mirror of
https://github.com/KusakabeShi/EtherGuard-VPN.git
synced 2025-03-02 05:41:10 +01:00
415 lines
19 KiB
Markdown
415 lines
19 KiB
Markdown
# Etherguard
|
||
[English](#) | [中文](README_zh.md)
|
||
|
||
## Super mode
|
||
|
||
This mode is inspired by [n2n](https://github.com/ntop/n2n). There 2 types of node: SuperNode and EdgeNode
|
||
EdgeNode must connect to SuperNode first,get connection info of other EdgeNode from the SuperNode
|
||
The SuperNode runs [Floyd-Warshall Algorithm](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Floyd–Warshall_algorithm),and distribute the result to all other EdgeNodes.
|
||
|
||
## Quick start
|
||
|
||
Edit the file `gensuper.yaml` based on your requirement first.
|
||
|
||
```yaml
|
||
Config output dir: /tmp/eg_gen
|
||
Enable generated config overwrite: false # Allow overwrite while output the config
|
||
Add NodeID to the interface name: false # Add NodeID to the interface name in generated edge config
|
||
ConfigTemplate for super node: ""
|
||
ConfigTemplate for edge node: ""
|
||
Network name: eg_net
|
||
Super Node:
|
||
Listen port: 3456
|
||
EdgeAPI prefix: /eg_net/eg_api
|
||
Endpoint(IPv4)(optional): example.com
|
||
Endpoint(IPv6)(optional): example.com
|
||
Endpoint(EdgeAPI): http://example.com:3456/eg_net/eg_api
|
||
Edge Node:
|
||
Node IDs: "[1~10,11,19,23,29,31,55~66,88~99]"
|
||
MacAddress prefix: "" # Leave blank to generate randomly
|
||
IPv4 range: 192.168.76.0/24 # The IP part can be omitted
|
||
IPv6 range: fd95:71cb:a3df:e586::/64 #
|
||
IPv6 LL range: fe80::a3df:0/112 #
|
||
```
|
||
Then run this, and the required configuration file will be generated.
|
||
```
|
||
$ ./etherguard-go -mode gencfg -cfgmode super -config example_config/super_mode/gensuper.yaml
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
Run this in SuperNode
|
||
```
|
||
./etherguard-go -config [config path] -mode super
|
||
```
|
||
Run this in EdgeNode
|
||
```
|
||
./etherguard-go -config [config path] -mode edge
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
## Documentation
|
||
|
||
This is the documentation of the super_mode of this example_config
|
||
Before reading this, I'd like to suggest you read the [static mode](../static_mode/README.md) first.
|
||
|
||
In the super mode of the edge node, the `NextHopTable` and `Peers` section are useless. All infos are download from super node.
|
||
Meanwhile, super node will generate pre shared key for inter-edge communication(if `UsePSKForInterEdge` enabled).
|
||
|
||
### SuperMsg
|
||
There are new type of DstID called `SuperMsg`(65534). All packets sends to and receive from super node are using this packet type.
|
||
This packet will not send to any other edge node, just like `DstID == self.NodeID`
|
||
|
||
## Control Message
|
||
In Super mode, Beside `Normal Packet`. We introduce a new packet type called `Control Message`. In Super mode, we will not relay any control message. We just receive or send it to target directly.
|
||
We list all the control message we use in the super mode below.
