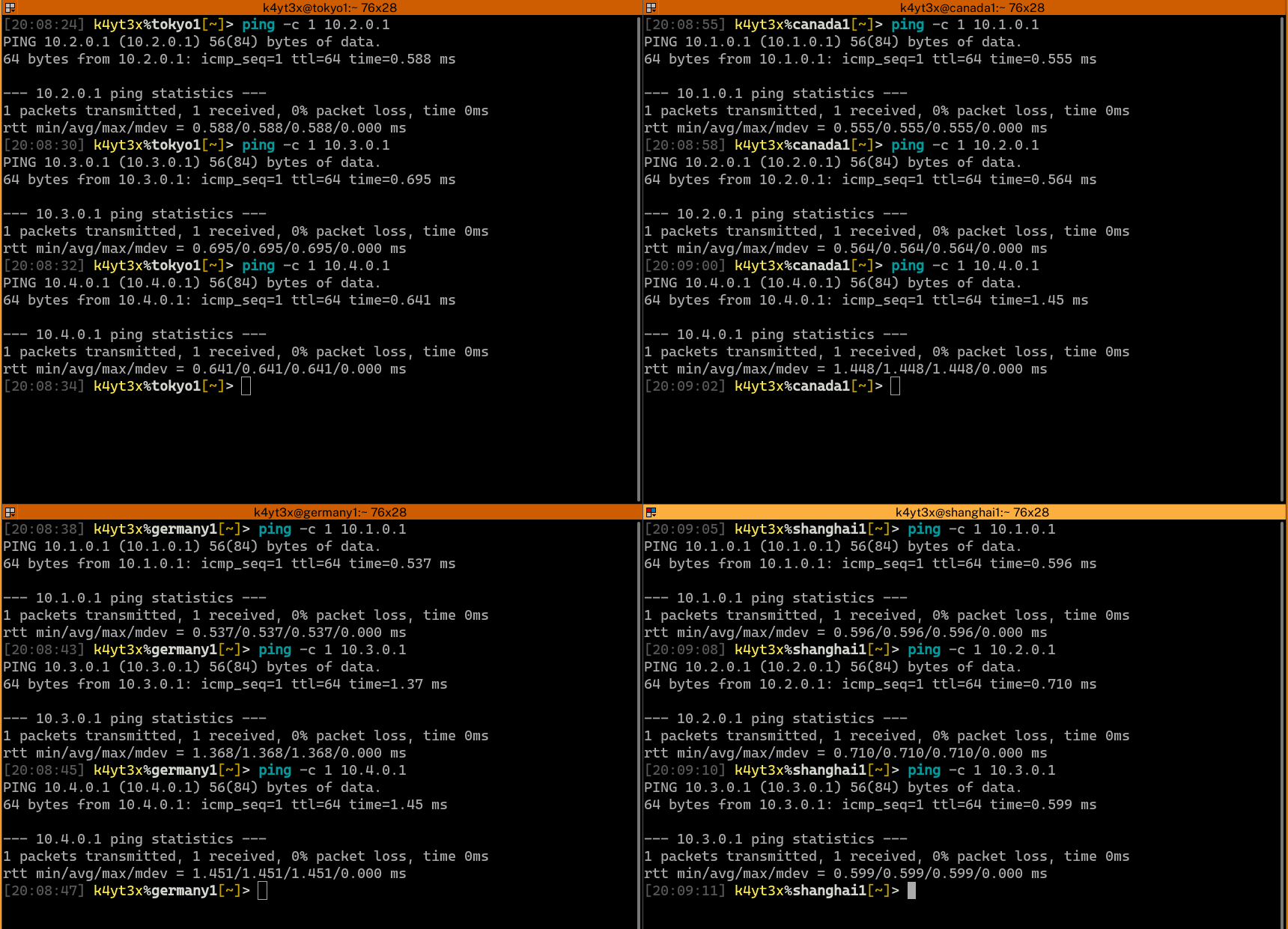
|
|
|
|
Done. Now a mesh network has been created between the four servers.
|
|
|
|
## Updating Peer Information
|
|
|
|
If you would like to update a peer's information, use the `updatepeer` command. The syntax of `updatepeer` is the same as that of the `addpeer` command. Instead of adding a new peer, this command overwrites values in existing entries.