|
||
|
||
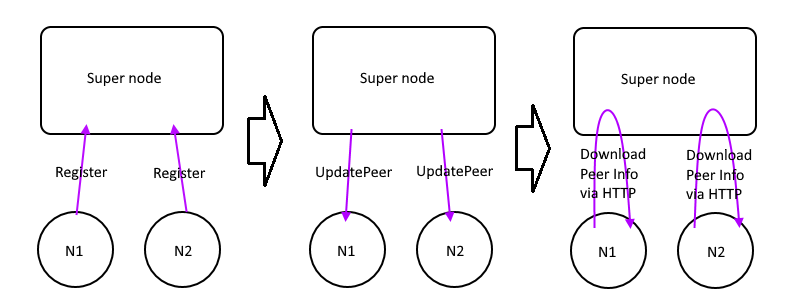
### Register
|
||
This control message works like this picture:
|
||
|
||
|
||
1. EdgeNode send Register to the super node
|
||
2. SuperNode knows it's external IP and port number
|
||
3. Update it to database and distribute `UpdatePeerMsg` to all edges
|
||
4. Other EdgeNodes get the notification, download the updated peer infos from SuperNode via HTTP API
|
||
|
||
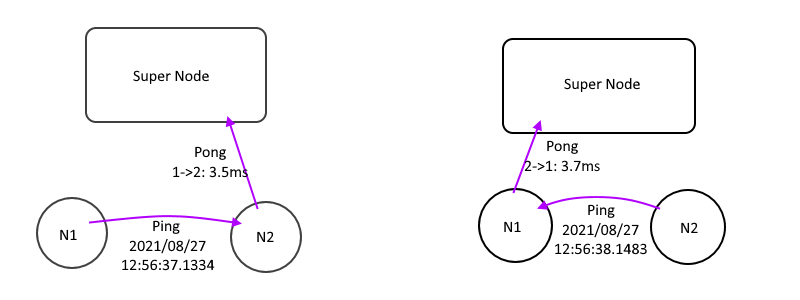
### Ping/Pong
|
||
While EdgeNodes get their peer info, they will trying to talk each other directly like this picture:
|
||
|
||
|
||
1. Send `Ping` to all other edges with local time with TTL=0
|
||
2. Receive a `Ping`, Subtract the peer time from local time, we get a single way latency.
|
||
3. Send a `Pong` to SuperNode with single way latency, let SuperNode calculate the NextHopTable
|
||
4. Wait the SuperNode push `UpdateNhTable` message and download it.
|
||
|
||
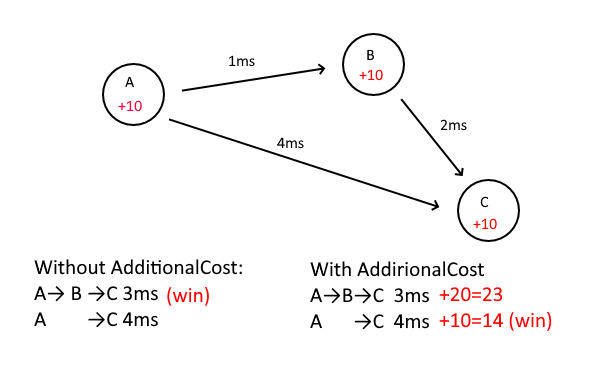
### <a name="AdditionalCost"></a>AdditionalCost
|
||
While we have all latency data of all nodes, `AdditionalCost` will be applied before `Floyd-Warshall` calculated.
|
||
|
||
Take the situation of this picture as an example:
|
||
|
||
Path | Latency |Cost|Win
|
||
--------|:--------|:---|:--
|
||
A->B->C | 3ms | 3 |
|
||
A->C | 4ms | 4 | O
|
||
|
||
In this situation, the difference between 3ms and 4ms is only 1ms
|
||
It’s not worth to save this 1ms, and the forwarding itself takes time
|
||
|
||
With the `AdditionalCost` parameter, each node can set the additional cost of forwarding through this node
|
||
|
||
If ABC is all set to `AdditionalCost=10`
|
||
Path | Latency |AdditionalCost|Cost|Win
|
||
--------|:--------|:-------------|:---|:--
|
||
A->B->C | 3ms | 20 | 23 |
|
||
A->C | 4ms | 10 | 14 | O
|
||
|
||
A->C will use direct connection instead of forward via `B` in order to save 1ms
|
||
Here `AdditionalCost=10` can be interpreted as: It have to save 10ms to transfer by this Node.
|
||
|
||
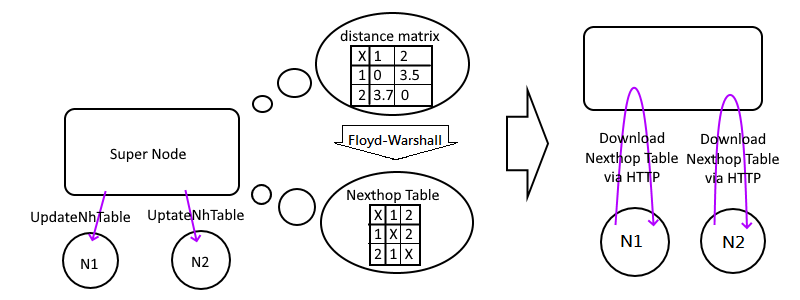
### UpdateNhTable
|
||
While supernode get a `Pong` message, it will update the `Distance matrix` and run the [Floyd-Warshall Algorithm](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Floyd–Warshall_algorithm) to calculate the NextHopTable.
|
||
|
||
If there are any changes of this table, it will distribute `UpdateNhTable` to all edges to till then download the latest NextHopTable via HTTP API as soon as possible.
|
||
|
||
### ServerUpdate
|
||
Send message to EdgeMode from SuperNode
|
||
1. Turn off EdgeNode
|
||
* Version Not match
|
||
* Wrong NodeID
|
||
* Deleted by SuperNode
|
||
2. Notify EdgeNode there are something new
|
||
* UpdateNhTable
|
||
* UpdatePeer
|
||
* UpdateSuperParams
|
||
|
||
## HTTP EdgeAPI
|
||
Why we use HTTP API instead of pack all information in the `UpdateXXX`?
|
||
Because UDP is an unreliable protocol, there is an limit on the amount of content that can be carried.
|
||
But the peer list contains all the peer information, the length is not fixed, it may exceed
|
||
So we use `UpdateXXX` to tell we have a update, please download the latest information from SuperNode via HTTP API as soon as possible.
|
||
And `UpdateXXX` itself is not reliable, maybe it didn't reach the edge node at all.
|
||
So the information of `UpdateXXX` carries the `state hash`. Bring it when with HTTP API. When the super node receives the HTTP API and sees the `state hash`, it knows that the edge node has received the `UpdateXXX`.
|
||
Otherwise, it will send `UpdateXXX` to the node again after few seconds.
|
||
|
||
The default configuration is to use HTTP. **But for the sake of your security, it is recommended to use an reverse-proxy ot convert it into https**
|
||
I have thought about the development of SuperNode to natively support https, but the dynamic update of the certificate costs me too much time.
|
||
|
||
## HTTP Manage API
|
||
HTTP also has some APIs for the front-end to help manage the entire network
|
||
|
||
### super/state
|
||
|
||
```bash
|
||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:3456/eg_net/eg_api/manage/super/state?Password=passwd_showstate"
|
||
```
|
||
It can show some information such as single way latency or last seen time.
|
||
We can visualize it by Force-directed graph drawing.
|
||
|
||
There is an `Infinity` section in the json response. It should be 9999. It means infinity if the number larger than it.
|
||
Cuz json can't present infinity so that I use this trick.
|
||
While we see the latency larger than this, we doesn't need to draw lines in this two nodes.
|
||
|
||
Example return value:
|
||
```json
|
||
{
|
||
"PeerInfo": {
|
||
"1": {
|
||
"Name": "Node_01",
|
||
"LastSeen": "2021-12-05 21:21:56.039750832 +0000 UTC m=+23.401193649"
|
||
},
|
||
"2": {
|
||
"Name": "Node_02",
|
||
"LastSeen": "2021-12-05 21:21:57.711616169 +0000 UTC m=+25.073058986"
|
||
}
|
||
},
|
||
"Infinity": 99999,
|
||
"Edges": {
|
||
"1": {
|
||
"2": 0.002179297
|
||
},
|
||
"2": {
|
||
"1": -0.00030252
|
||
}
|
||
},
|
||
"Edges_Nh": {
|
||
"1": {
|
||
"2": 0.012179297
|
||
},
|
||
"2": {
|
||
"1": 0.00969748
|
||
}
|
||
},
|
||
"NhTable": {
|
||
"1": {
|
||
"2": 2
|
||
},
|
||
"2": {
|
||
"1": 1
|
||
}
|
||
},
|
||
"Dist": {
|
||
"1": {
|
||
"1": 0,
|
||
"2": 0.012179297
|
||
},
|
||
"2": {
|
||
"1": 0.00969748,
|
||
"2": 0
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
Section meaning:
|
||
1. PeerInfo: NodeID,Name,LastSeen
|
||
2. Edges: The **Single way latency**,99999 or missing means unreachable(UDP hole punching failed)
|
||
3. Edges_Nh: Edges with AdditionalCost
|
||
3. NhTable: Calculate result.
|
||
4. Dist: The latency of **packet through Etherguard**
|
||
|
||
### peer/add
|
||
We can add new edges with this API without restart the SuperNode
|
||
|
||
Exanple:
|
||
```bash
|
||
curl -X POST "http://127.0.0.1:3456/eg_net/eg_api/manage/peer/add?Password=passwd_addpeer" \
|
||
-H "Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded" \
|
||
-d "NodeID=100&Name=Node_100&PubKey=DG%2FLq1bFpE%2F6109emAoO3iaC%2BshgWtdRaGBhW3soiSI%3D&AdditionalCost=1000&PSKey=w5t64vFEoyNk%2FiKJP3oeSi9eiGEiPteZmf2o0oI2q2U%3D&SkipLocalIP=false"
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
Parameter:
|
||
1. URL query: Password: Password. Configured in the config file.
|
||
1. Post body:
|
||
1. NodeID: Node ID
|
||
1. Name: Name
|
||
1. PubKey: Public Key
|
||
1. PSKey: Pre shared Key
|
||
1. AdditionalCost: Additional cost for packet transfer. Unit: ms
|
||
1. SkipLocalIP: Skip local IP reported by the node
|
||
1. nexthoptable: If the `graphrecalculatesetting` of your super node is in static mode, you need to provide a new `NextHopTable` in json format in this parameter.
|
||
|
||
Return value:
|
||
1. http code != 200: Error reason
|
||
2. http code == 200,An example edge config.
|
||
* generate by contents in `edgetemplate` with custom data (nodeid/name/pubkey)
|
||
* Convenient for users to copy and paste
|
||
|
||
### peer/del
|
||
Delete peer
|
||
|
||
There are two deletion modes, namely password deletion and private key deletion.
|
||
Designed to be used by administrators, or for people who join the network and want to leave the network.
|
||
|
||
Use Password to delete any node. Take the newly added node above as an example, use this API to delete the node
|
||
```bash
|
||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:3456/eg_net/eg_api/manage/peer/del?Password=passwd_delpeer&NodeID=100"
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
We can also use privkey to delete, the same as above, but use privkey parameter only.
|
||
```bash
|
||
curl "http://127.0.0.1:3456/eg_net/eg_api/manage/peer/del?PrivKey=iquaLyD%2BYLzW3zvI0JGSed9GfDqHYMh%2FvUaU0PYVAbQ%3D"
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
Parameter:
|
||
1. URL query:
|
||
1. Password: Password: Password. Configured in the config file.
|
||
1. nodeid: Node ID that you want to delete
|
||
1. privkey: The private key of the edge
|
||
|
||
Return value:
|
||
1. http code != 200: Error reason
|
||
2. http code == 200: Success message
|
||
|
||
### peer/update
|
||
|
||
```bash
|
||
curl -X POST "http://127.0.0.1:3456/eg_net/eg_api/manage/peer/update?Password=passwd_updatepeer&NodeID=1" \
|
||
-H "Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded" \
|
||
-d "AdditionalCost=10&SkipLocalIP=false"
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
### super/update
|
||
|
||
```bash
|
||
curl -X POST "http://127.0.0.1:3456/eg_net/eg_api/manage/super/update?Password=passwd_updatesuper" \
|
||
-H "Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded" \
|
||
-d "SendPingInterval=15&HttpPostInterval=60&PeerAliveTimeout=70&DampingFilterRadius=3"
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
### SuperNode Config Parameter
|
||
|
||
Key | Description
|
||
--------------------|:-----
|
||
NodeName | node name
|
||
PostScript | Running script after initialized
|
||
PrivKeyV4 | Private key for IPv4 session
|
||
PrivKeyV6 | Private key for IPv6 session
|
||