|
|
|
|
In the example below, suppose you would like to update `tokyo1`'s endpoint address and change it to `tokyo321.com`. Use the `updatepeer` command and specify the new endpoint to be `tokyo321.com`. This will overwrite `tokyo1`'s existing `Endpoint` value.
|
|
|
|

|
|
|
|
## Show Peer Information
|
|
|
|
The `showpeers` command prints all peers' information by default.
|
|
|
|

|
|
|
|
Now that's a lot of info and a lot of unnecessary columns which only have `None`s. Therefore, I added the `-s`/`--simplify` command which omits those useless columns.
|
|
|
|
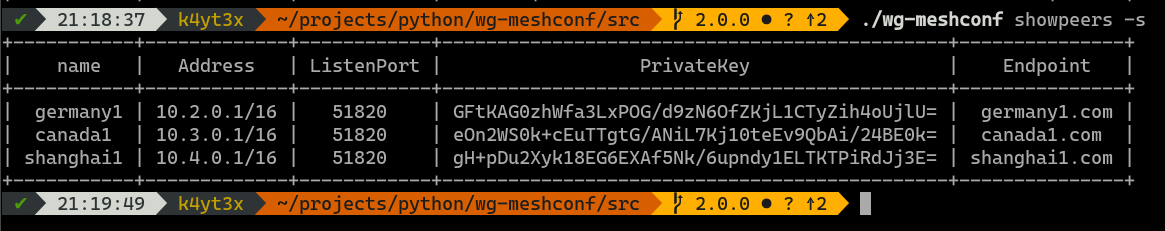
|
|
|
|
You may also query information about a specific peer.
|
|
|
|
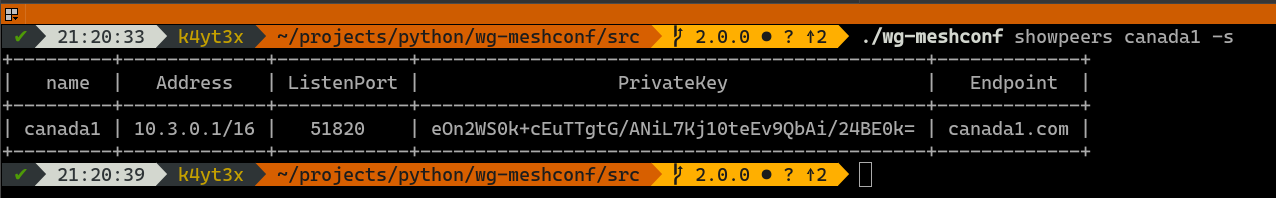
|
|
|
|
Plaintext mode has a similar usage. It's just a bit harder to read, at least for me.
|
|
|
|