ListenPort | UDP listen port
|
||
ListenPort_EdgeAPI | HTTP EdgeAPI listen port
|
||
ListenPort_ManageAPI| HTTP ManageAPI listen port
|
||
API_Prefix | HTTP API prefix
|
||
RePushConfigInterval| The interval of push`UpdateXXX`
|
||
HttpPostInterval | The interval of report by HTTP Edge API
|
||
PeerAliveTimeout | The time of inactive which marks peer offline
|
||
SendPingInterval | The interval that send pings/pongs between EdgeNodes
|
||
[LogLevel](../static_mode/README.md#LogLevel)| Log related settings
|
||
[Passwords](#Passwords) | Password for HTTP ManageAPI, 5 API passwords are independent
|
||
[GraphRecalculateSetting](#GraphRecalculateSetting) | Some parameters related to [Floyd-Warshall algorithm](https://zh.wikipedia.org/zh-tw/Floyd-Warshall algorithm)
|
||
[NextHopTable](../static_mode/README.md#NextHopTable) | `NextHopTable` used by StaticMode
|
||
EdgeTemplate | for HTTP ManageAPI `peer/add`. Refer to this configuration file and show a sample configuration file of the edge to the user
|
||
UsePSKForInterEdge | Whether to enable pre-share key communication between edges.<br>If enabled, SuperNode will generate PSK for edges automatically
|
||
[Peers](#EdgeNodes) | EdgeNode information
|
||
|
||
<a name="Passwords"></a>Passwords | Description
|
||
--------------------|:-----
|
||
ShowState | HTTP ManageAPI Password for `super/state`
|
||
AddPeer | HTTP ManageAPI Password for `peer/add`
|
||
DelPeer | HTTP ManageAPI Password for `peer/del`
|
||
UpdatePeer | HTTP ManageAPI Password for `peer/update`
|
||
UpdateSuper | HTTP ManageAPI Password for `super/update`
|
||
|
||
<a name="GraphRecalculateSetting"></a>GraphRecalculateSetting | Description
|
||
--------------------|:-----
|
||
StaticMode | Disable `Floyd-Warshall`, use `NextHopTable`in the configuration instead.<br>SuperNode for udp hole punching only.
|
||
ManualLatency | Set latency manually, ignore Edge reported latency.
|
||
JitterTolerance | Jitter tolerance, after receiving Pong, one 37ms and one 39ms will not trigger recalculation<br>Compared to last calculation
|
||
JitterToleranceMultiplier | high ping allows more errors<br>https://www.desmos.com/calculator/raoti16r5n
|
||
DampingFilterRadius | Windows radius for the low pass filter for latency damping prevention
|
||
TimeoutCheckInterval | The interval to check if there any `Pong` packet timed out, and recalculate the NhTable
|
||
RecalculateCoolDown | Floyd-Warshal is an O(n^3)time complexity algorithm<br>This option set a cooldown, and prevent it cost too many CPU<br>Connect/Disconnect event ignores this cooldown.
|
||
|
||
<a name="EdgeNodes"></a>Peers | Description
|
||
--------------------|:-----
|
||
NodeID | Peer's node ID
|
||
PubKey | Peer's public key
|
||
PSKey | Pre shared key
|
||
[AdditionalCost](#AdditionalCost) | AdditionalCost(unit:ms)<br> `-1` means uses client's self configuration.
|
||
SkipLocalIP | Ignore Edge reported local IP, use public IP only while udp-hole-punching
|
||
|
||
### EdgeNode Config Parameter
|
||
|
||
#### [EdgeConfig Root](../static_mode/README.md#EdgeConfig)
|
||
|
||
<a name="DynamicRoute"></a>DynamicRoute | Description
|
||
--------------------|:-----
|
||
SendPingInterval | The interval that send pings/pongs between EdgeNodes(sec)
|
||
PeerAliveTimeout | The time of inactive which marks peer offline(sec)
|
||
TimeoutCheckInterval | The interval of check PeerAliveTimeout(sec)
|
||
ConnNextTry | After marked offline, the interval of switching Endpoint(sec)
|
||
DupCheckTimeout | Duplication chack timeout.(sec)
|
||
[AdditionalCost](#AdditionalCost) | AdditionalCost(unit:ms)
|
||
SaveNewPeers | Save peer info to local file.
|
||
[SuperNode](#SuperNode) | SuperNode related configs
|
||
[P2P](../p2p_mode/README.md#P2P) | P2P related configs
|
||
[NTPConfig](#NTPConfig) | NTP related configs
|
||
|
||
<a name="SuperNode"></a>SuperNode | Description
|
||
---------------------|:-----
|
||
UseSuperNode | Enable SuperMode
|
||
PSKey | PreShared Key to communicate to SuperNode
|
||
EndpointV4 | IPv4 Endpoint of the SuperNode
|
||
PubKeyV4 | Public Key for IPv4 session to SuperNode
|
||
EndpointV6 | IPv6 Endpoint of the SuperNode
|
||
PubKeyV6 | Public Key for IPv6 session to SuperNode
|
||
EndpointEdgeAPIUrl | The EdgeAPI of the SuperNode
|
||
SkipLocalIP | Do not report local IP to SuperNode.
|
||
SuperNodeInfoTimeout | Experimental option, SuperNode offline timeout, switch to P2P mode<br>P2P mode needs to be enabled first<br>This option is useless while `UseP2P=false`<br>P2P mode has not been tested, stability is unknown, it is not recommended for production use
|
||
|
||
|
||
<a name="NTPConfig"></a>NTPConfig | Description
|
||
--------------------|:-----
|
||
UseNTP | Sync time at startup
|
||
MaxServerUse | Use how many server to sync time
|
||
SyncTimeInterval | The interval of syncing time
|
||
NTPTimeout | NTP server connection Timeout
|
||
Servers | NTP server list
|
||
|
||
|
||
## V4 V6 Two Keys
|
||
Why we split IPv4 and IPv6 into two session?
|
||
Because of this situation
|
||
|
||
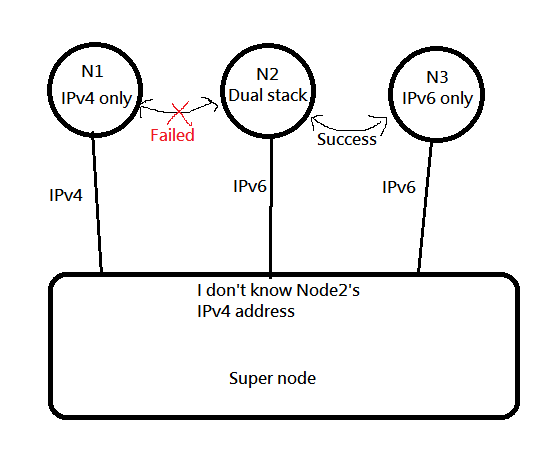
|
||
|
||
In this case, SuperNode does not know the external ipv4 address of Node02 and cannot help Node1 and Node2 to UDP hole punch.
|
||
|
||
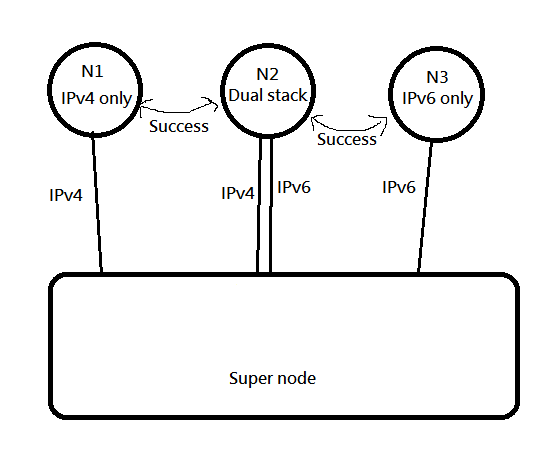
|
||
|
||
So like this, both V4 and V6 establish a session, so that both V4 and V6 can be taken care of at the same time.