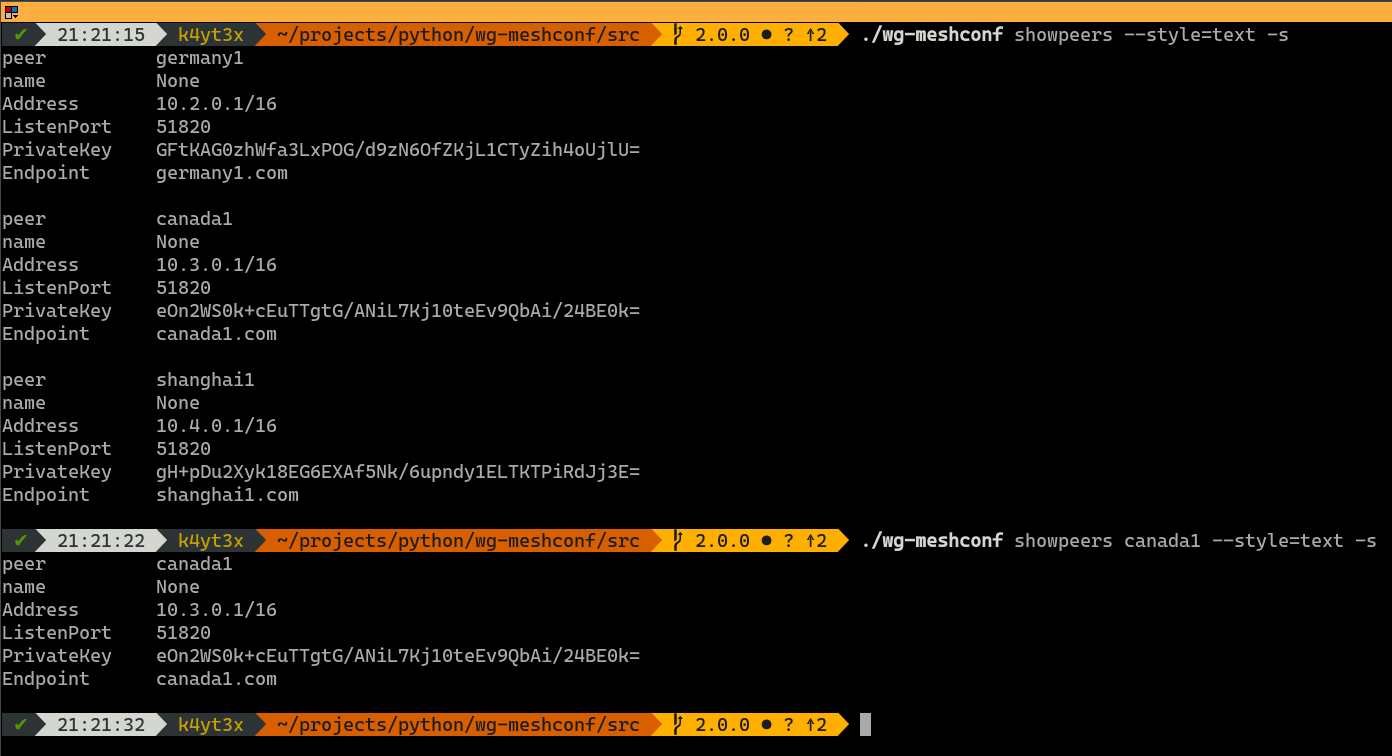
|
|
|
|
## Deleting Peers
|
|
|
|
Use the `delpeer` command to delete peers. The syntax is `delpeer PEER_NAME`.
|
|
|
|
This example below shows how to delete the peer `tokyo1` from the database.
|
|
|
|
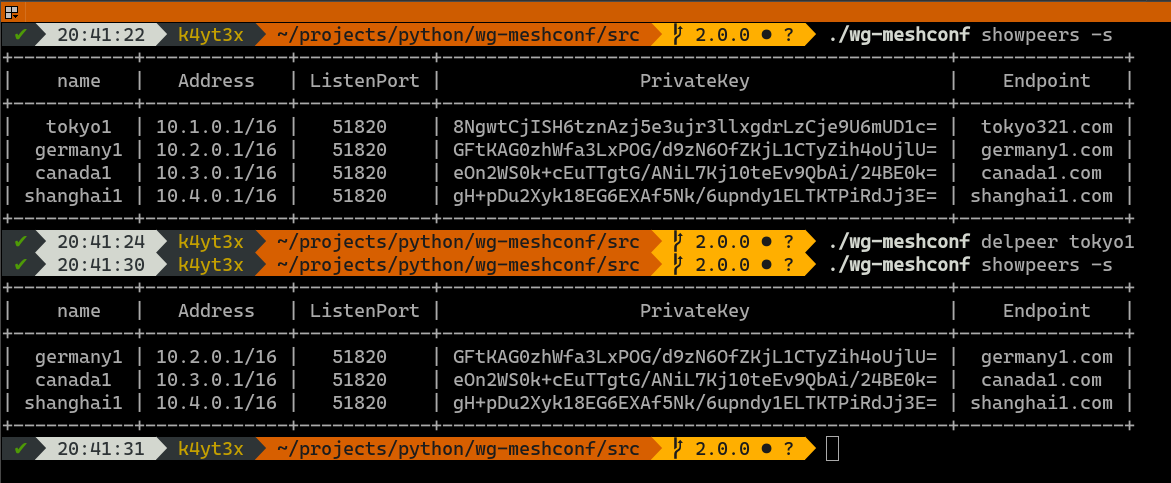
|
|
|
|
## Database Files
|
|
|
|
Unlike 1.x.x versions of wg-meshconf, version 2.0.0 does not require the user to save or load profiles. Instead, all add peer, update peer and delete peer operations are file operations. The changes will be saved to the database file immediately. The database file to use can be specified via the `-d` or the `--database` option. If no database file is specified, `database.csv` will be used.
|
|
|
|
Database files are essentially just CSV files (it was JSON before version 2.4.0). Below is an example.