|
||
|
||
## UDP hole punch reachability
|
||
For different NAT type, the UDP hole punch reachability can refer this table.([Origin](https://dh2i.com/kbs/kbs-2961448-understanding-different-nat-types-and-hole-punching/))
|
||
|
||
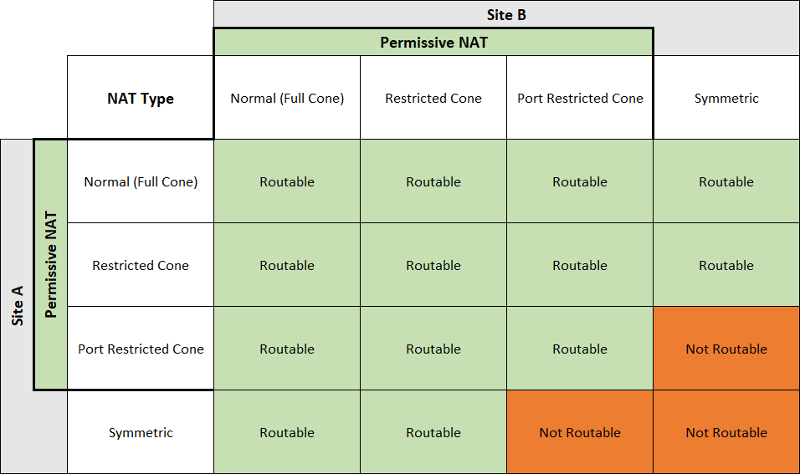
|
||
|
||
And if both sides are using ConeNAT, it's not gerenteed to punch success. It depends on the topology and the devices attributes.
|
||
Like the section 3.5 in [this article](https://bford.info/pub/net/p2pnat/#SECTION00035000000000000000), we can't punch success.
|
||
|
||
## Notice for Relay node
|
||
Unlike n2n, our supernode do not relay any packet for edges.
|
||
If the edge punch failed and no any route available, it's just unreachable. In this case we need to setup a relay node.
|
||
|
||
Relay node is a regular edge in public network, but `interface=dummy`.
|
||
|
||
And we have to note that **do not** use 127.0.0.1 to connect to supernode.
|
||
Because supernode well distribute the source IP of the nodes to all other edges. But 127.0.0.1 is not accessible from other edge.
|
||
|
||
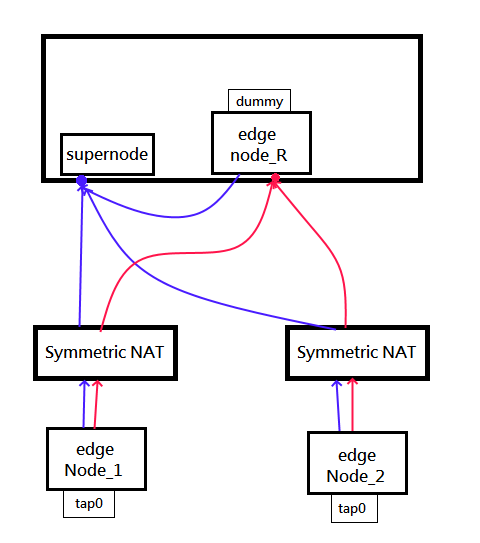
|
||
|
||
To avoid this issue, please use the external IP of the supernode in the edge config.
|
||
|
||
## Quick start
|
||
Run this example_config (please open three terminals):
|
||
```bash
|
||
./etherguard-go -config example_config/super_mode/Node_super.yaml -mode super
|
||
./etherguard-go -config example_config/super_mode/Node_edge001.yaml -mode edge
|
||
./etherguard-go -config example_config/super_mode/Node_edge002.yaml -mode edge
|
||
```
|
||
Because it is in `stdio` mode, stdin will be read into the VPN network
|
||
Please type in one of the edge windows
|
||
```
|
||
b1aaaaaaaaaa
|
||
```
|
||
b1 will be converted into a 12byte layer 2 header, b is the broadcast address `FF:FF:FF:FF:FF:FF`, 1 is the ordinary MAC address `AA:BB:CC:DD:EE:01`, aaaaaaaaaa is the payload, and then feed it into the VPN
|
||
You should be able to see the string b1aaaaaaaaaa on another window. The first 12 bytes are converted back
|
||
|
||
## Next: [P2P Mode](../p2p_mode/README.md) |