|
|
|
|
```csv
|
|
"Name","Address","Endpoint","AllowedIPs","ListenPort","PersistentKeepalive","FwMark","PrivateKey","DNS","MTU","Table","PreUp","PostUp","PreDown","PostDown","SaveConfig"
|
|
"tokyo1","10.1.0.1/16","tokyo1.com","","51820","","","yJndNh80ToNWGOfDlbtho1wHAEZGa7ZhNpsHf7AJVUM=","","","","","","","",""
|
|
"germany1","10.2.0.1/16","germany1.com","","51820","","","SEOaOjTrhR4do1iUrTTRRHZs6xCA3Q/H0yHW3ZpkHko=","","","","","","","",""
|
|
"canada1","10.3.0.1/16","canada1.com","","51820","","","2D34jpbTsU+KeBqfItTEbL5m7nYcBomWWJGTYCT6eko=","","","","","","","",""
|
|
"shanghai1","10.4.0.1/16","shanghai1.com","","51820","","","CGyR7goj/uGH3TQHgVknpb9ZBR+/yMfkve+kVNGBYlg=","","","","","","","",""
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
## Detailed Usages
|
|
|
|
You may refer to the program's help page for usages. Use the `-h` switch or the `--help` switch to print the help page.
|
|
|
|
```shell
|
|
$ wg-meshconf -h
|
|
usage: wg-meshconf [-h] [-d DATABASE] {addpeer,updatepeer,delpeer,showpeers,genconfig} ...
|
|
|
|
positional arguments:
|
|
{addpeer,updatepeer,delpeer,showpeers,genconfig}
|
|
|
|
optional arguments:
|
|
-h, --help show this help message and exit
|
|
-d DATABASE, --database DATABASE
|
|
path where the database file is stored (default: database.json)
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
Specify `-h` or `--help` after a command to see this command's usages.
|
|
|
|
```shell
|
|
$ wg-meshconf addpeer -h
|
|
usage: wg-meshconf addpeer [-h] --address ADDRESS [--endpoint ENDPOINT] [--privatekey PRIVATEKEY] [--listenport LISTENPORT] [--fwmark FWMARK] [--dns DNS] [--mtu MTU] [--table TABLE] [--preup PREUP] [--postup POSTUP] [--predown PREDOWN] [--postdown POSTDOWN] [--saveconfig] name
|
|
|
|
positional arguments:
|
|
name Name used to identify this node
|
|
|
|
optional arguments:
|
|
-h, --help show this help message and exit
|
|
--address ADDRESS address of the server
|
|
--endpoint ENDPOINT peer's public endpoint address
|
|
--privatekey PRIVATEKEY
|
|
private key of server interface
|
|
--listenport LISTENPORT
|
|
port to listen on
|
|
--fwmark FWMARK fwmark for outgoing packets
|
|
--dns DNS server interface DNS servers
|
|
--mtu MTU server interface MTU
|
|
--table TABLE server routing table
|
|
--preup PREUP command to run before interface is up
|
|
--postup POSTUP command to run after interface is up
|
|
--predown PREDOWN command to run before interface is down
|
|
--postdown POSTDOWN command to run after interface is down
|
|
--saveconfig save server interface to config upon shutdown
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
## License
|
|
|
|
This project is licensed under the [GNU General Public License Version 3 (GNU GPL v3)](https://www.gnu.org/licenses/gpl-3.0.txt)\
|
|
Copyright (c) 2018-2023 K4YT3X and contributors.
|
|
|
|

|
|
|
|
This project includes or dependson the following software and projects:
|
|
|
|
| **Project** | **License** |
|
|
| ---------------------------------------------------- | ----------- |
|
|
| [Rich](https://github.com/Textualize/rich) | MIT License |
|
|
| [WireGuard](https://git.zx2c4.com/wireguard) | MIT License |
|
|
| [cryptography](https://github.com/pyca/cryptography) | BSD License |
|
|
|
|
## Related Project: `wg-dynamic`
|
|
|
|
`wg-dynamic` is a tool designed officially by the WireGuard developing team. This new utility will provide a convenient way of configuring networks dynamically, where mesh network being one of the them. If you're interested, check it out at [wg-dynamic@github](https://github.com/WireGuard/wg-dynamic) or [wg-dynamic@official repository](https://git.zx2c4.com/wg-dynamic). You might also want to read this project's [idea page](https://github.com/WireGuard/wg-dynamic/blob/master/docs/idea.md).
|
|
|
|
This section used to be on the top of the page, but has been moved since there has been no new commits observed in this project since 2019.
|